![]() 5 Dec 2023
5 Dec 2023
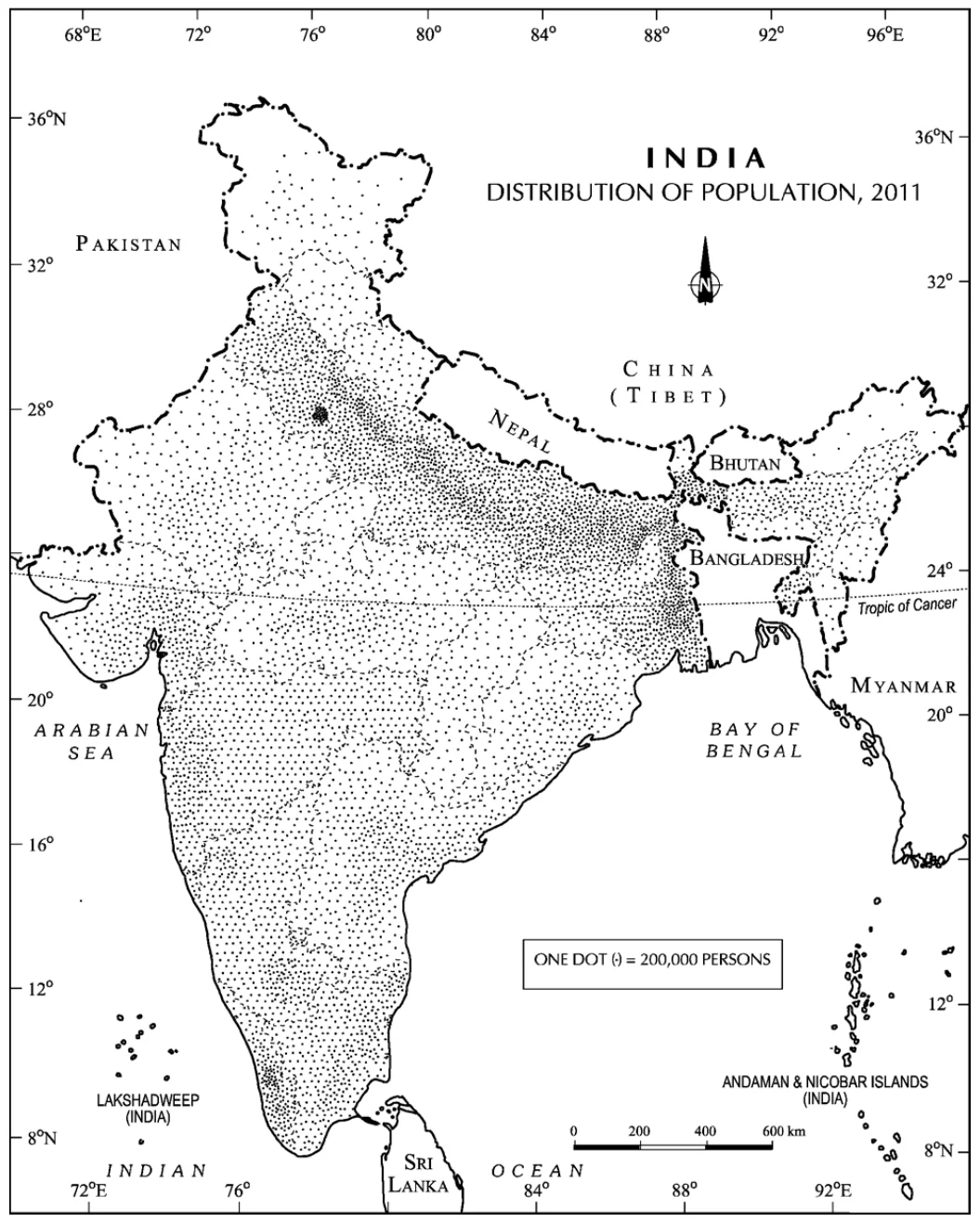
India-Distribution of Population
Census in India: Tracking Population Dynamics Through Time for Holistic Social, Demographic, and Economic Insights
|
|---|
Population Dynamics in India: Demographic Landscapes, Global Shifts, and the Strain of Overpopulation
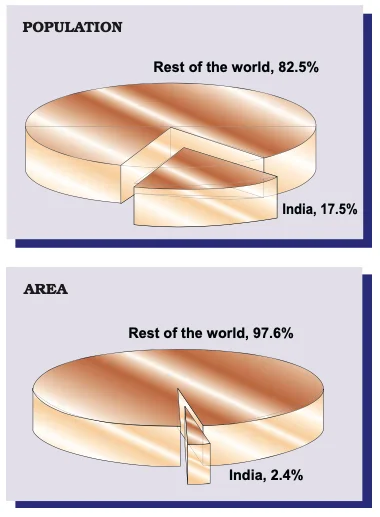
India’s Share of World’s Area and Population
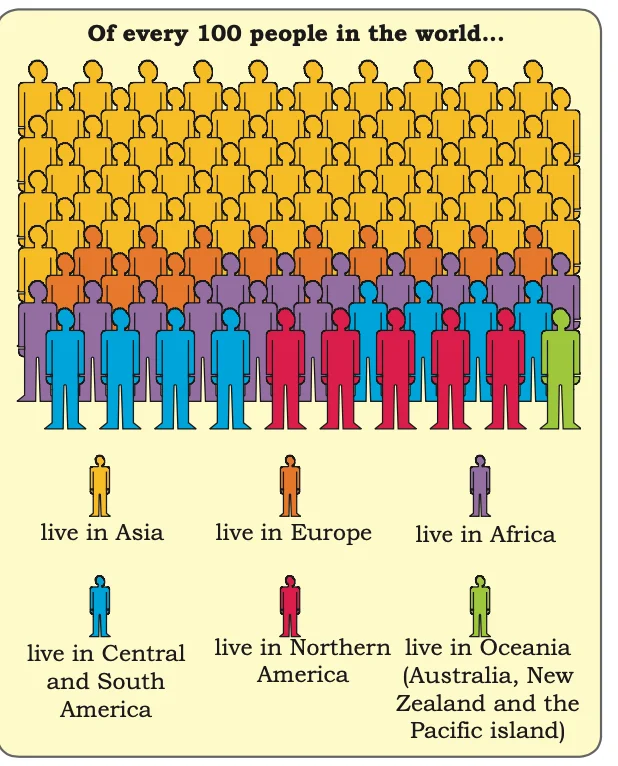
World Population by Continents
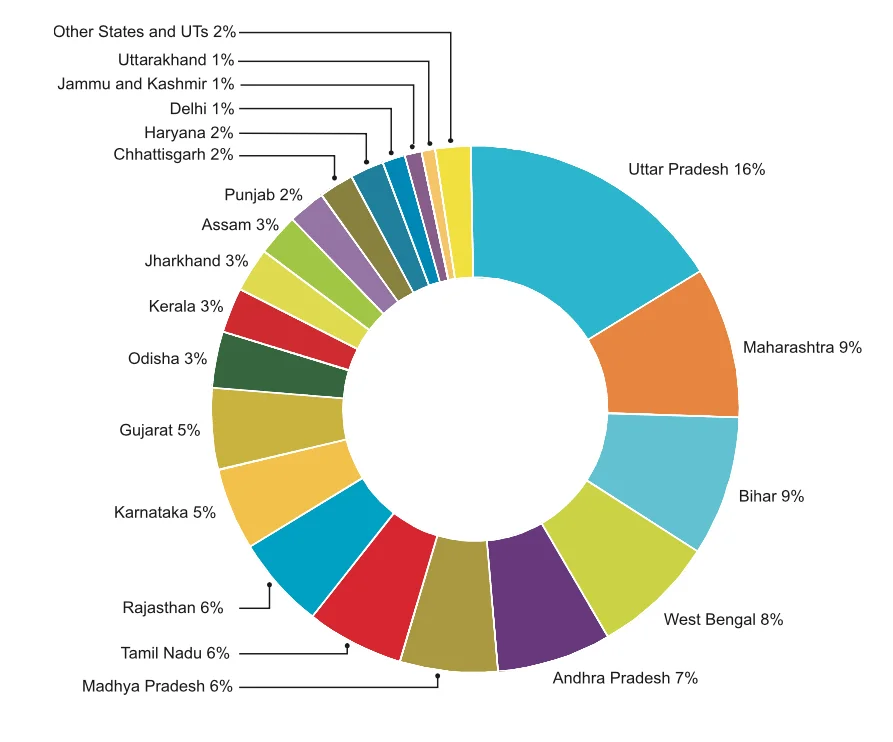
State-wise distribution of Population in india
India showcases a diverse and uneven distribution of its population , largely driven by a blend of physical, socio-economic, and historical factors.
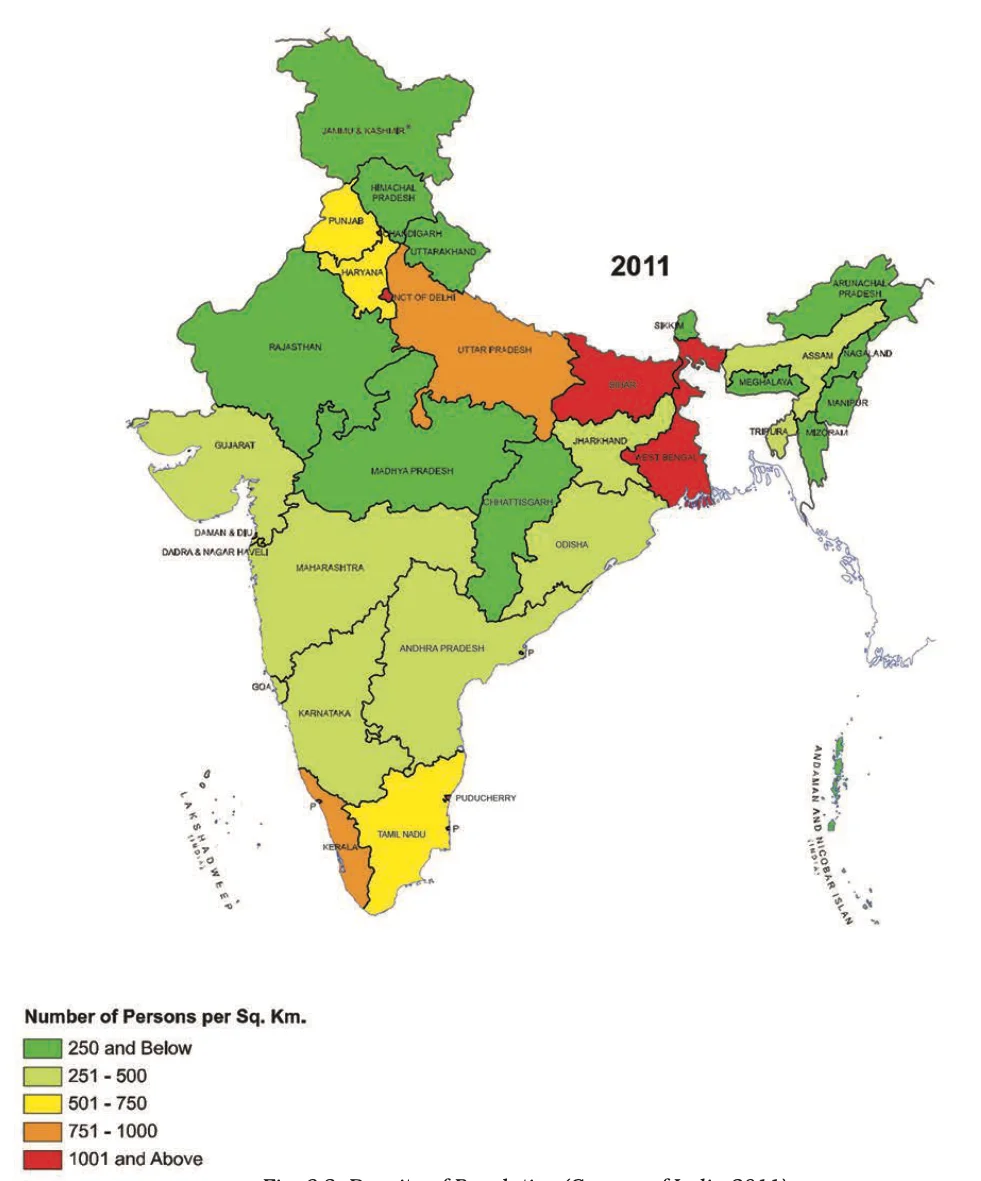
Density of Population (Census of India 2011)
India’s Population Dynamics: Standing as one of the world’s most densely populated countries, with only Bangladesh and Japan having a higher average population density.
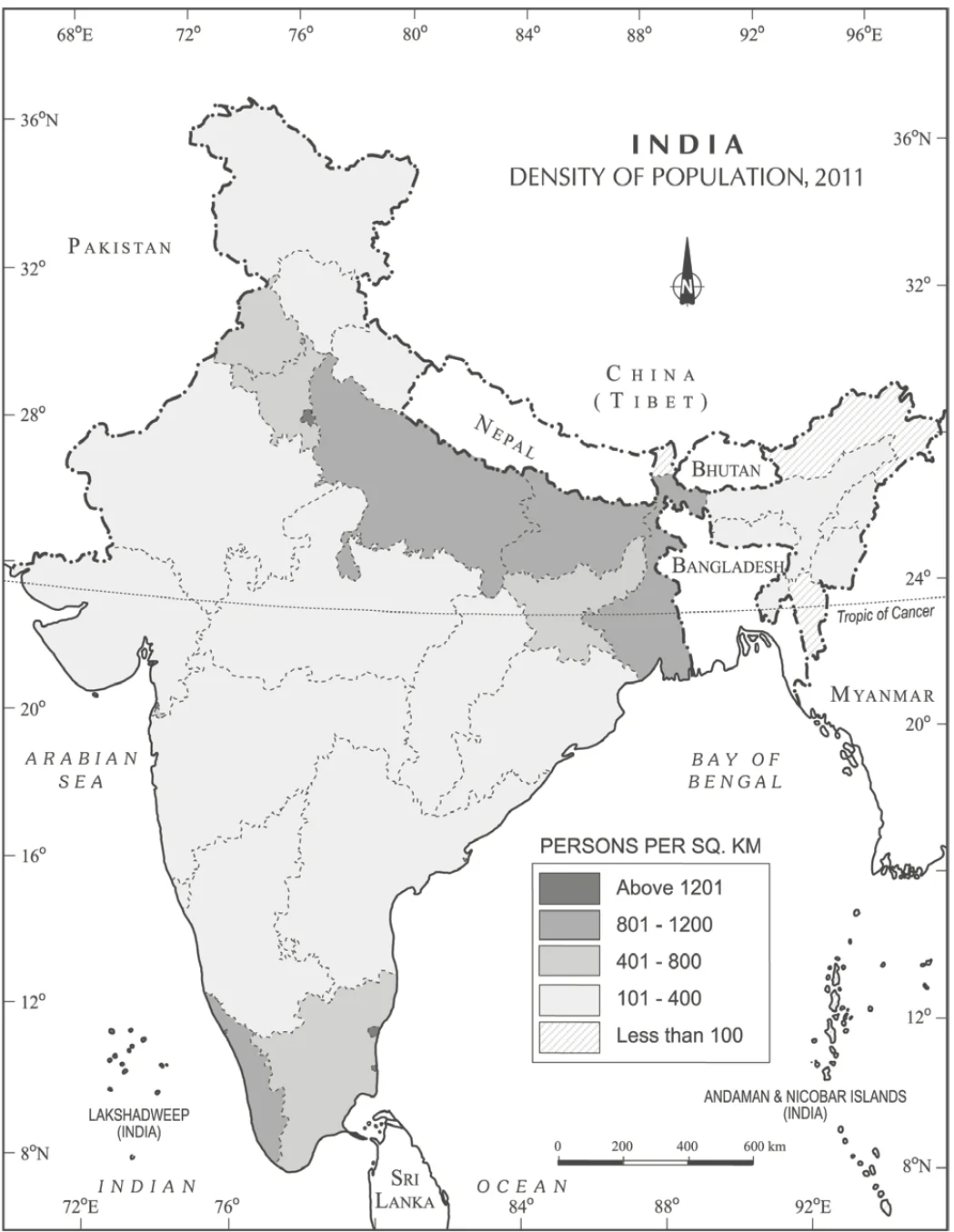
India- Density of Population
| Density Level | Regions/States | Influencing Factors |
| Low Densities | Areas with population Dynamics below 250 persons/sq km (specific states not provided) | Rugged terrain, unfavorable climatic conditions |
| Moderate Densities | Assam and most Peninsular states | Hilly and rocky terrain, moderate to low rainfall, less fertile soils |
| High to Very High Densities | Northern plains and Kerala | Flat plains, fertile soils, abundant rainfall |
Table: Factors Influencing Population Density
<div class="new-fform">
</div>