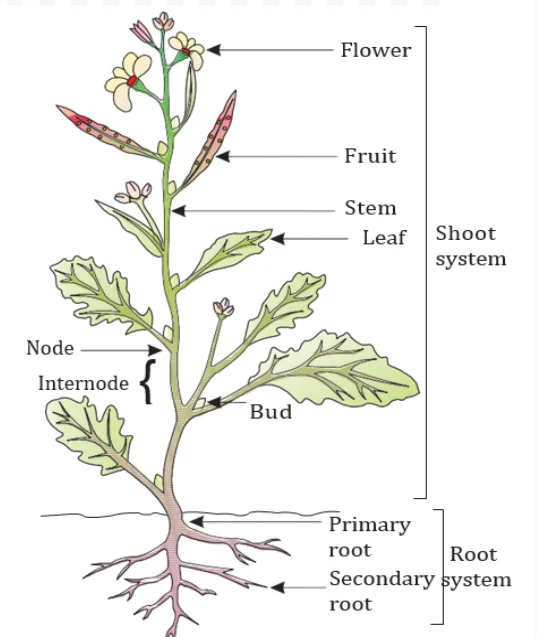
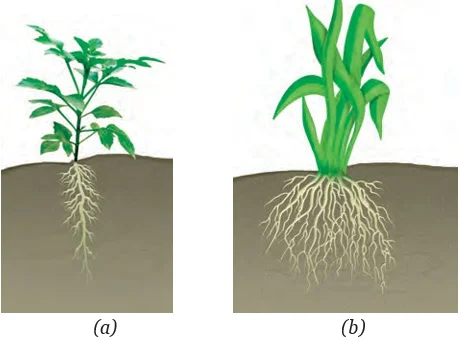
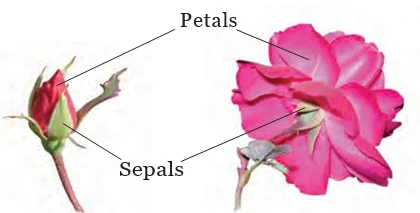
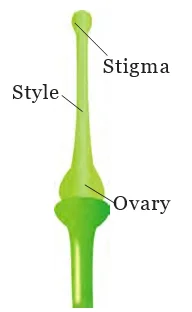
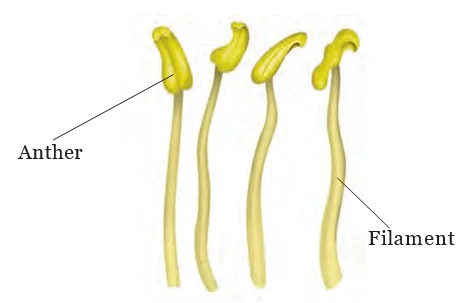
Plant Organisms: There is a diversity of plants around us. All living beings directly or indirectly depend on plants for their nutrition. There are vegetative and reproductive parts of the plant and each is responsible for performing different functions. Seed dispersal plays an important role in maintaining the kind of diversity in plants that we notice around ourselves. Furthermore, it is the reproduction in plants that helps the plant kingdom proliferate. But serious conservation efforts are needed in order to maintain the diversity in the plant kingdom, which is soon depleting.



Conclusion
In conclusion, the diverse world of plant organisms intricately weaves the fabric of life, providing essential nutrition for all. Understanding their varied parts, functions, and reproductive mechanisms is crucial. As we marvel at the beauty of plant organisms, conservation efforts become imperative to safeguard their existence.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
