Get list of Ganga River tributaries, including major left and right bank tributaries like Yamuna, Son, Ghaghara, Gandak, Kosi, Ramganga, Gomti, and Damodar. Explore their origin, confluence points, and importance in the Ganga river system and Ganga basin rivers.

The Ganga River is one of the most important and sacred rivers of Asia, forming the backbone of the Ganga basin rivers and supporting millions of people across India and Bangladesh. Its extensive network of Ganga river tributaries not only maintains the river’s perennial flow but also sustains agriculture, ecology, and human settlements along its course.
For UPSC aspirants, a thorough understanding of the Ganga river system and its tributaries of Ganga river is crucial for Geography, Environment, and General Studies papers.
The Ganga originates as the Bhagirathi from the Gangotri Glacier in Uttarakhand at an elevation of about 3,892 metres. Several small streams form the headwaters of the Ganga system. The important tributaries in the upper course include the Alaknanda, Dhauliganga, Pindar, Mandakini, and Bhilangana rivers.
At Devprayag, where the Alaknanda meets the Bhagirathi, the river officially takes the name Ganga. From this point, the Ganga flows for nearly 2,525 km before finally emptying into the Bay of Bengal. The river system is formed by six major headstreams and five important confluences, known as the Panch Prayag.
The major confluences Ganga River are:
Vishnuprayag: Confluence of the Dhauliganga and Alaknanda rivers
Nandaprayag: Confluence of the Nandakini and Alaknanda rivers
Karnaprayag: Confluence of the Pindar and Alaknanda rivers
Rudraprayag: Confluence of the Mandakini and Alaknanda rivers
Devprayag: Confluence of the Bhagirathi and Alaknanda rivers
The Bhagirathi, regarded as the main source stream of the Ganga, rises from Gaumukh at the foot of the Gangotri Glacier. After its long journey across the northern plains of India, the Ganga finally drains into the Bay of Bengal.
Ganga Basin extends across India, Tibet (China), Nepal, and Bangladesh, covering a total area of about 10,86,000 sq km. The largest share of the basin lies in India, making it the biggest river basin in the country. In India, it drains an area of 8,61,452 sq km, which is slightly more than one-fourth (26.3 percent) of the country’s total geographical area. The basin covers parts of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, West Bengal, Uttarakhand, Jharkhand, Haryana, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, and Delhi.
Ganga Basin extends across India, Tibet (China), Nepal, and Bangladesh, covering a total area of about 10,86,000 sq km. The largest share of the basin lies in India, making it the biggest river basin in the country. In India, it drains an area of 8,61,452 sq km, which is slightly more than one-fourth (26.3 percent) of the country’s total geographical area. The basin covers parts of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, West Bengal, Uttarakhand, Jharkhand, Haryana, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, and Delhi.
The Ganga river system originates in the western Himalayas in Uttarakhand, flowing approximately 2,525 km through northern India before entering Bangladesh. In Bangladesh, it is known as the Padma, where it eventually merges with the Jamuna (Brahmaputra) and Meghna, forming the Ganga Delta, one of the largest river deltas in the world.
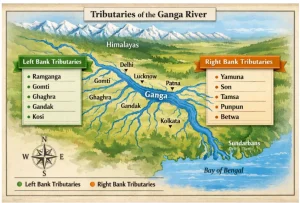
The river system is fed by numerous left bank tributaries of Ganga from the Himalayas and right bank tributaries of Ganga from the Peninsular Plateau. These rivers collectively form the Ganga river tributaries list, which is essential knowledge for UPSC Geography and current affairs.
Left bank tributaries of Ganga mainly originate from the Himalayas and contribute the maximum flow to the river, especially during the monsoon. Some of the major tributaries of Ganga on the left bank include:
The Ramganga river tributary of Ganga originates from the Dudhatoli Hills in Uttarakhand and flows through the Jim Corbett National Park. The river joins the Ganga near Kannauj, providing water for agriculture and irrigation. Bareilly is an important urban settlement along its banks.
The Gomti river tributary of Ganga rises from Gomat Taal (Pilibhit, UP). Flowing for about 900 km, it joins the Ganga at Ghazipur. Cities like Lucknow, Jaunpur, and Sultanpur are located on its banks. The Sai River is a significant tributary of the Gomti.
The Ghaghara river tributary of Ganga, also known as Karnali in Nepal, originates from the Tibetan Plateau near Lake Mansarovar. It enters India at Brahmaghat and joins the Ganga at Chhapra, Bihar. Major tributaries include Rapti, Sarayu, and Sharda, making it one of the major tributaries of Ganga.
The Gandak river tributary of Ganga is formed by the Kali and Trisuli rivers in Nepal, known as Narayani in its upper course. Entering India, it joins the Ganga near Sonepur, Bihar. The Gandak river has deep valleys in the upper reaches and fertile floodplains in the lower course.
The Kosi river tributary of Ganga, also called the “Sorrow of Bihar”, originates in Tibet and Nepal. It joins the Ganga near Kursela, Bihar. This river is highly unstable due to heavy silt deposition, causing frequent flooding. It is one of the major tributaries of Ganga that contribute significantly to the river’s volume.
Right bank tributaries of Ganga mostly originate from the Peninsular Plateau. They generally carry less water than left bank tributaries but play an important role in irrigation, water management, and regional ecology.
The Yamuna tributary of Ganga is the largest and most important right bank tributary. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier in Uttarakhand, it flows through Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Delhi, and Uttar Pradesh, joining the Ganga at Prayagraj (Triveni Sangam). The Yamuna forms the Yamuna–Ganga Doab, a fertile agricultural region critical for food security.
The Son river tributary of Ganga originates near Amarkantak in Madhya Pradesh. Flowing through MP, UP, Jharkhand, and Bihar, it joins the Ganga near Patna. Important tributaries of the Son include the Rihand and North Koel rivers. The river valley is sparsely populated but ecologically significant.
The Damodar river tributary of Ganga rises in the Chota Nagpur Plateau and is historically prone to floods. It now joins the Hooghly River, a distributary of the Ganga. The river supports industrial and coal-rich regions of Jharkhand and West Bengal.
Other important right bank tributaries of the Ganga include Tamsa (Tons), Karmanasa, Punpun, Falgu, Kiul, Chandan, Ajay, and Rupnarayan, which play critical roles in irrigation and local ecosystems.
The Ganga tributaries map reveals the spatial distribution of rivers in the Ganga basin:
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
The tributaries of Ganga river are crucial for:
Understanding the Ganga river system and its Ganga basin rivers helps UPSC aspirants answer questions related to water resources, rivers, and environmental geography.
Ready to boost your UPSC preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Ganga river tributaries are rivers that flow into the Ganga, contributing to its water volume and forming part of the Ganga river system. They include rivers originating from both the Himalayas (left bank tributaries) and the Peninsular Plateau (right bank tributaries).
The Yamuna tributary of Ganga joins the Ganga at Prayagraj (Triveni Sangam). It is the largest right bank tributary and forms the fertile Yamuna-Ganga Doab region.
The Son river tributary of Ganga originates from Amarkantak (Madhya Pradesh) and joins the Ganga near Patna, Bihar. Its important tributaries include Rihand and North Koel.
A Ganga tributaries map visually shows all left and right bank tributaries of Ganga, the origin points, and their confluence locations. It is a key tool for understanding the Ganga basin rivers and their distribution.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
