![]() 22 Jul 2024
22 Jul 2024
India has maintained good relations with all post-communist countries. India’s relations with Russia are an important aspect of India’s foreign policy. Actors of Indian cinema from Raj Kapoor to Amitabh Bachchan are household names in Russia and many post-Soviet countries. One can hear Hindi film songs all over the region, and India is part of popular memory. More than 80 bilateral agreements have been signed between India and Russia as part of the Indo-Russian Strategic Agreement of 2001.
Mutual Benefits: Russia and India share a vision of a multipolar world order and theirs is a relationship of mutual benefit. India stands to benefit from its relationship with Russia on issues like Kashmir, energy supplies, sharing information on international terrorism, access to Central Asia, and balancing its relations with China.
European Union

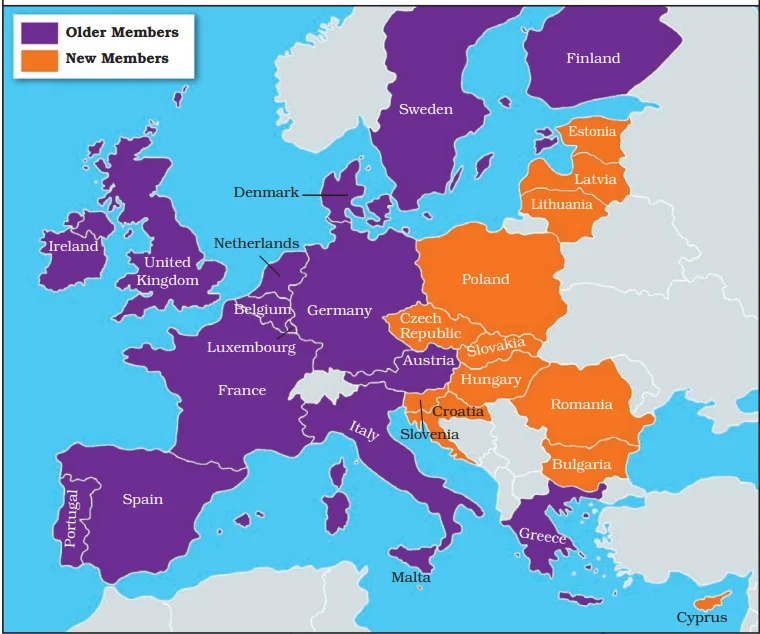
| Timeline of EU Integration |
| 1951 April: Six Western European countries, France, West Germany, Italy, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg signed the Treaty of Paris establishing the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC). |
| 1957 March 25: These six countries signed the Treaties of Rome establishing the European Economic Community (EEC) and the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom). |
| 1973 January: Denmark, Ireland and the United Kingdom join the European Community (EC). |
| 1979 June: First direct elections to the European Parliament |
| 1981 January: Greece joins the EC. |
| 1985 June: The Schengen Agreement abolishes border controls among the EC members. |
| 1986 January: Spain and Portugal join the EC. |
| 1990 October: Unification of Germany. |
| 1992 February 7: The Treaty of Maastricht was signed establishing the European Union (EU). |
| 1993 January: The single market was created. |
| 1995 January: Austria, Finland, and Sweden join the EU. |
| 2002 January: Euro, the new currency, was introduced in the 12 EU members. |
| 2004 May: Ten new members Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia, and Slovenia join the EU. |
| 2007 January: Bulgaria and Romania join the EU. Slovenia adopts the Euro. |
| 2009 December: The Lisbon Treaty came into force. |
| 2012: The EU is awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. |
| 2013: Croatia becomes the 28th member of the EU. |
| 2016: Referendum in Britain, 51.9 percent of voters decide that Britain will exit (Brexit) from the EU. |
Founding Members: ASEAN was established in 1967 by five countries of this region — Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand — by signing Bangkok Declaration. (Refer Figure 11.7)

| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
India’s close relations with former communist nations, particularly Russia, demonstrate its focus on strategic, economic, and cultural interests. Russia backs India’s position on Kashmir, provides energy and military equipment, and cooperates on scientific projects. Global politics has been transformed by the decline of the bipolar world order and the emergence of regional blocs such as the EU and ASEAN. India uses its connections with these groups to promote cooperation within the region, boost economic development, and ensure political stability, ultimately strengthening its global presence.
| Related Articles | |
| ASEAN | ECOWAS: Economic Community of West African States |
| EUROPEAN UNION (EU) | India-Russia Trade Relations |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>