![]() 6 Dec 2023
6 Dec 2023
People are a country’s true wealth. They utilize the nation’s resources and determine its policies. It is vital to know the key demographic Indicators like sex ratio, death rate, birth rate, literacy rate , and the density of population, for thorough analysis of countries.
The world at the beginning of the 21st century recorded the presence of over 6 billion people. It crossed the 8 billion mark on 15 November 2022.
Population Disparities: The Global Trend through George B. Cressey’s Insight on the Density of Population in Asia
|
|---|
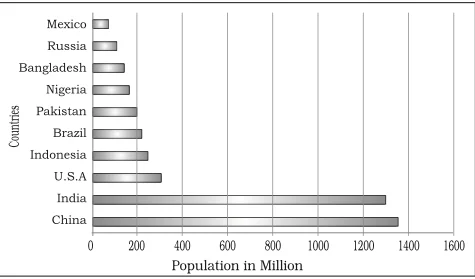
Most Populous Countries
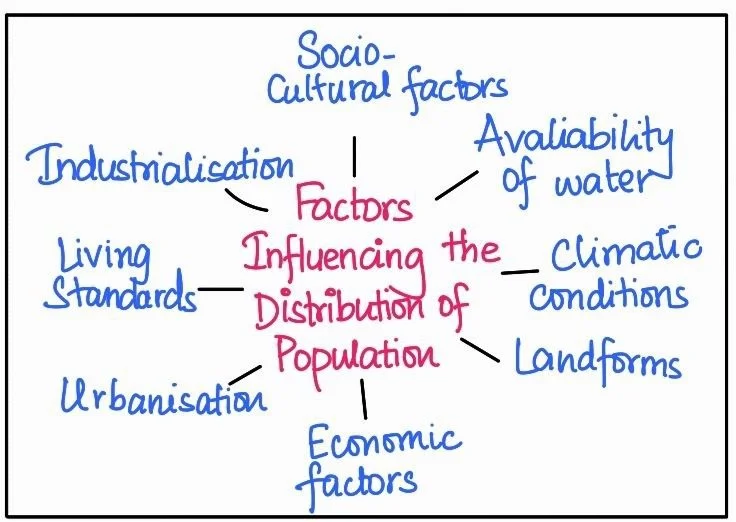

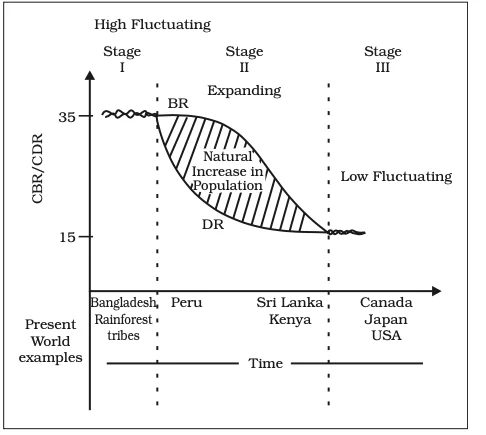
Demographic Transition Theory
Thomas Malthus’s Insight:
|
|---|
Population Control Measures with a Focus on Family Planning
|
Note: In 1952, India became the first country in the developing world to create a state-sponsored family planning program, the National Family Planning Program. |
|---|
Also Read: Indian Society: Demography, Growth Rate & Theory
Conclusion
Recognizing the pivotal role of Density of Population is crucial in shaping effective policies for sustainable global demographics. As nations undergo demographic transitions, the interplay of factors influences population density. Strategic population control measures, such as family planning, are essential for maintaining a balanced and sustainable density worldwide.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>