![]() 20 Jun 2024
20 Jun 2024
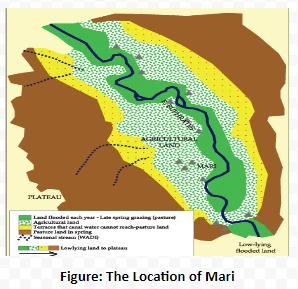
After 2000 BCE the royal capital of Mari flourished in the unique setting of Pastoral Zones. Mari stands not on the southern plain with its highly productive agriculture but much further upstream on the Euphrates. Some communities in the kingdom of Mari had both farmers and pastoralists, but most of its territory was used for pasturing sheep and goats.

| POINTS TO PONDER
The connection between trade and writing is highlighted in the text, with reference to Enmerkar trade mission to Aratta. How do you think writing plays a crucial role in facilitating long-distance trade and diplomatic relations in Mesopotamia? Do you think this ability to write gave them an edge over the contemporary civilisations in trading? |
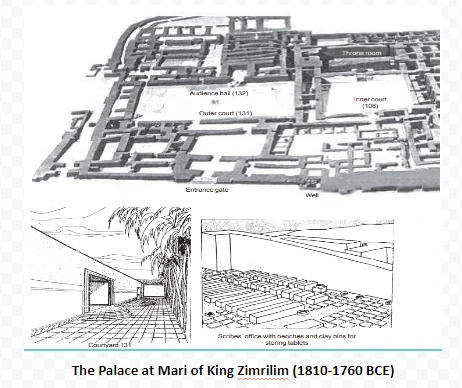
The Palace at Mari of King Zimrilim (1810-1760 BCE)
|
| An Early Library
In the iron age, the Assyrians of the north created an empire, at its height between 720 and 610 BCE, that stretched as far west as Egypt. The great Assyrian kings, who had been immigrants, acknowledged the southern region, Babylonia, as the centre of high culture and the last of them, Assurbanipal (668-627 BCE), collected a library at his capital, Nineveh in the north. He made great efforts to gather tablets on history, epics, omen literature, astrology, hymns and poems. Copies were made of important texts such as the Epic of Gilgamesh, the copier stating his name and writing the date. |
|
TIMELINE |
|
| c. 7000-6000 BCE | Beginning of agriculture in the northern Mesopotamian plains |
| c. 5000 BCE | Earliest temples in southern Mesopotamia built |
| c. 3200 BCE | First writing in Mesopotamia |
| c. 3000 BCE | Uruk develops into a huge city, increasing use of bronze tools |
| c. 2700-2500 BCE | Early kings, including, possibly, the legendary ruler Gilgamesh |
| c. 2600 BCE | Development of the cuneiform script |
| c. 2400 BCE | Replacement of Sumerian by Akkadian |
| 2370 BCE | Sargon, king of Akkad |
| c. 2000 BCE | Spread of cuneiform writing to Syria, Turkey and Egypt; Mari and Babylon emerge as important urban centres |
| c.1800 BCE | Mathematical texts composed; Sumerian no longer spoken |
| c.1100 BCE | Establishment of the Assyrian kingdom |
| c. 1000 BCE | Use of iron |
| 720-610 BCE | Assyrian empire |
| 668-627 BCE | Rule of Assurbanipal |
| 331 BCE | Alexander conquers Bablyon |
| c. 1st century CE | Akkadian and cuneiform remain in use |
| 1850s | Decipherment of the cuneiform script |
Glossary
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>