Answer:
|
How to approach the question
- Introduction
- Write about Lithium as a resource briefly.
- Body
- Write about the global distribution of major lithium-producing countries.
- Write about the impacts of its global distribution considering economic factors.
- Write about the impacts of its global distribution considering environmental factors.
- Write about the impacts of its global distribution considering geopolitical factors.
- Conclusion
- Give appropriate conclusion in this regard.
|
Introduction
Lithium is soft, silvery-white alkali metal, found in trace amounts in the earth’s crust. It is a valuable resource used primarily as a component in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries for electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage.
Body
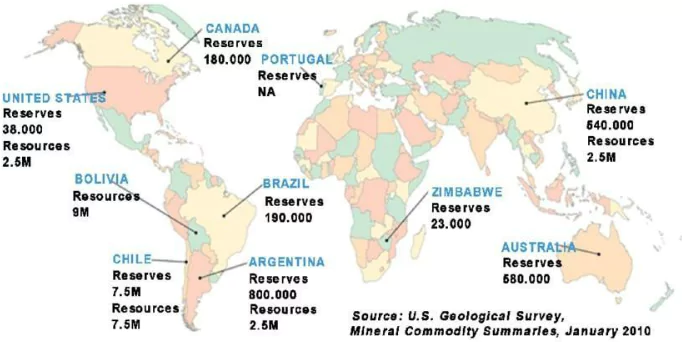
Global distribution of major lithium-producing countries
- Australia: It is home to the Greenbushes lithium mine, which is the world’s largest hard-rock lithium mine and a major contributor to global lithium supply.
- Chile: The country’s Salar de Atacama is one of the most prominent lithium-rich salt flats globally, hosting several lithium extraction operations.
- China: China is a major producer of lithium, primarily through its operations in Tibet and Qinghai provinces.
- Argentina: Argentina is home to the vast lithium reserves in the “Lithium Triangle” region, shared with Bolivia and Chile with projects like the Salar del Hombre Muerto.
- United States: Lithium reserves primarily located in Nevada and North Carolina. The Silver Peak lithium mine in Nevada has been a longstanding source of lithium production in the country.
Impacts of its global distribution considering economic factors
- Regional Development: For example, lithium mining in regions like the Lithium Triangle in South America has spurred economic growth, job creation, and the development of local industries.
- Economic growth and investment opportunities: For example, Australia has become a major lithium producer and exporter, which has contributed to its economic growth and attracted significant foreign investment.
- Exploitation of vulnerable sections: The demand for lithium has led to concerns about child labor and poor working conditions in some mining operations.
- Economic dependence and resource concentration: For instance, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina collectively hold the majority of global lithium reserves. If these countries were to restrict or control their lithium exports, it could significantly impact the global supply chain.
Impacts of its global distribution considering environmental factors
- Ecological considerations: Lithium mining requires significant amounts of water, and in regions with limited water resources, such as the Atacama Desert in Chile, it can strain local ecosystems and communities.
- Environmental degradation: For instance, in Bolivia’s Salar de Uyuni, one of the world’s largest lithium reserves, mining activities have resulted in soil contamination, threatening local ecosystems.
- Carbon emissions: For example, in Australia, a major lithium producer, the energy-intensive conversion of spodumene concentrate into battery-grade lithium compounds leads to substantial carbon dioxide emissions.
- Sustainable alternatives: The reliance on lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage has raised concerns about the long-term availability and environmental impacts of lithium.
Impacts of its global distribution considering geopolitical factors
- Resource nationalism and domestic policies: For example, Argentina has implemented export quotas and imposed regulations to ensure a certain percentage of lithium production is processed within the country.
- Geopolitical competition for lithium resources: For example, China has invested heavily in lithium mining projects in countries such as Australia and Chile, ensuring a steady supply for its rapidly growing electric vehicle industry. Some other countries too can join this competition of investing in these countries.
- Geopolitical Influence: As China is the world’s largest producer and consumer of Lithium, it exert geopolitical influence and potentially control the global lithium market.
- Strategic Dominance: For instance, countries like Chile, Australia, and Argentina, which possess abundant lithium reserves, have gained strategic leverage as global demand for lithium-ion batteries rises.
Conclusion
Overall, the global distribution of lithium-producing countries influences economic, geopolitical, technological, environmental, and social aspects, necessitating careful management and collaboration to maximize the benefits while mitigating the challenges associated with lithium extraction and its global distribution.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.


Latest Comments