![]() 27 Jul 2024
27 Jul 2024
In the North-East, which now consists of seven States, also referred to as ‘seven sisters, regional aspirations reached a turning point in the 1980s. The region has only 4% of the country’s population and is connected to the rest of the country by a small corridor of about 22 Km. The region shares boundaries with China, Myanmar, and Bangladesh and serves as India’s gateway to SouthEast Asia (Refer to Figure 7.2).
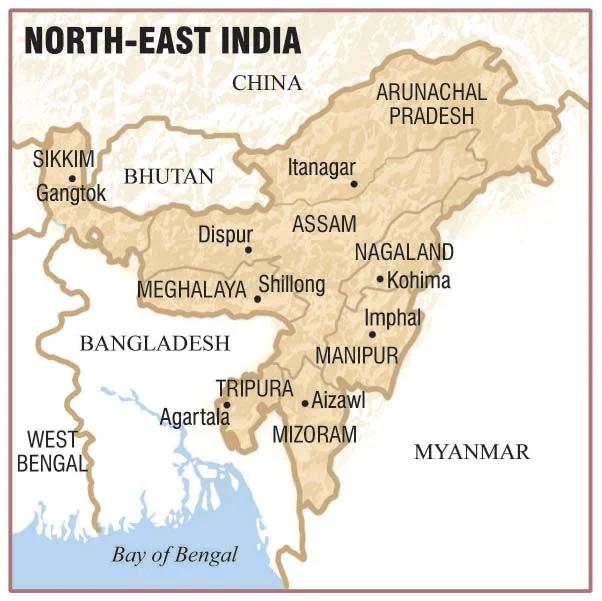
Political Reorganisation of North-East: Entire region has undergone considerable political reorganization as Nagaland State was created in 1963; Manipur, Tripura, and Meghalaya in 1972 while Mizoram and Arunachal Pradesh became separate States only in 1987.
At independence the entire region except Manipur and Tripura comprised the State of Assam. Demands for political autonomy arose when non-Assamese felt that the Assam government was imposing Assamese language on them.
Demands for autonomy were easier to respond to, but it was much more difficult when some groups demanded a separate country, not in momentary anger but consistently as a principled position.
After Independence, the Mizo Hills area was made an autonomous district within Assam. Some Mizos believed that they were never a part of British India and therefore did not belong to the Indian Union.
The large-scale migration either from India or abroad, into the North-East gave rise to a special kind of problem that pitted local communities against people who were seen as outsiders or migrants. These latecomers are seen as encroachers on scarce resources like land and potential competitors to employment opportunities and political power.
Anti-Illegal Migration Movement: The movement was against illegal migrations, against domination of Bengalis and other outsiders, and faulty voter registers that included the names of lakhs of immigrants.

Eventually, the Rajiv Gandhi-led government entered into negotiations with AASU leaders and signed an accord in 1985. According to this accord those foreigners who migrated into Assam during and after the Bangladesh war and since were to be identified and deported.
With the successful completion of the movement, AASU and Asom Gana Sangram Parishad organized themselves as a regional political party called Asom Gana Parishad (AGP).

Leaders and Their Work
| Key Figures | About |

E.V. Ramasami Naicker (1879-1973) |
|

Sheikh Mohammad Abdullah (1905-1982) |
|

Master Tara Singh (1885–1967) |
|

Sant Harchand Singh Longowal (1932–1985) |
|

Laldenga (1937-1990) |
|

Angami Zapu Phizo (1904-1990) |
|

Kazi Lhendup Dorji Khangsarpa (1904) |
|

Rajiv Gandhi (1944–1991) |
|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Nation-building is a slow process. It can not be achieved overnight. Regional demands from different parts of India exemplify the principle of unity with diversity. In many cases the challenge of diversity was met by redrawing internal boundaries of a country. Yet this did not lead to resolution of all problems and for all times. Even today, some of the issues of national integration are not fully resolved. Regional aspirations ranging from demands of statehood and economic development to autonomy and separation keep coming up. A large and diverse democracy like India must deal with these issues regularly. Thus, politics in India has succeeded in accepting regionalism as part and parcel of democratic politics.
| Timeline | Event |
| 1925 | Self-Respect Movement |
| 1963 | Creation of Nagaland |
| 1966 | Creation of Punjab |
| 1972 | Creation of Manipur, Tripura and Meghalaya |
| June 1984 | Operation Blue Star |
| July 1985 | Punjab Accord |
| 1987 | Creation of Mizoram and Arunachal Pradesh |
| 2016 | Mahbooba Mufti became the first woman Chief Minister of J & K |
| 5 August 2019 | Article 370 was abolished |
Glossary
|
| Related Articles | |
| Democracy Report 2024 | PART – III (CENTRAL GOVERNMENT) |
| POPULATION IN INDIA | Southeast Asian Countries Looking To Join BRICS |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>