![]() 27 Nov 2023
27 Nov 2023
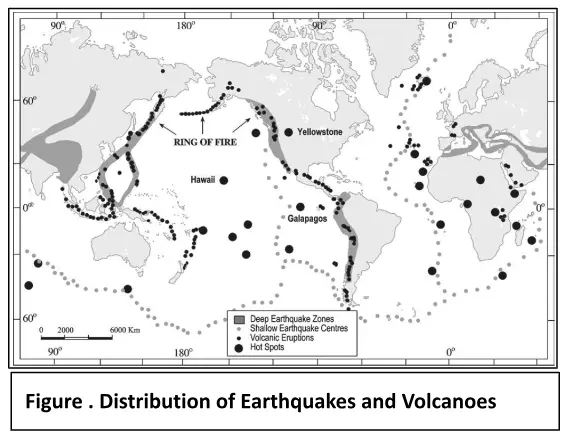
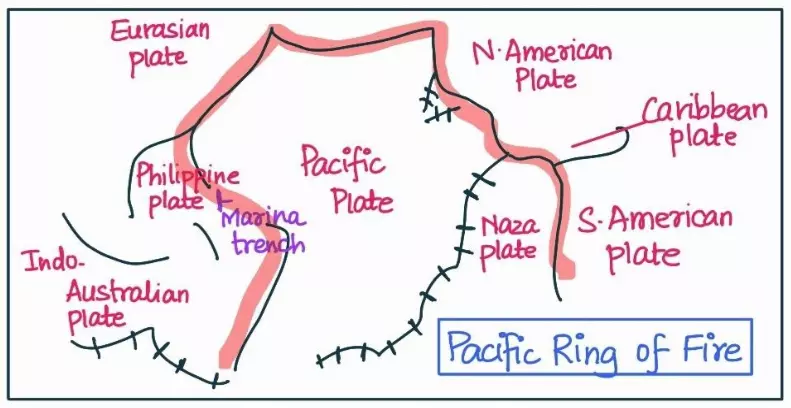
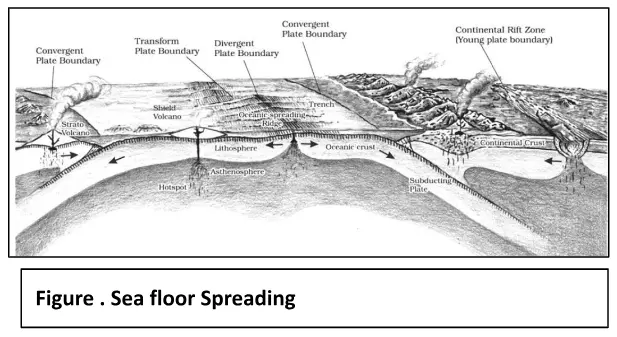
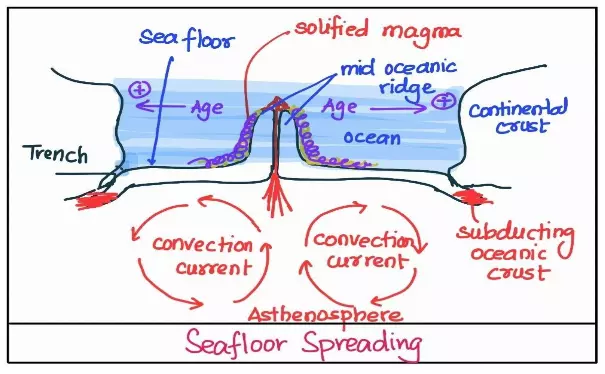
Post-drift studies and sea floor spreading have significantly advanced our understanding of the Earth’s dynamic geology. Building upon Alfred Wegener’s continental drift theory, these studies have revealed the intricate processes that shape our planet. The concept of sea floor spreading, driven by the movement of tectonic plates, has become a cornerstone in modern geology, elucidating the mechanisms responsible for Earth’s evolving surface.
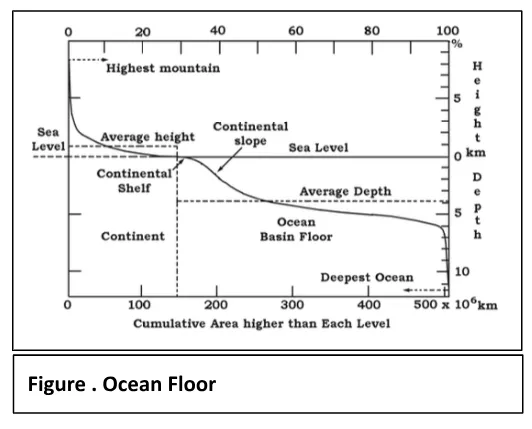
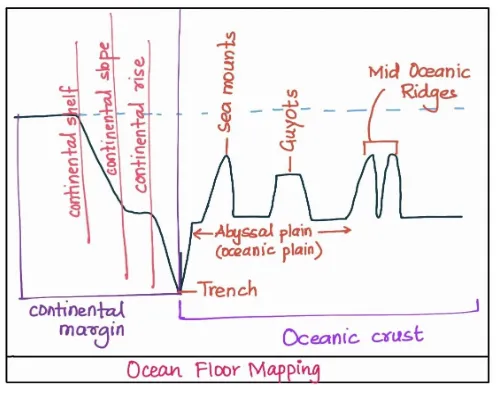
The ocean floor can be segmented into three based on depth and relief:
<div class="new-fform">
</div>