Globalization is a relatively new term, but the process of people, goods, and ideas interacting across borders is centuries old. Thus, all through history, human societies have become steadily more interlinked. Globalization is an economic system that has emerged over the past 50 years, shaped by trade, conquest, and world war. It has changed the global economy, affecting people and societies around the world.
The global world has a long history – of trade, of migration, of people in search of work, movement of capital.
About: Silk Roads comprised an extensive system of trade pathways connecting Asia to Europe and North Africa. It has been in existence since well before Christian Era and remained vibrant until nearly the fifteenth century.
Food is a testament to exchange of ideas and ingredients across cultures over long distances. Traders and travelers introduced new crops to the lands they visited, which were often adopted by the local people.
Age of Exploration and Discovery: In the 16th century, European sailors discovered new sea routes to Asia and America.
The 19th century was a time of great change, with economic, political, social, cultural, and technological factors transforming societies and reshaping international relations. Economists identify three types of movement or ‘flows’ within international economic exchanges:
Before the 19th century, countries tried to be self-sufficient in food. But the Industrial Revolution in Europe changed the way food was produced and consumed. The population of Britain increased in the late 18th century, which led to a higher demand for food. This, along with the growth of urban centers and industry, pushed up food prices.
Pioneer Technologies: The railways, steamships, and the telegraph transformed the nineteenth-century world.
Colonial Expansion: During the late 1800s, European nations increased their territories by colonizing various regions in Africa and Asia.
Forced Labor and Human Trafficking: During the 19th century, numerous Indian and Chinese workers were hired to labor on plantations, in mines, and road and railway development projects globally.
Indian bankers(the Shikaripuri shroffs and Nattukottai Chettiars) and traders played a vital role in financing export agriculture and trade in Central and Southeast Asia, Africa, and beyond.
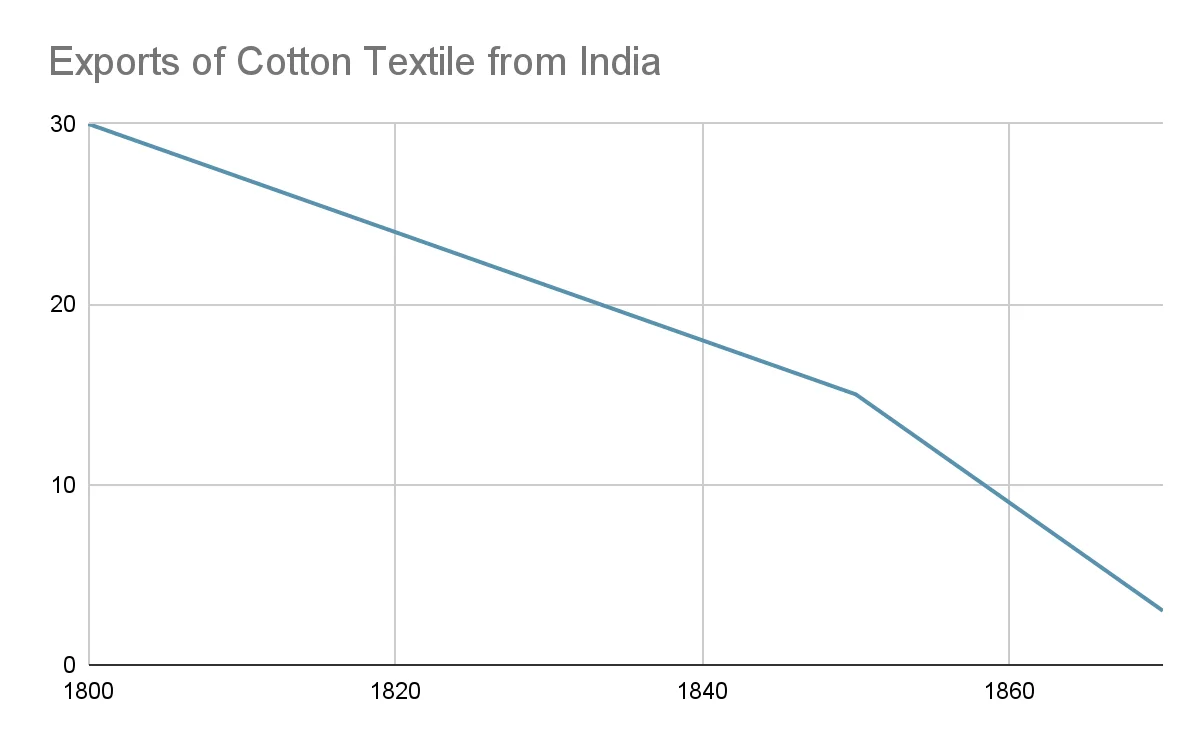
Decline of Indian Textile Industry: British industrialization and tariff barriers led to a decline in Indian cotton textile exports and an increase in raw material exports. ( raw cotton, Indigo, opium)
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Globalization manifests through trade, migration, and cultural exchange. Ancient routes like the Silk Road facilitated economic and cultural interactions. The 19th century, marked by technological advancements and colonial expansions, transformed global economies and societies. This era saw significant shifts in labour, capital, and trade flows, influencing global food production and migration patterns. Despite its benefits, globalization often comes at the cost of local economies and communities.
| Related Articles | |
| GLOBALISATION | JAINISM AND BUDDHISM |
| INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION | EUROPEAN UNION (EU) |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
