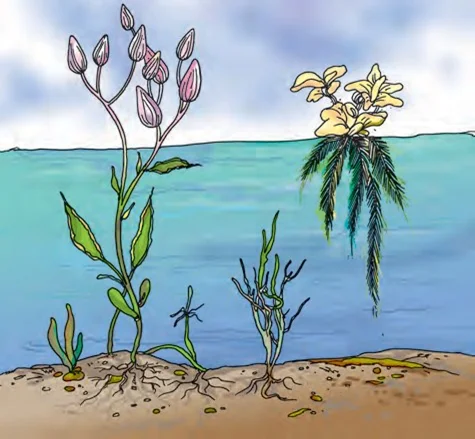
Plants exhibit remarkable diversity in plant habitats and adaptations, reflecting their ability to thrive in various environmental conditions.

Exploring Plant Habitats: Understanding Diverse Environments from Terrestrial to Aquatic



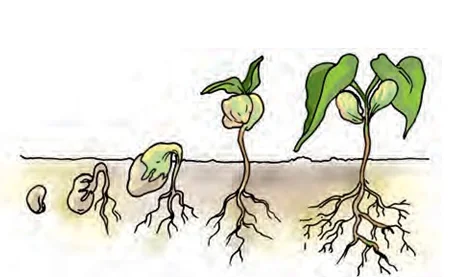
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate processes within the plant habitat highlight the adaptability of plants. From growth to reproduction, understanding how substances move seamlessly emphasizes the importance of plant habitats in sustaining botanical life.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
