![]() 30 Nov 2023
30 Nov 2023
The earth maintains a constant temperature by ensuring the heat it receives (insolation) equals the heat it emits (terrestrial radiation). Thus earth as a whole neither accumulates nor loses heat, hence it maintains its temperature.
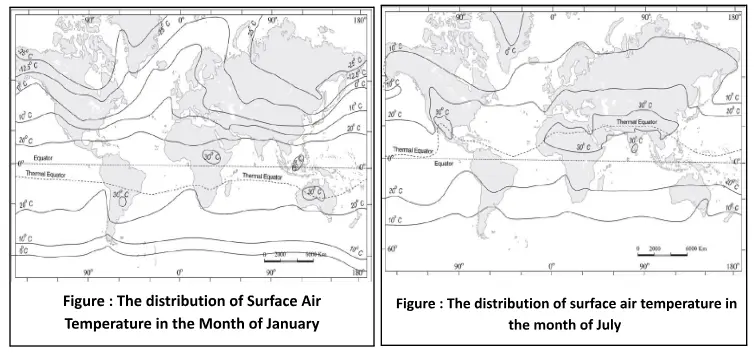
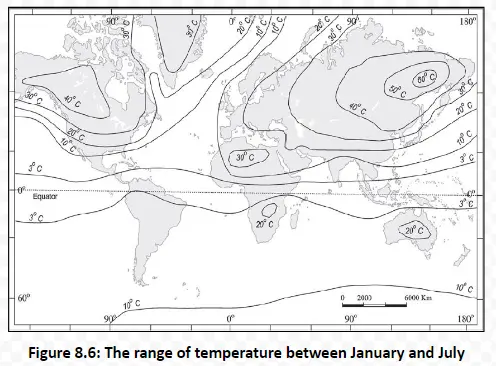
Temperature distribution across the globe isn’t uniform. It’s a dynamic pattern influenced by various factors, and it changes with seasons.
Temperature inversion is an atmospheric phenomenon that flips our usual understanding of how temperature behaves with altitude.
Plank’s law states that hotter a body, the more energy it will radiate and shorter the wavelength of that radiation.
Specific heat is the energy needed to raise the temperature of one gram of substance by one Celsius.
Surface temperature inversions can have significant effects on the atmosphere and the environment, leading to phenomena like fog and frost protection in certain terrains.
In summary, surface temperature inversions can lead to stable atmospheric conditions, the trapping of airborne particles, fog formation, and protective effects like frost protection in specific terrains. The dispersal of the inversion typically occurs as the sun rises and warms the Earth’s surface, promoting air mixing.
Glossary
<div class="new-fform">
</div>