![]() 18 Dec 2023
18 Dec 2023
A Journey into the Chemistry, Heat, and Illumination of Fire
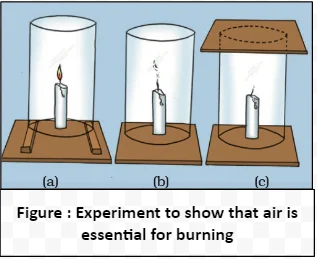
Combustion is a chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidizing agent, typically oxygen, resulting in the release of heat and light. Flames are characteristic of various processes, serving as visible indicators of the release of energy through chemical reactions.



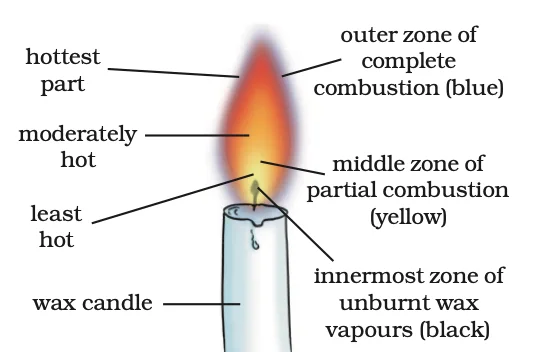

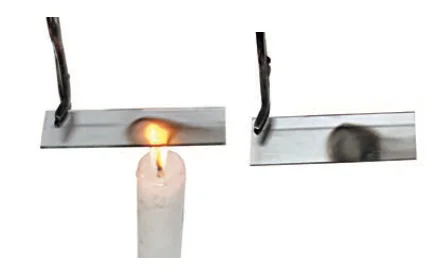

Flame Diversity: Colors, Vaporization, and Zones

<div class="new-fform">
</div>