![]() 15 Jul 2024
15 Jul 2024
Geography and resource development in North America have shaped the continent’s historical narrative. Its diverse landforms and natural resources, such as forests, oil, and minerals, facilitated economic growth driven by immigrants from Europe, Africa, and China. Indigenous communities, with their rich cultural traditions and sustainable lifestyles, had lived on the continent for millennia before European arrival.
North America, spanning from the Arctic Circle to the Tropic of Cancer and between the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, offers diverse geographical features.

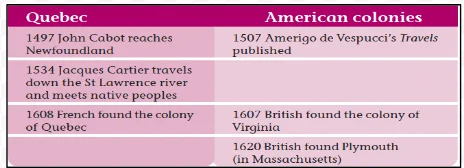
Ancient Migrations: The earliest inhabitants of North America came from Asia over 30,000 years ago on a land-bridge across the Bering Straits, and during the last Ice Age 10,000 years ago they moved further south.
Initial Encounters: In the seventeenth century, European traders arrived on the north coast of North America, and they were pleasantly surprised to find the native peoples to be friendly and welcoming.

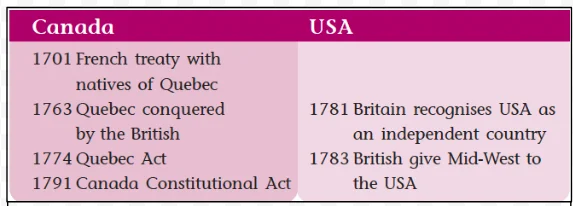
European Standards of Civilization: In the eighteenth century, Western Europeans had their own criteria for defining ‘civilized’ people, which included literacy, organized religion, and urban living.
|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
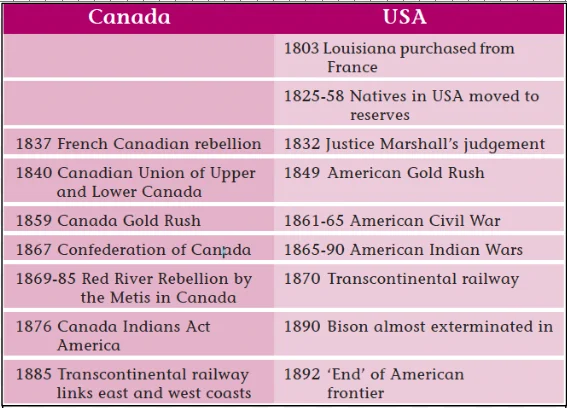
The historical interactions between Native Americans and European settlers highlight a complex legacy of trade, cultural exchange, and conflict. Initial mutual perceptions shifted over time, revealing a clash of worldviews that shaped North America’s evolution from colonial beginnings to a modern, diverse continent.
| Related Articles | |
| GEOGRAPHY | ECONOMIC GROWTH |
| Indo Pacific Region | European Parliament Elections |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>