Answer:
Approach:
|
Introduction:
The term “jobless growth” refers to an economic paradox wherein a country experiences GDP growth without a corresponding increase in employment opportunities. In India, recent economic trends have displayed symptoms of this phenomenon. Despite impressive growth rates, employment generation remains a significant concern, bringing into question the inclusivity and sustainability of the country’s growth model.
Body:
Jobless growth occurs when unemployment remains high even as the economy grows. This can happen due to various reasons including technological advancements, capital-intensive growth, or structural shifts in the economy.
For example, despite India’s services sector experiencing rapid growth, the manufacturing sector, traditionally a large employer, has not seen the same expansion, leading to limited job creation.
Present Status of Jobless Growth in India:
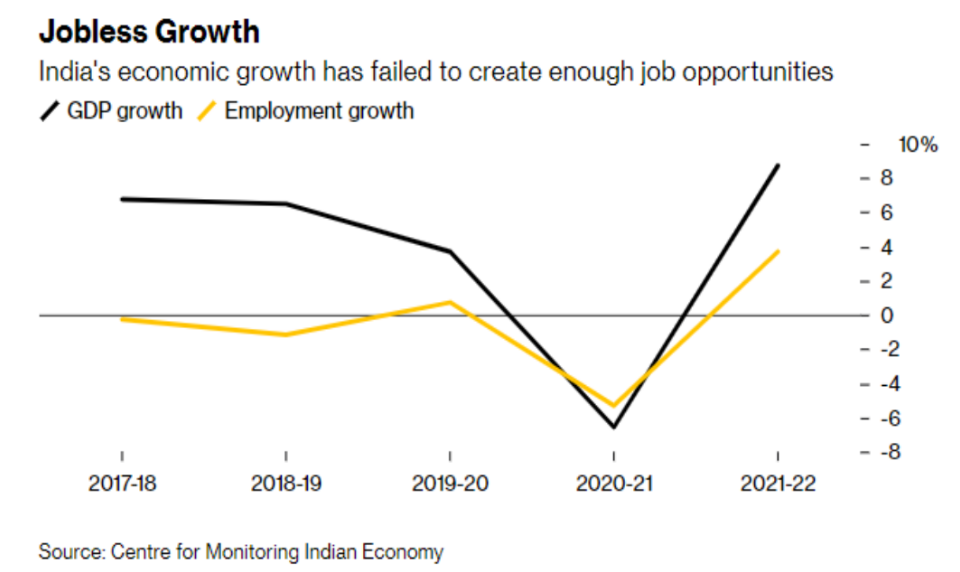
Challenges/Impacts of Jobless Growth:
Government Interventions:
Conclusion:
Jobless growth poses a formidable challenge to India’s vision of inclusive and sustainable development. The onus lies not just on achieving high GDP growth figures but ensuring that this growth translates into tangible improvements in employment and livelihoods for the masses. As India progresses, a multi-pronged strategy encompassing labor reforms, skilling initiatives, and industrial incentives will be essential. Only then can India transform its demographic potential into a genuine demographic dividend, turning economic growth into broad-based prosperity.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Global Capability Centres in India: From Back Offi...
Freedom of Speech of MPs: Constitutional Privilege...
Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam: Women’s Reservatio...
International Mother Language Day 2026- BHASHA Mat...
Gen Z and the Dynamics of Democratic Engagement
Galgotias Robodog Scandal: India’s AI Sovereignt...
India-AI Impact Summit 2026: New Delhi Declaration...
Nature Studies Reveal Fluorescent Proteins as Quan...
U.S. Drops ALARA Principle from Radiation Safety F...
Supreme Court Directs Pan-India Compliance with SW...
Cybercrime in India 2025: Investment Frauds Accoun...
News in Shorts: 23 February 2026

<div class="new-fform">
</div>
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/dfbce655434b9c153965f32ea18f64488c9b0aad756726549ed77268c45883b1.jpg https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/66d9016bde99607d42f288f9f65e80b3bcea7b96e7abc1437e64b6f74374964b.jpg https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/722b068b0acf1e65831748df82f6f6ddf1e93dd78363f39c1b2712a105cb23a1.jpg
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/2750faadd08e59996843083a71ffea9095489fc80c78552decd953c6ed33c25d.jpg https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/12819543f3f71f627b12ff8b2300931fdfed0063e54f336534534322e807d6b4.jpg https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/c372e02b6e0aa92a6fbec1d764e28a75ee5107cf353672b3253921796a95aa2e.jpg
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/32f23eb0736ad2263bc289d7248b0833a555c299a043ab8ca853a7693108c046.jpg https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/a87bcefedf7aa3ba321b35d2bec1b2631c8f7e73f96fe718f6c7b9366dfbeb87.jpg