![]() 6 Dec 2023
6 Dec 2023
India’s demographic landscape has witnessed distinct phases of population growth, shaped by historical, social, and economic factors. The early years were marked by slow growth, reflective of a predominantly agrarian society. The mid-20th century saw a significant acceleration, fueled by improved healthcare and a decline in mortality rates. Subsequently, contemporary trends reflect a transition towards stabilizing population dynamics, indicative of evolving societal norms and developmental strides.
Adolescent Population:
|
India’s National Population Policy (NPP) 2000:
|
|---|
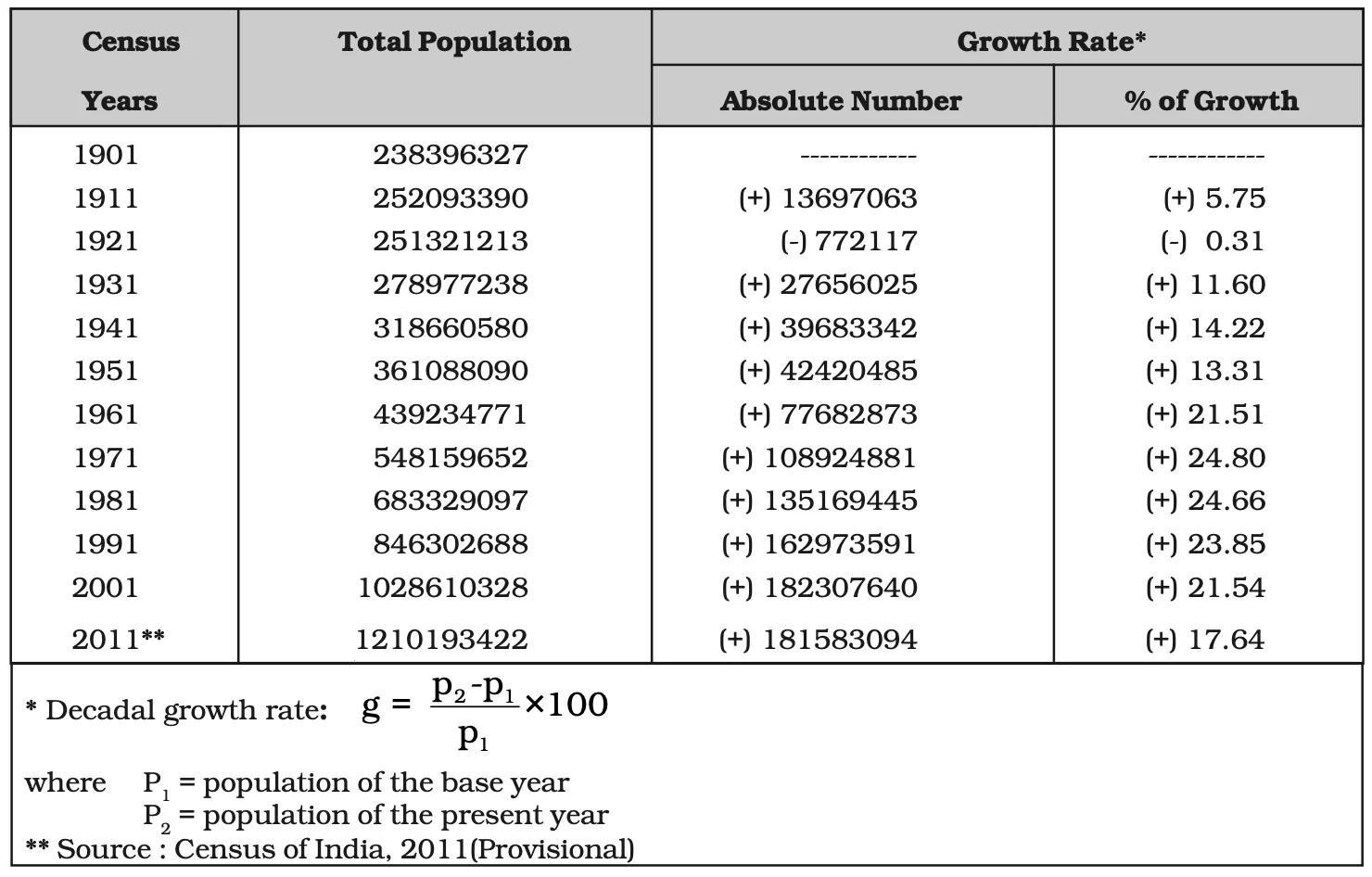
Decadal Growth Rates in India, 1901-2011
| Phase | Duration | Key Characteristics |
| Phase I: Stagnant Phase | 1901-1921 |
|
| Phase II: Steady Growth | 1921-1951 |
|
| Phase III: Population Explosion | 1951-1981 |
|
| Phase IV: Decelerating Growth | Post-1981 |
|
Table: Historical Phases of Population Growth
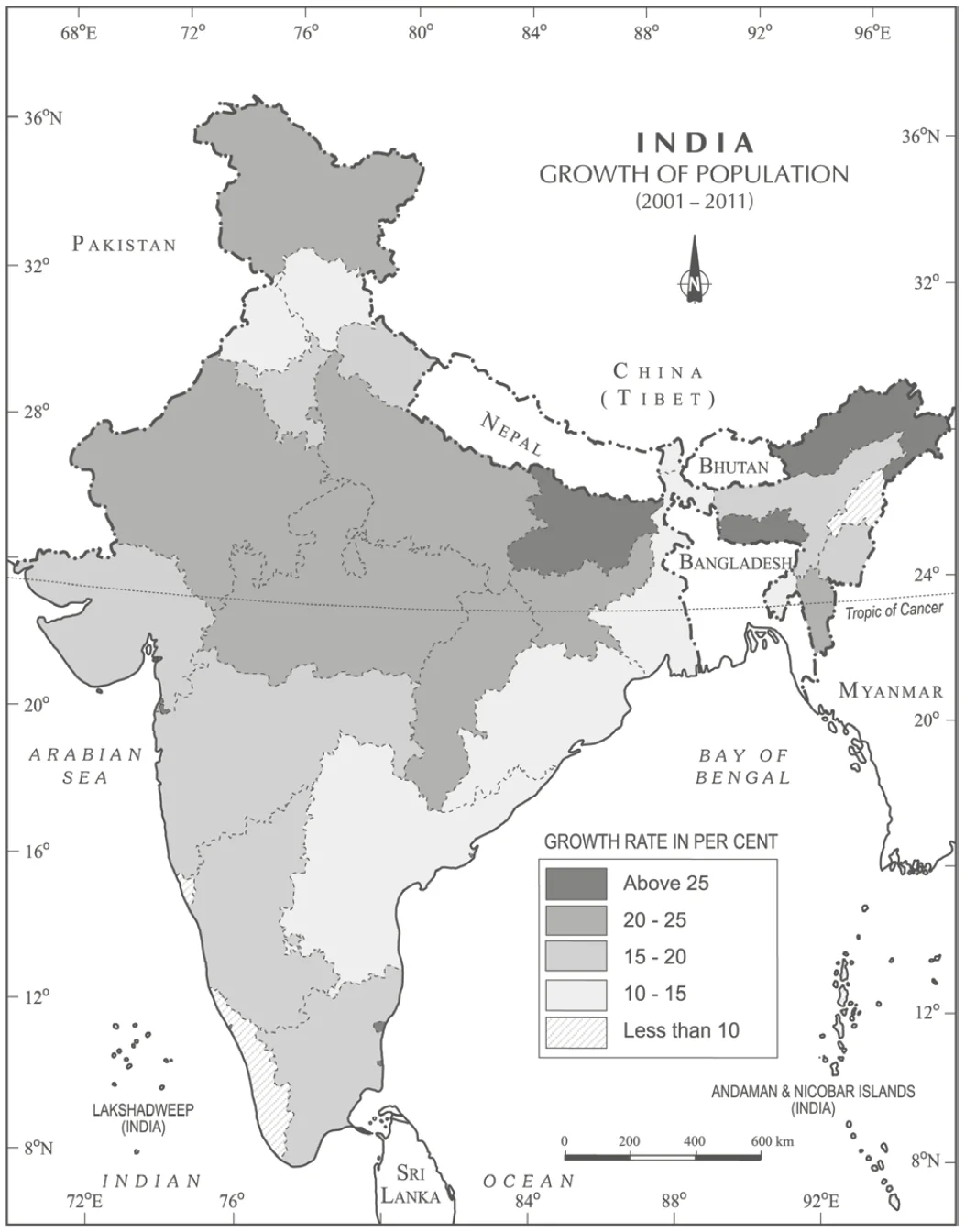
India – Growth of Population
Also Read: Population Dynamics: Distribution, Density, & Growth In India
<div class="new-fform">
</div>