![]() 8 Dec 2023
8 Dec 2023
A variety of food and non food crops are grown in different parts of the country depending
upon the variations in soil, climate and cultivation practices. Major crops grown in India are rice, wheat, millets, pulses, tea, coffee, sugarcane, oil seeds, cotton and jute, etc.
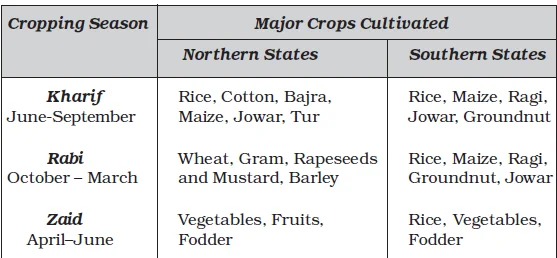
Cropping Seasons in India
Rice Fields of India: Sowing the Seeds of Agricultural Dominance

Rice Cultivation
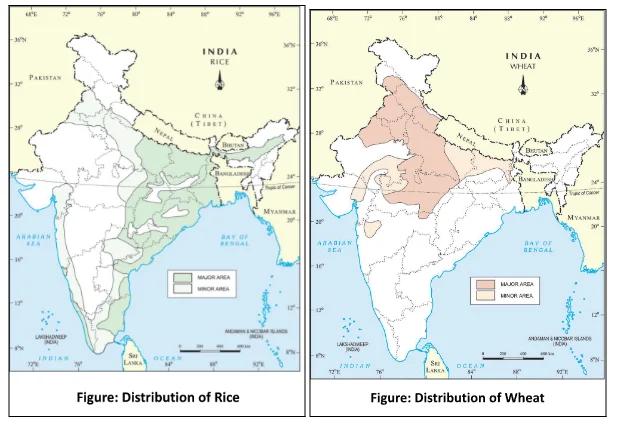

Wheat Harvesting

Bajra Cultivation
| Maize is also known as corn. Various colourful varieties of maize are found across the world. |
|---|

Maize Cultivation
Also Read: Beyond Grains: A Comprehensive Exploration of Food Crops in Indian Agriculture
<div class="new-fform">
</div>