![]() 18 Dec 2023
18 Dec 2023
The cell has a basic structural organization involving various components, including cell organelles. This helps the cells to perform functions like respiration, obtaining nutrition, and clearing of waste material, or forming new proteins. This means that a particular function is carried out by a cluster of cells at a definite place in the body. This cluster of cells, called a tissue, is arranged and designed so as to give the highest possible efficiency of function.
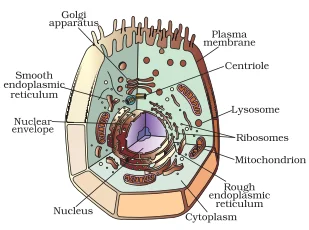
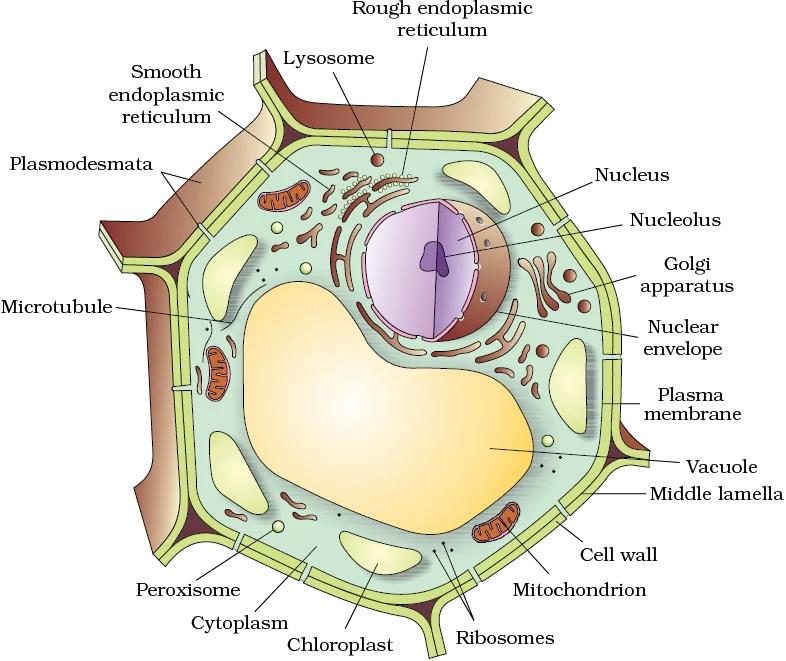
Golgi Apparatus:
Lysosomes:
Mitochondria:
POINTS TO PONDER
Mitochondria contains a small amount of DNA which is also the source of some genetic diseases. Can you think of such genetic diseases and what modern biotechnology solution has been used to eliminate them from the fetus?(hint: Three parent baby)
Plastids:
Vacuoles:
The new cells only have half the number of chromosomes than that of the mother cells.
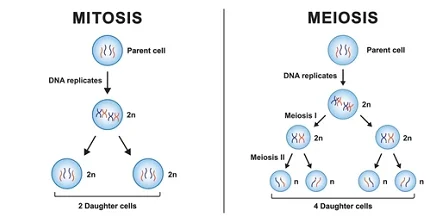
Conclusion
Cell organelles play a crucial role in orchestrating mitosis and meiosis, ensuring accurate genetic transmission. From the endoplasmic reticulum’s structural support to mitochondria’s energy production, cell organelles actively contribute to essential cellular functions. Their collaboration underscores the intricate precision within the microscopic realm of cell division.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>