![]() 27 Nov 2023
27 Nov 2023
Article 75 of the Indian Constitution outlines the structure of the Union Council of Ministers (CoM), with the Prime Minister at its helm. This article establishes the fundamental guidelines for the organization of the council. Within the Indian political system, the Council of Ministers holds a pivotal and influential role, functioning as the actual executive authority.
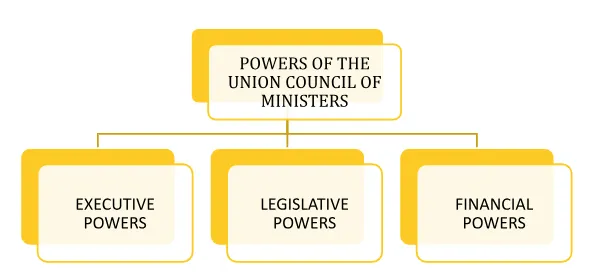
Legislative Powers: Central Role in Shaping India’s Laws and Governance
<div class="new-fform">
</div>