![]() 23 Jul 2024
23 Jul 2024
The non-traditional conceptions— both human security and global security—focus on changing the nature of security threats. Non-traditional conceptions such as human security and global security redefine security concerns beyond traditional military threats. They emphasize contemporary challenges like terrorism, poverty, migration, refugees, and health epidemics, reflecting a shift towards safeguarding individuals, communities, and global stability in an interconnected world.
Define: Terrorism refers to political violence that targets civilians deliberately and indiscriminately. International terrorism involves citizens or territory of more than one country. Terrorist groups seek to change a political context or condition that they do not like by force or threat of force.
Global poverty is another source of insecurity. High per capita income and low population growth make rich states or rich social groups get richer, whereas low incomes and high population growth reinforce each other to make poor states and poor groups get poorer.

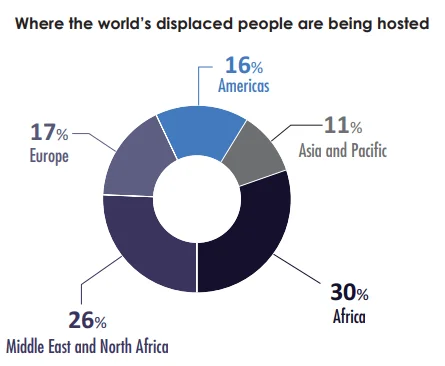
Migrants vs Refugees: International law and norms make a distinction between migrants (those who voluntarily leave their home countries) and refugees (those who flee from war, natural disaster, or political persecution).
India has faced traditional (military) and non-traditional threats to its security that have emerged from within as well as outside its borders. Its security strategy has four broad components.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
The changing security environment, marked by unconventional challenges such as terrorism, poverty, displacement, and health epidemics, requires a shift in focus toward collaborative security. This strategy focuses on collective action rather than unilateral force by utilizing international organizations, NGOs, and global partnerships. India’s comprehensive security approach highlights significance of preparedness of armed forces, adherence to global standards, maintaining internal peace, and advancement in economic growth. Dealing with these challenges together guarantees a stronger global community, protecting national interests and global stability in an interconnected world.
| Related Articles | |
| TERRORISM AND EXTREMISM | The Challenge of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis (EPTB) |
| CITIZENSHIP | Population Dynamics: Distribution, Density, & Growth In India |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>