![]() 18 Dec 2023
18 Dec 2023
Nurturing Essentials: The Vital Role of Natural Resources in Our Lives
Materials used for basic needs come from nature or are made by human efforts. Air, water, soil, and minerals like Coal and Petroleum are such natural resources.
Classification of Natural resources: Exhaustible and Inexhaustible


It is one of the most important natural resources
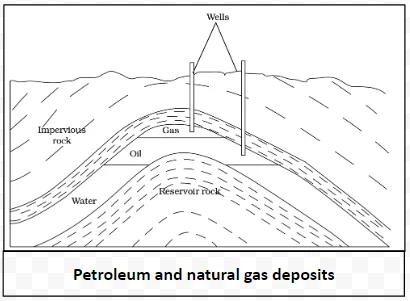

| S. No. | Constituents of Petroleum | Uses |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Petroleum Gas in Liquid form (LPG) |
|
| 2. | Petrol |
|
| 3. | Kerosene |
|
| 4. | Diesel |
|
| 5. | Lubricating oil |
|
| 6. | Paraffin wax |
|
| 7. | Bitumen |
|
Limited Natural Resources: Exploring the Challenges of through Conservation and Sustainable Practices
<div class="new-fform">
</div>