![]() 16 Dec 2023
16 Dec 2023
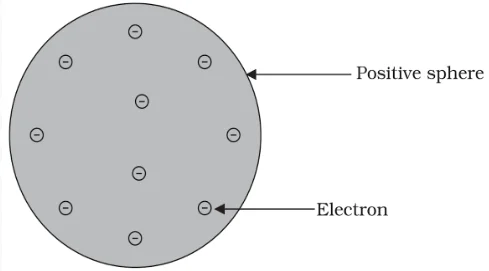
An atom is the fundamental unit of matter, consisting of a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in orbit.The study of atoms is fundamental to chemistry and physics, providing insights into the structure, behavior, and interactions that govern the properties of matter, particularly the intricate details of atomic structure.
Atoms: Fundamental Building Blocks of our world:
1/109m = 1 nm
1m = 109 nm

J.J. Thomson (1856-1940)
A British physicist, was born in Cheetham Hill, a suburb of Manchester, on 18 December 1856. He was awarded the Nobel prize in Physics in 1906 for his work on the discovery of electrons. He directed the Cavendish Laboratory at Cambridge for 35 years and seven of his research assistants subsequently won Nobel prizes.

Rutherford (1871-1937)
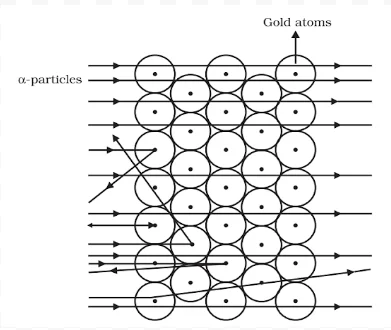
He was born at Spring Grove on 30 August 1871. He was known as the ‘Father’ of nuclear physics. He is famous for his work on radioactivity and the discovery of the nucleus of an atom with the gold foil experiment. He got the Nobel prize in chemistry in 1908.

Neils Bohr
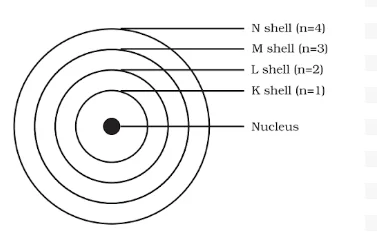
He was born in Copenhagen on 7 October 1885. He was appointed professor of physics at Copenhagen University in 1916 and got the Nobel prize for his work on the structure of atom in 1922. Among Professor Bohr’s numerous writings, three appearing as books are:
(i) The Theory of Spectra and Atomic Constitution,
(ii) Atomic Theory and,
(iii) The Description of Nature.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>