![]() December 9, 2023
December 9, 2023
![]() 686
686
![]() 0
0
The factors affecting the industrial location are the availability of raw material, land, water, labor, power, capital, transport and market. Industries should be located at points where the production costs are minimum. Hence, Industries are situated where some or all of these factors are easily available.
Industrial location, a key aspect in this decision-making process, plays a pivotal role in determining the success and efficiency of an industry. Sometimes, the government provides incentives like subsidized power, lower transport cost and other infrastructure so that industries may be located in backward areas. Industrialisation often leads to development and growth of towns and cities.
Some of the factors that influence the industrial location are as follows:
| Access to Market |
|
| Access to Raw Material |
|
| Access to Labour Supply |
|
| Access to Sources of Energy |
|
| Access to Transportation and Communication Facilities |
|
| Government Policy |
|
| Access to Agglomeration Economies/ Links between Industries |
|
Table: Factors influencing industrial location
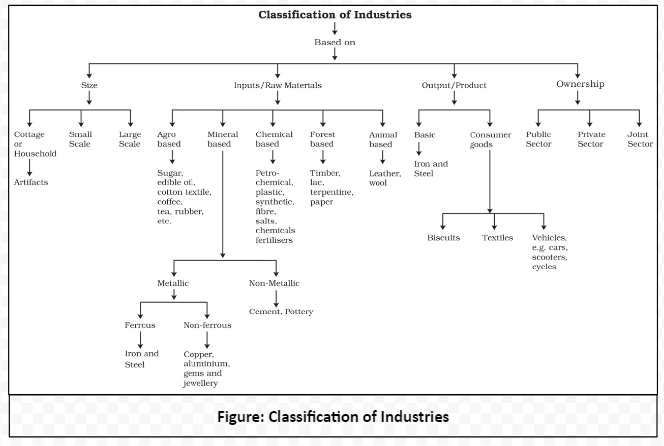
Manufacturing industries are classified on the basis of their size, inputs/raw materials, output/products and ownership. This classification plays a crucial role in the broader context of industrial location, shaping the economic landscape. Let’s delve into the details of this classification.
Let’s analyse this classification of industries in detail.

Foot Loose Industries:Foot loose industries can be located in a wide variety of places. They are not dependent on any specific raw material, weight losing or otherwise. They largely depend on component parts which can be obtained anywhere. They produce in small quantities and also employ a small labour force. These are generally not polluting industries. The important factor in their location is accessibility by road network. |

Read Also: Cultivating Prosperity: The Dynamics of Agro-Based Industries and Their Impact on Economy
<div class="new-fform">
</div>

Latest Comments