![]() 22 Jun 2024
22 Jun 2024
Wildlife Conservation in the background of rapid decline in wildlife population and forestry has become essential. Wildlife Conservation preserves ecological diversity and our life support systems – water, air and soil. It also preserves the genetic diversity of plants and animals for better growth of species and breeding.
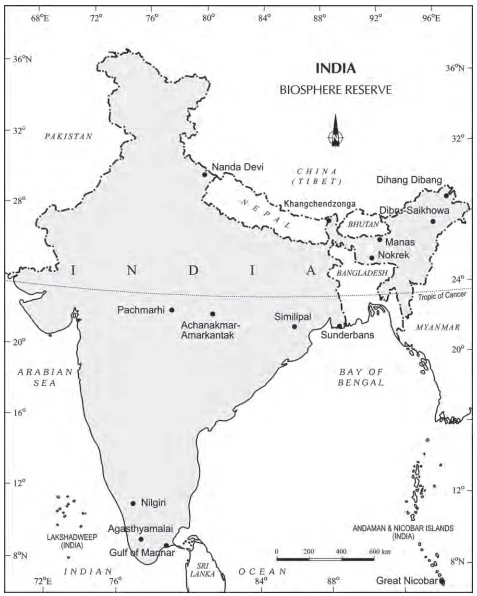
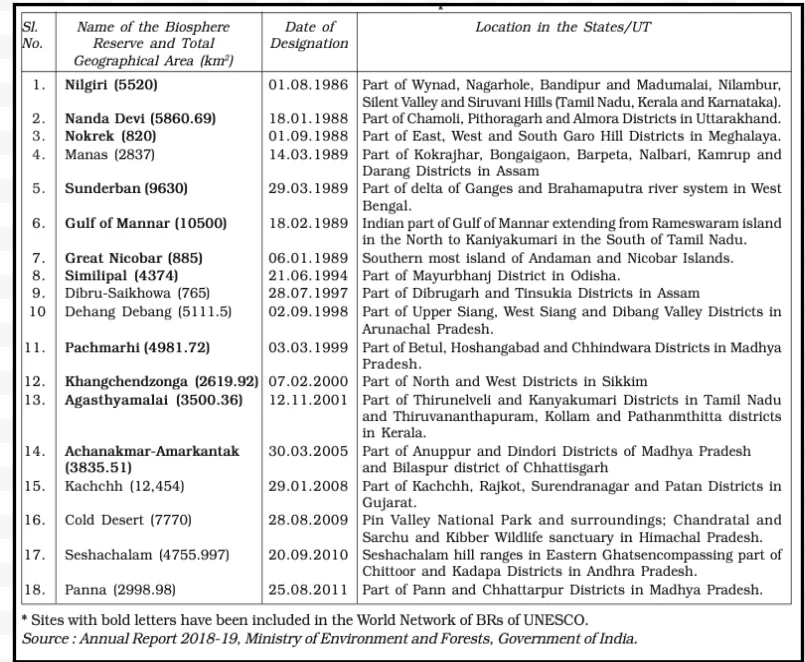
The central government announced several projects for protecting specific animals, which were gravely threatened, including the tiger, the one horned rhinoceros, the Kashmir stag or hangul, three types of crocodiles – freshwater crocodile, saltwater crocodile and the Gharial, the Asiatic lion, and others.
|
|---|
Conclusion
| Glossary
Fauna : The animal life of a given area or time. National Park : A National park is an area which is strictly reserved for the protection of the wildlife and where activities such as forestry, grazing or cultivation are not allowed. Protected Forest : An area notified under the provisions of Indian Forest Act or the State Forest Acts having limited degree of protection. In Protected Forests, all activities are permitted unless prohibited. Reserved Forest : An area notified under the provisions of Indian Forest Act or the State Forest Acts having full degree of protection. In Reserved Forests, all activities are prohibited unless permitted. Sanctuary : A sanctuary is an area, which is reserved for the Wildlife Conservation of animals only and operations such as harvesting of timber, collection of minor forest products are allowed so long as they do not affect the animals adversely. Unclassed Forest : An area recorded as forest but not included in reserved or protected forest category. Ownership status of such forests varies from state to state. Virgin Vegetation: Virgin vegetation refers to plant communities that have developed naturally without human interference and have remained untouched by human activities. |
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>