In political philosophy and everyday life, Freedom is the state of being free from constraints or limitations. It encompasses personal autonomy, which relates to an individual’s autonomy over their choices and actions, and political freedom, which concerns the capacity to participate in governance and influence decision-making.
| Aspect | Negative Liberty | Positive Liberty |
| Focus |
|
|
| Nature |
|
|
| Society’s Role |
|
|
| Interrelation |
|
|
| Potential Misuse |
|
|
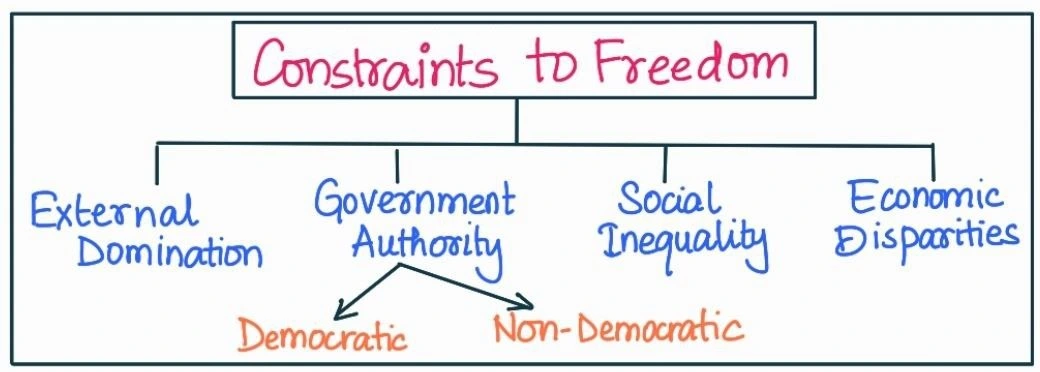
|
How Did Mandela and Suu Kyi Define Freedom Through Struggles and Sacrifices? |
|
|
What are the Core Tenets of Liberalism, Including Tolerance, Individualism, and Views on Inequality?
What are the Perspectives of Voltaire and John Stuart Mill on the Value of Freedom?
Voltaire:

John Stuart Mill:

<div class="new-fform">
</div>
