![]() 25 Jun 2024
25 Jun 2024
The expansion of Company Rule refers to the 18th and 19th-century period when the British East India Company extended its control over Indian territories. This era marked a significant shift from trade to direct governance, impacting India’s political, economic, and social landscape, ultimately laying the groundwork for British colonial rule.

Gradual Expansion of Company
Through Diplomatic Means: East India Company from 1757 to 1857 used a variety of political, economic and diplomatic methods to extend its influence before annexing an Indian kingdom.
Residents in Indian States:After the Battle of Buxar in 1764, the Company appointed Residents in Indian states, who served as political or commercial agents to advance the Company’s interests,
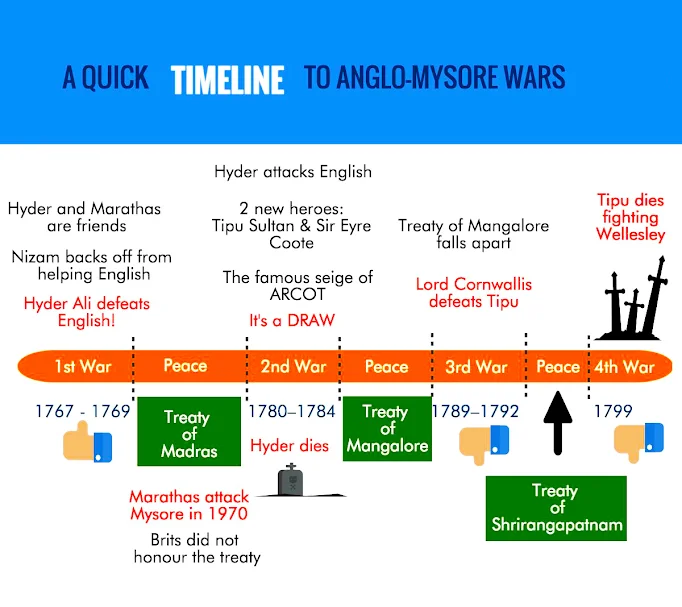
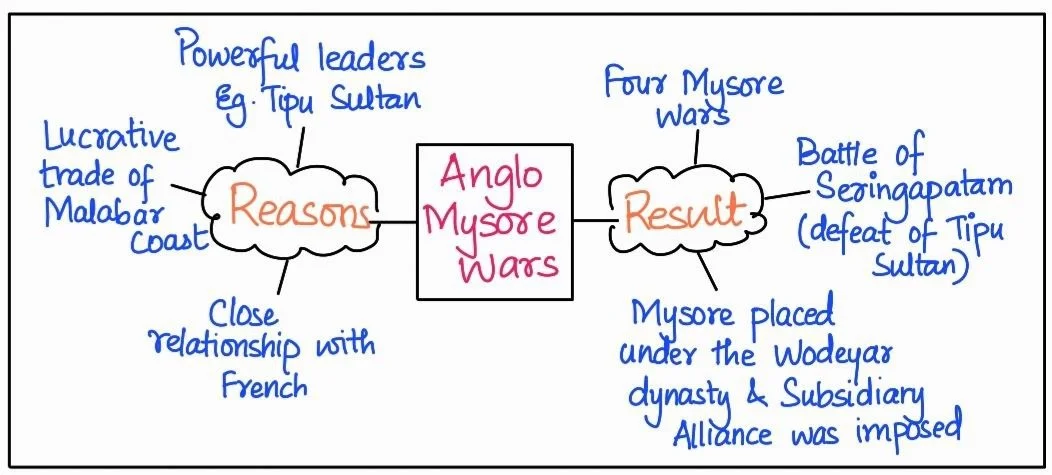

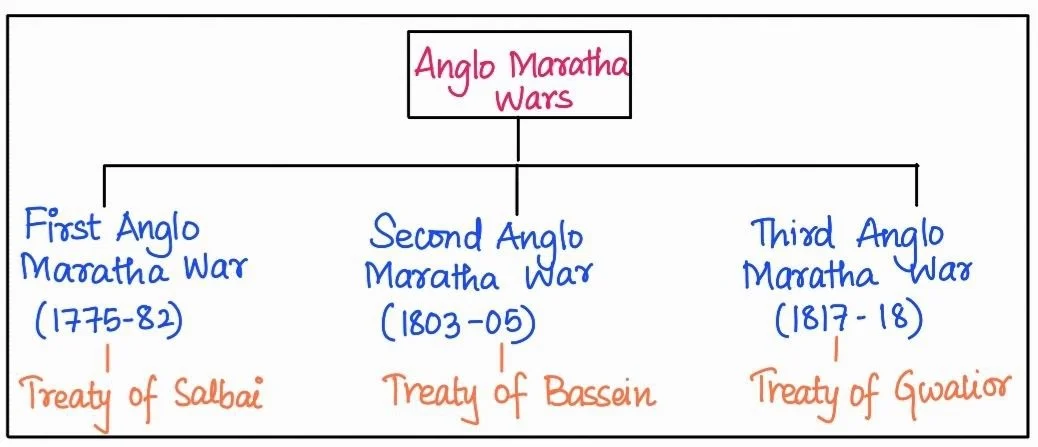
Political Structure: The third Battle of Panipat in 1761, shattered Maratha ambition of ruling from Delhi.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
The East India Company’s gradual expansion, using diplomatic tools like Residents and Subsidiary Alliances, alongside military victories in conflicts like the Anglo-Mysore Wars and Anglo-Maratha Wars, laid the foundation for a vast British colonial empire in India. This political dominance significantly reshaped the subcontinent’s social and economic landscape.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>