![]() 22 Dec 2023
22 Dec 2023
Microorganisms exhibit diverse modes of reproduction, contributing to their adaptability and survival. Common modes include binary fission (bacteria), budding (yeast), sporulation (fungi), and both sexual and asexual reproduction (protozoa), showcasing the remarkable versatility of microbial life.
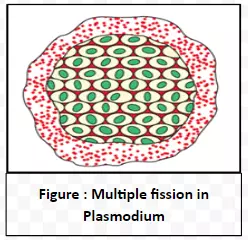
Diverse patterns of Microorganism Reproduction through Fission: Fission is a form of asexual reproduction where a single cell divides to produce two or more separate daughter cells.
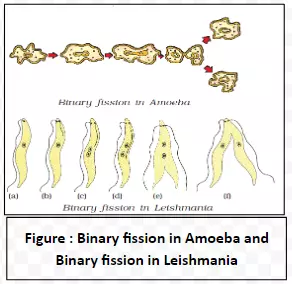
Fragmentation in Microbial Asexual Reproduction: Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction where an organism breaks into fragments, and each fragment develops into a mature, fully-grown individual.
Regeneration in Microorganisms and the intricate mechanisms behind new individual formation: Regeneration is the ability of fully differentiated organisms to develop into new individuals from their body parts.
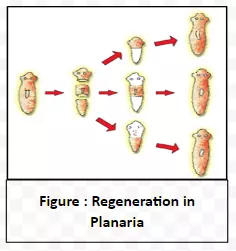
|
Difference between regeneration and reproduction |
||
| Criteria | Regeneration | Reproduction |
| Definition | Growth of an organism from a fragment of its body. | Natural process of producing offspring. |
| Dependence on Fragmentation | Yes (organisms can grow from their body fragments). | No (organisms typically don’t rely on being fragmented). |
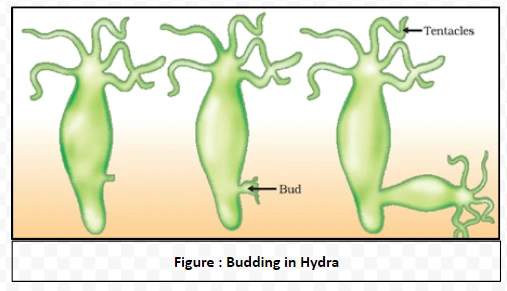
Budding: Asexual Reproductive process in Hydra and the emergence of independent organisms: Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth, or bud, due to cell division at one particular site on a parent organism.
Story of Dolly, the First Cloned MammalCloning refers to the production of an exact replica of a cell, a specific living part, or an entire organism. Dolly’s Historic Birth
Process of Cloning Dolly
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
