Core Demand of the Question
- Discuss the key holdings of the Coelho case.
- Discuss judicial review as the key basic feature of the constitution.
|
Answer
Judicial review is a key aspect of the Basic Structure Doctrine, ensuring laws stay within constitutional limits. The I.R. Coelho v. State of Tamil Nadu (2007) ruling reaffirmed judicial review’s role in protecting fundamental rights from arbitrary amendments, with significant implications for constitutional governance in India.
The Coelho Case (2007) : Key Observations
- Reaffirmation of the Basic Structure Doctrine: The Supreme Court held that any law violating the basic structure is subject to judicial review, even if placed in the Ninth Schedule.
- Doctrine of Prospective Overruling: Laws added to the Ninth Schedule after April 24, 1973 (Keshwanand Bharti case) can be struck down if they violate fundamental rights, while laws added before this date remain valid.
- Judicial Review: The Court ruled that judicial review is part of the basic structure of the Constitution and cannot be taken away.
- Ninth Schedule & Fundamental Rights: Laws in the Ninth Schedule are subject to judicial review if they violate fundamental rights under the basic structure.
- Separation of Powers Upheld: The judiciary asserted its power to check legislative excesses, reinforcing constitutional balance.
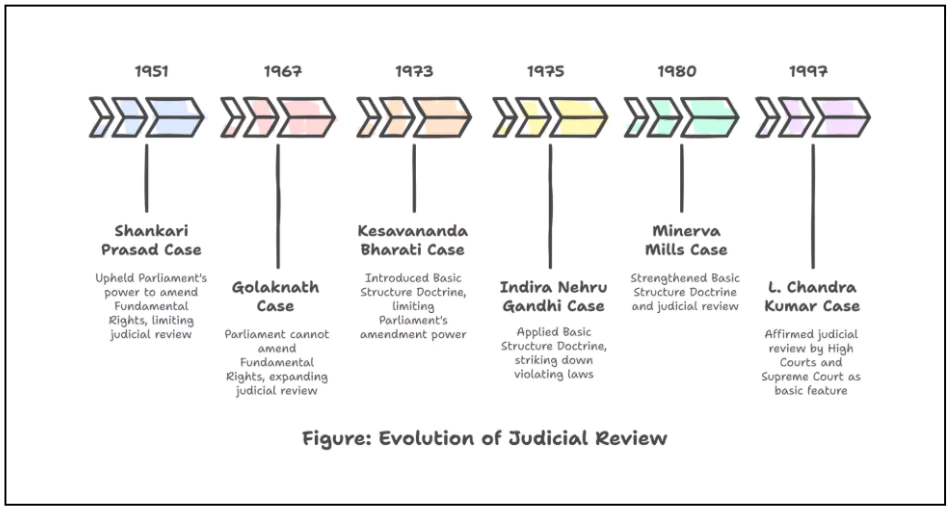
Judicial Review as a Key Feature of the Constitution
- Guardian of the Constitution: Ensures laws and amendments adhere to constitutional principles.
- Checks on Parliament’s Amending Power: Ensures that Basic Structure is not diluted via constitutional amendments.
Eg. NJAC Case (2015) got struck down as unconstitutional.
- Protection of Fundamental Rights: Prevents government actions from violating citizens’ rights.
Eg.: Aadhaar Case (2018) upheld Aadhaar but struck down mandatory linking to bank accounts.
- Balances Separation of Powers: Keeps executive, legislature, and judiciary in check, maintaining constitutional equilibrium.
Eg: In the Tribunals Reforms Case (2021), the SC struck down provisions limiting judicial freedom, preserving the separation of powers.
- Preserves Democratic Integrity: Prevents majoritarianism and safeguards the rule of law.
Eg.: Electoral Bonds Case (2024) declared the Electoral bond scheme unconstitutional.
The Coelho case reaffirmed that laws violating the Basic Structure, even in the Ninth Schedule, are subject to judicial review, strengthening fundamental rights and preventing legislative overreach.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.



Latest Comments