![]() 18 Dec 2023
18 Dec 2023
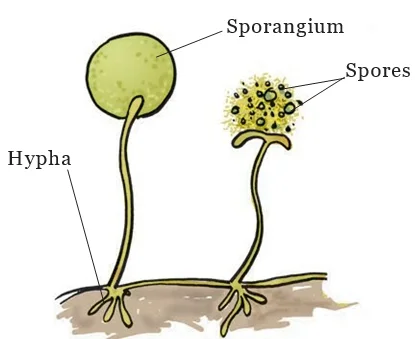
Plant reproduction is a fascinating process crucial for the survival of species. From the simplicity of asexual reproduction to the complexity of sexual reproduction, plants employ diverse strategies for propagation and genetic diversity.
Plant Reproductive Function:
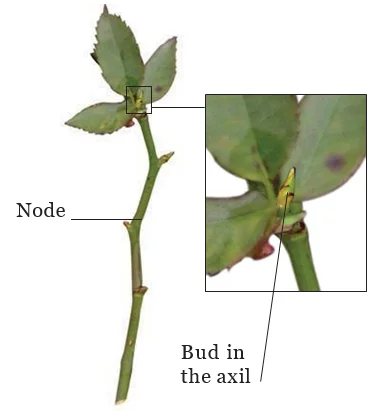
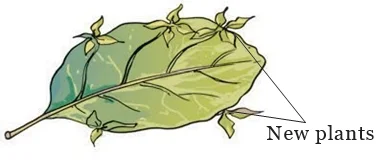
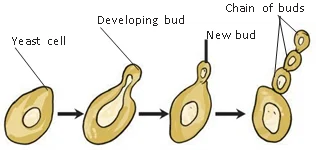
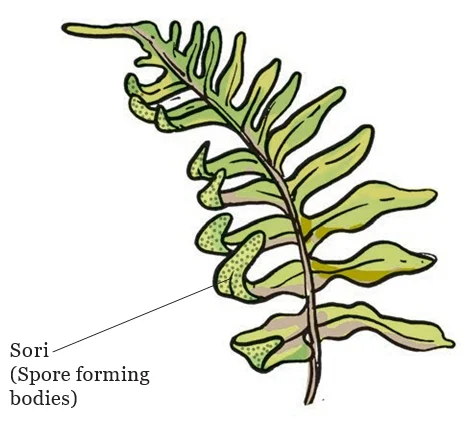
Conclusion
The intricate dance of plant reproduction unveils the remarkable journey from vegetative parts to blooming flowers. Plant reproduction, through fragmentation in multicellular organisms, showcases the simplicity of effective reproductive methods. These processes are essential chapters in the book of life, where plants, with their relatively simple body organization, reveal the wonders of creating new life. By delving into the nuances of plant reproduction, we gain insights into the diverse strategies that contribute to the thriving existence of these botanical wonders.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>