![]() 20 Dec 2023
20 Dec 2023
Understanding How We’re Alike and Different in the Process of Reproduction
The process of reproduction is fundamental to the perpetuation of life, and it is marked by the intriguing phenomenon of the accumulation of variation. This concept encapsulates the dynamic interplay of genetic information, where offspring inherit traits from their parents but also exhibit unique characteristics.
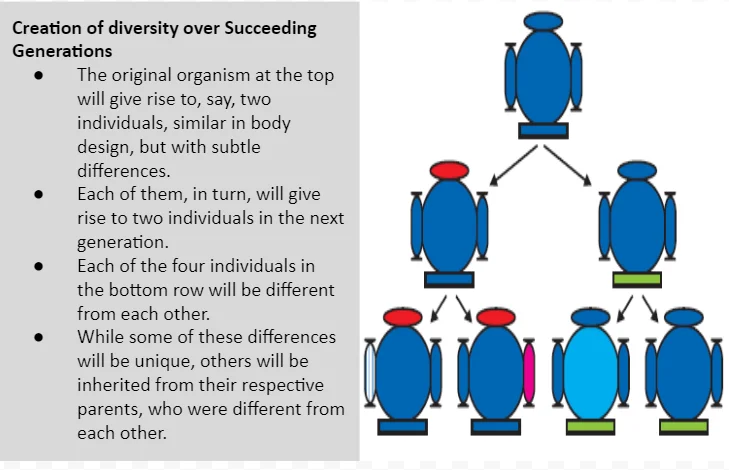
Inheritance: Inheritance from the previous generation provides a common basic body design for the next generation.

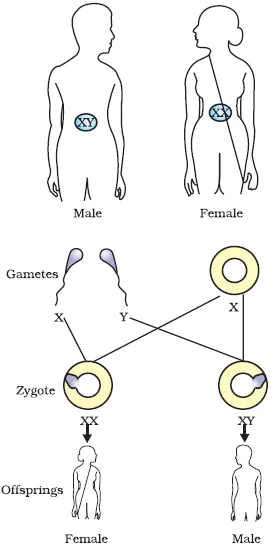
Rules for the Inheritance of Traits – Mendel’s Contributions
<div class="new-fform">
</div>