![]() 9 Dec 2023
9 Dec 2023
Population of a region or country is a dynamic phenomenon. Its numbers, distribution and composition undergo continuous changing. This is the influence of the interaction of the three processes, namely — births, deaths and migrations, and the intricate dynamics of population change. These factors collectively govern and mold the demography of a region or country.
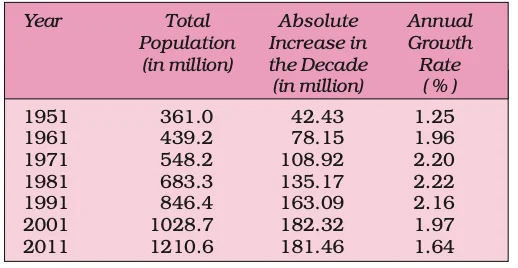
The Magnitude and Rate of India’s Population Growth
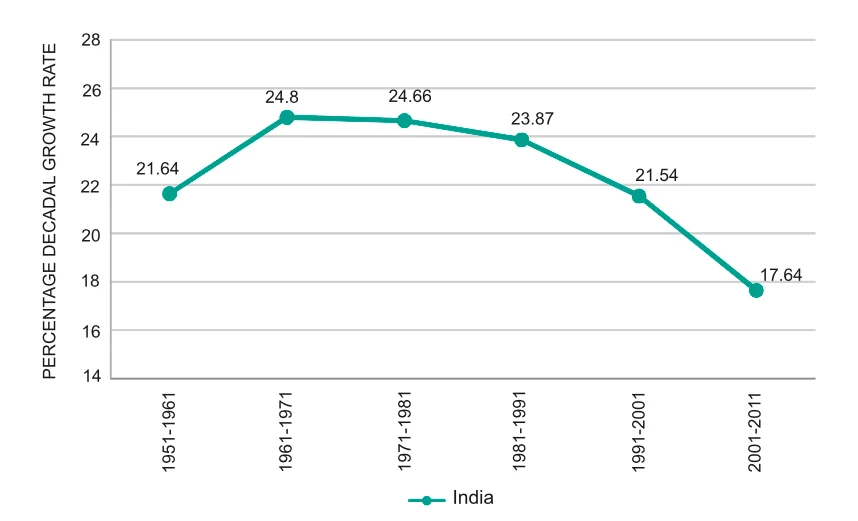
India’s Population Growth Rates during 1951-2011
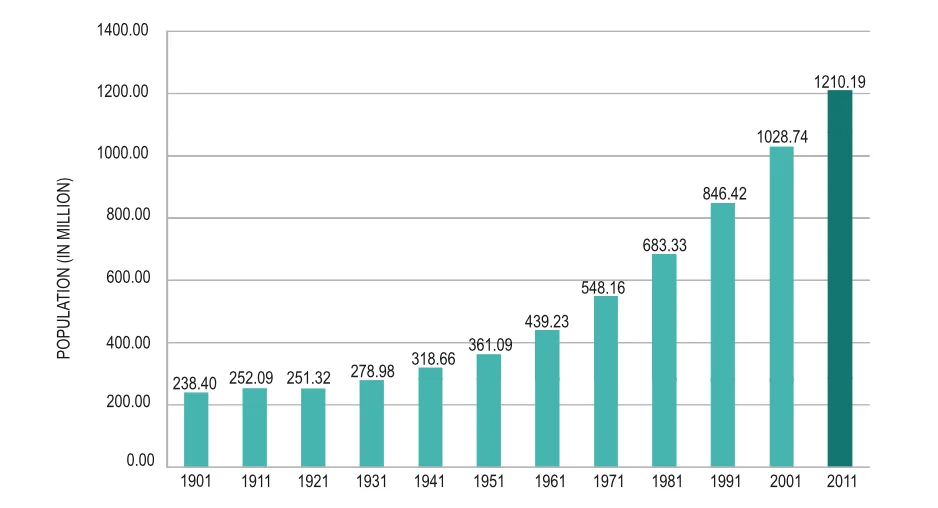
India’s Population 1901-2011
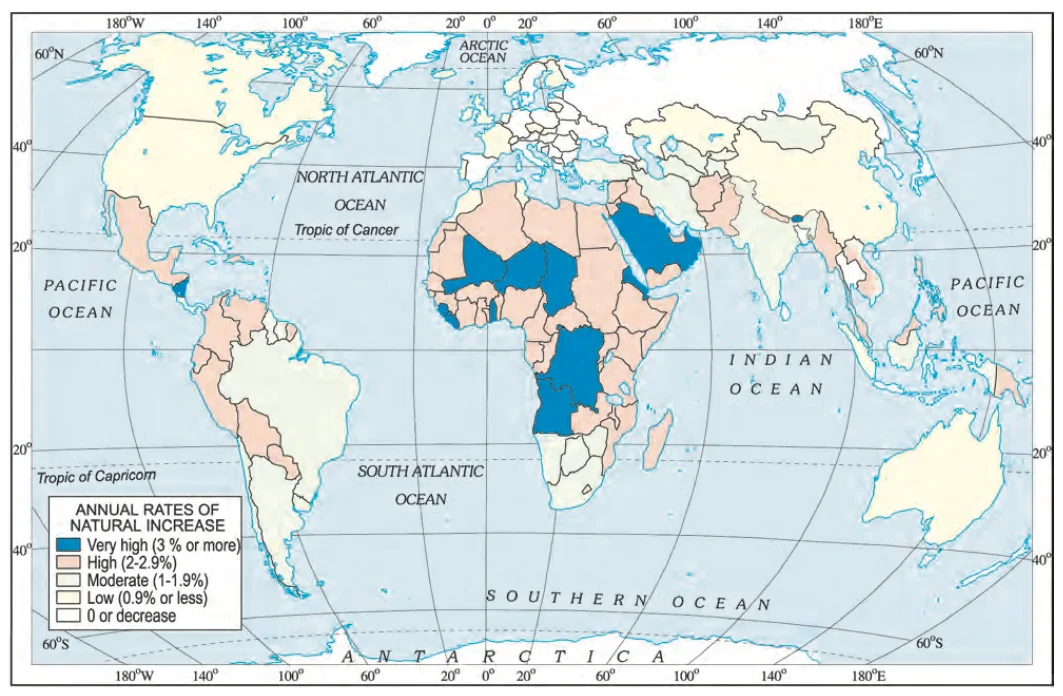
World: Differing rates of Population Growth
|
Key Concepts in Population Geography:
|
|---|
Also Read: India’s Population Growth: Historical Phases and Contemporary Trends
Conclusion
The study of population geography elucidates the complexities of population change, involving births, deaths, and migration. From growth rates to natural and actual growth, these concepts provide insights into the dynamic nature of population dynamics, shaping the evolving landscape of demographic patterns. Population change serves as a pivotal lens through which we understand the continual shifts in population size, composition, and distribution, reflecting the intricate interplay of various factors on a global scale.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>