![]() 12 Dec 2023
12 Dec 2023
Non-renewable resources have a limited stock. Once the Conventional Sources stocks are exhausted it may take thousands of years to be renewed or replenished. Minerals and fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum and natural gas are examples of such resources. Mineral fuels are essential for generation of power, required by agriculture, industry, transport and other sectors of the economy.
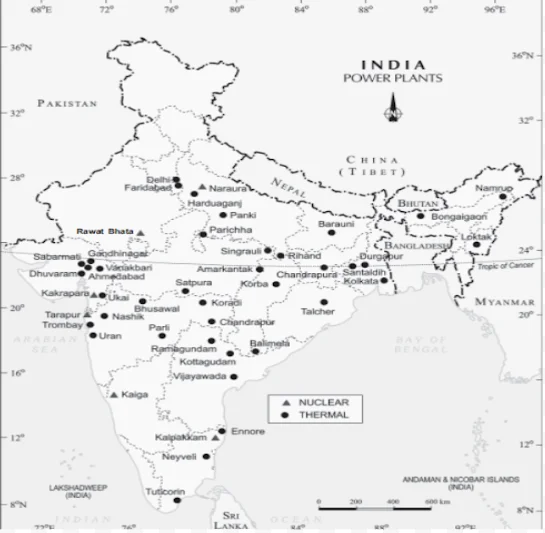
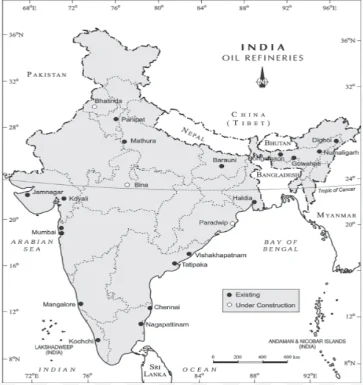
India – Oil Refineries
Conventional Sources of Power: Electricity has such a wide range of applications in today’s world that its per capita consumption is considered as an index of development.
It is generated mainly in two ways:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the overreliance on Conventional Sources raises environmental and security concerns. Swift adoption of renewable sources is imperative for a sustainable future. Let’s prioritize cleaner alternatives for a resilient and prosperous world.
Also Read: Views on Resource Management: Ownership, Land Use, and Development Status
<div class="new-fform">
</div>