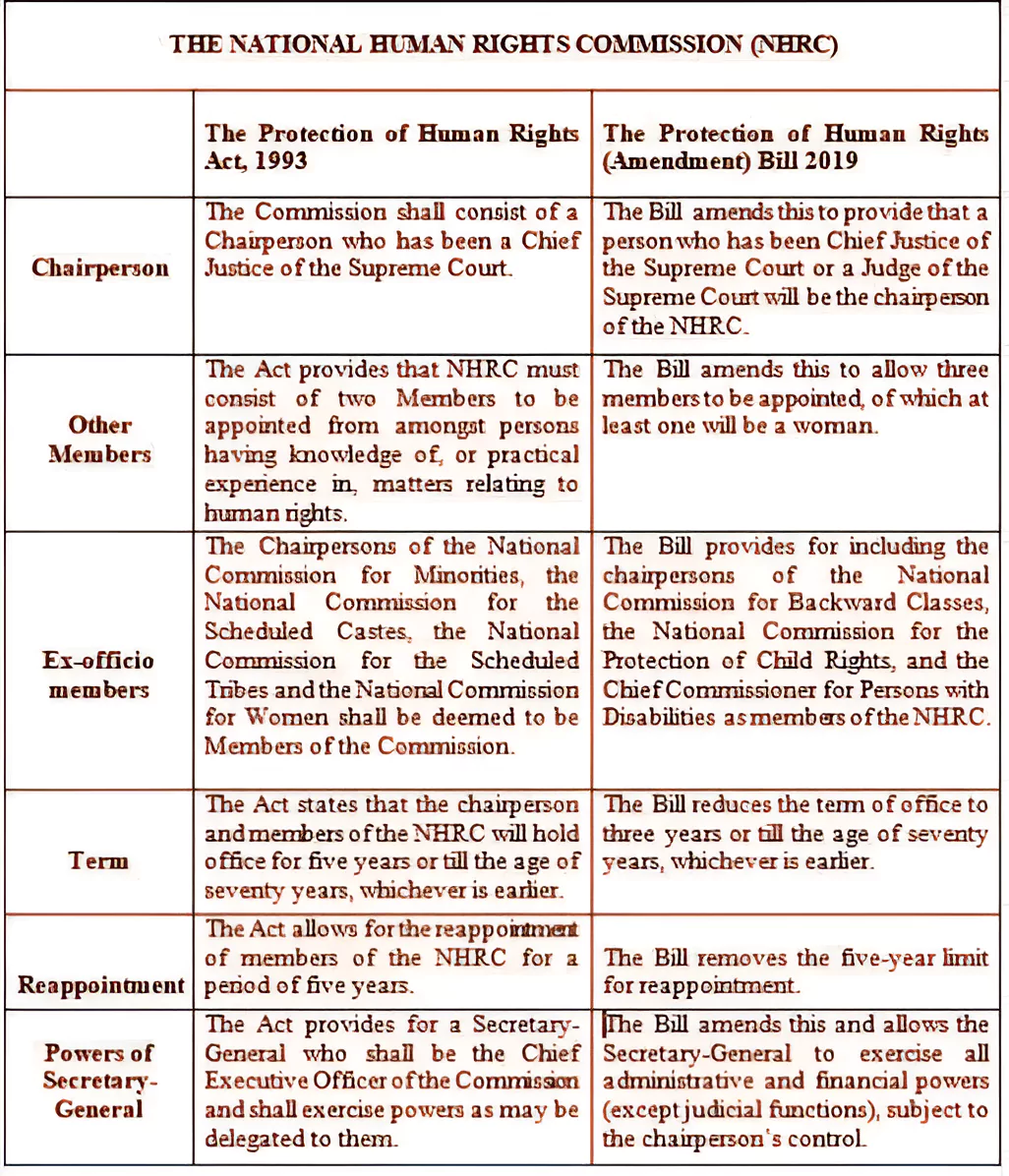
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) of India is a statutory body under the provisions of the Protection of Human Rights Act of 1993.

Provision: The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) of India is a statutory body under the provisions of the Protection of Human Rights Act of 1993.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The National Human Rights Commission of India is a statutory body under the provisions of the Protection of Human Rights Act of 1993.
NHRC is responsible for the protection and promotion of “rights relating to life, liberty, equality and dignity of the individual guaranteed by the Constitution or embodied in the International Covenants”.
They serve for a term of three years or until they attain the age of 70 years, whichever is earlier. Can the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) investigate all types of cases? No. The NHRC does not investigate cases that are older than one year, which are anonymous, pseudonymous, or vague, frivolous cases, and those pertaining to service matters.
The State Human Rights Commission (SHRC) was formed under the Protection of Human Rights Act of 1993. It functions at the state level.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>