Core Demand of the Question
- Discuss the Panchamrit targets set by India.
- Discuss the challenges which India faces in implementing these Panchamrit targets.
- Analyse how ecological sustainability can be integrated with development aspirations while fulfilling international goals towards future generations.
|
Answer
At the COP26 summit in Glasgow (2021), India announced its visionary ‘Panchamrit’ commitments, including net-zero emissions by 2070, 50% energy from renewables by 2030, and reducing emissions intensity by 45%. These goals demonstrate India’s global leadership in climate action. However, integrating ecological sustainability with economic development in a country with significant poverty and industrialisation needs presents multi-dimensional challenges.
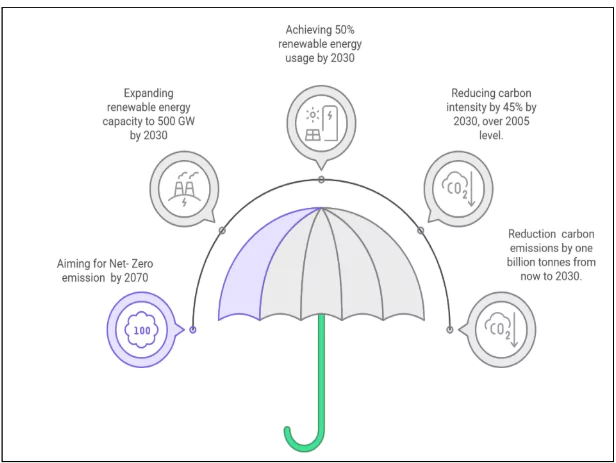
Panchamrit Targets of India
Implementation Challenges
- Inconsistent Policy Implementation Across States: Environmental programmes see uneven execution due to differing capacities, political priorities, and resource allocations among states.
- Insufficient Climate Finance and Technology Transfer: Funding gaps exist in scaling renewable energy, clean mobility, and climate-resilient infrastructure.
For example: India needs $10.1 trillion in investments to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070, but current flows fall short.
- Conflict Between Development and Conservation: Urbanization, infrastructure expansion, and industrialization often conflict with environmental protection.
- Pollution and Degradation Remain Acute: Air, water, and soil pollution persist despite major schemes, affecting health and productivity.
For example: As per World Air Quality Report 2023, 9 out of 10 most polluted cities were in India.
- Deforestation and Biodiversity Loss: Encroachments, illegal logging, and poorly planned projects continue to shrink forests and habitats.
Integrating ecological sustainability with development aspirations
Positives
- Long-Term Economic Growth and Resource Security: Sustainable development ensures resource availability and reduces costs over time, preventing economic losses from environmental degradation.
- Improved Public Health Outcomes: Cleaner air, water, and healthier ecosystems reduce disease burden and healthcare costs.
- Fulfillment of International Climate Commitments: Aligning policies with international agreements (e.g., Paris Agreement) strengthens India’s global standing and attracts climate finance.
For example: India becomes the third-largest producer of wind and solar energy, doubling solar power generation, aiming for 50% clean energy by 2030.
- Preservation of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Conserving natural habitats maintains biodiversity and the ecosystem services vital for food, water, and climate regulation.
- Ethical Stewardship and Intergenerational Equity: Ensuring sustainable use of resources honors the ethical responsibility to future generations.
Challenges
- Conflict Between Economic Growth and Environmental Protection: Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure expansion often clash with conservation efforts, resulting in habitat loss and increased pollution.
- Inadequate Climate Finance and Technology Access: Insufficient funding and limited access to green technologies hinder the large-scale adoption of sustainable practices.
- Weak Enforcement and Governance Gaps: Environmental laws are often poorly implemented due to limited institutional capacity, corruption, or competing priorities.
For example: The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)’s country-wise plastic data revealed that India mismanages 85 per cent of its plastic waste.
- Social and Regional Disparities in Implementation: Green growth and sustainability initiatives often benefit urban areas more, leaving rural, tribal, and marginalized communities behind.
- Balancing International Commitments with Domestic Needs: Meeting global climate targets can conflict with pressing domestic issues like poverty alleviation, energy access, and employment.
For example: As per CEA, by March 2024, fossil fuels—coal, gas and lignite—added up to 54 per cent of the installed capacity but were generating 77 per cent of the electricity.
Way Ahead
- Promote Renewable Energy Expansion: Accelerate investments in solar, wind, and other renewables to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower emissions.
- Strengthen Green Financing Mechanisms: Mobilize domestic and international green finance to bridge the climate funding gap and support sustainable infrastructure.
For example: The Reserve Bank of India launched a framework for green deposits in 2023 to channel funds into climate-friendly projects.
- Enhance Environmental Governance and Law Enforcement: Build institutional capacity and increase monitoring for effective implementation of environmental laws and targets.
- Promote Community-Based and Inclusive Development: Engage local communities, especially in rural and tribal areas, in planning and implementing sustainability initiatives to ensure equity and ownership.
India’s path must be one of green growth, where ecological limits are respected, development remains inclusive, and intergenerational equity becomes central. A synergistic strategy combining policy reform, innovation, finance, and citizen participation is key to balancing ambition with action.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.


Latest Comments