![]() 26 Jul 2024
26 Jul 2024
Being a nation that emerged in the aftermath of World War II, India chose to shape its foreign relations with a focus on upholding sovereignty of other nations and seeking security through preservation of peace. This objective is reflected in Directive Principles of State Policy. The British government left behind a legacy of various international disputes, and partition added its own set of challenges, while the imperative of addressing poverty was already pressing.
Global Confrontation: The Cold War period was marked by the political, economic, and military confrontation at the global level between the two blocs led by the superpowers, the US and the USSR.
The first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru played a crucial role in setting the national agenda. He exercised profound influence in formulation and implementation of India’s foreign policy from 1946 to 1964.
Unlike its relationship with Pakistan, free India began its relationship with China on a very friendly note. (Refer Figure 4.1)
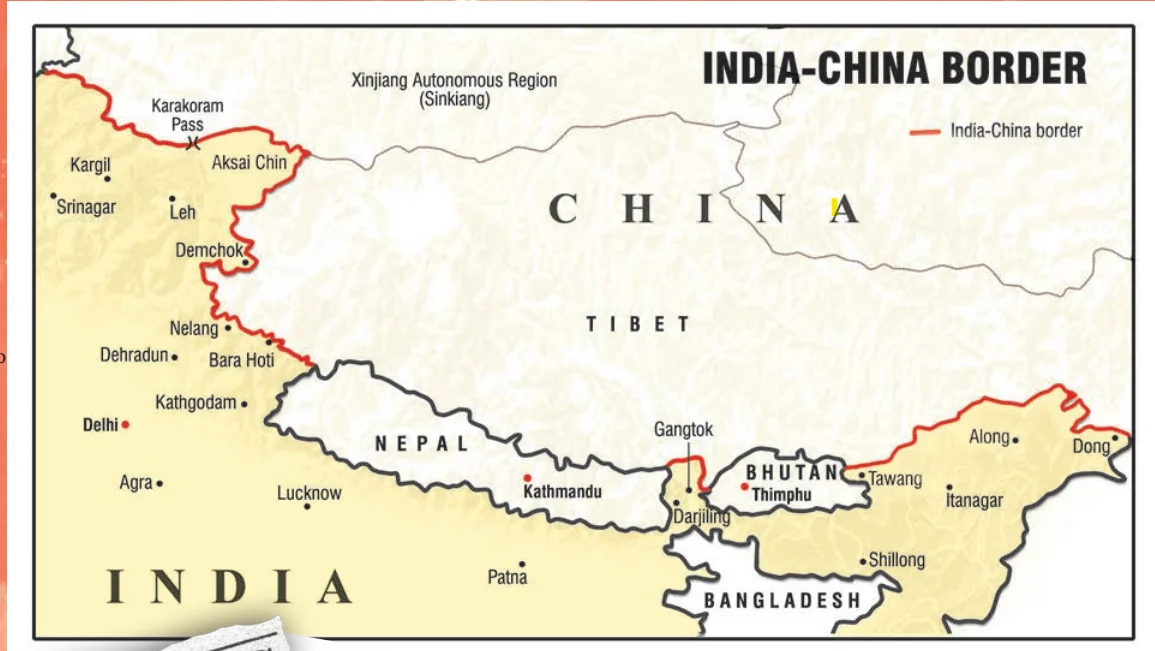
Tibet Issue:
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
India, emerging post-WWII, aimed to uphold sovereignty and peace in its foreign relations, influenced by Nehru’s non-alignment policy. Facing Cold War pressures, India resisted aligning with superpowers, fostering Afro-Asian unity and supporting UN peacekeeping. Nehru’s initiatives like Panchsheel aimed at friendly ties with China, though concerns over future aggression remained. India’s stance reflected its commitment to global peace and development.
| Related Articles | |
| NON ALIGNMENT MOVEMENT (NAM) | DIRECTIVE PRINCIPLES OF STATE POLICY |
| Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru | WORLD WAR II’S IMPACT ON INDIAN NATIONALISM |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>