![]() 21 Jun 2024
21 Jun 2024
Earthquake refers to the sudden shaking of the earth’s crust. It is highly destructive of all the natural disasters. They occur when there is a rupture in the Earth’s surface, typically along a fault line, leading to seismic waves that propagate through the ground.
The intensity and magnitude of the temblor vary, causing shaking and trembling of the ground.
|
Do You Know ? An earthquake with a magnitude 7.5 on the Richter scale releases 30 times the energy than one with 6.5 magnitudes. An earthquake of magnitude 3 is the smallest normally felt by humans. |
|---|
Key points about earthquakes: Causes, Measurement, and Intensity Scales
|
Do You Know ? The largest earthquake that has been recorded with Richter Scale is 9.25 (Alaska, 1969 and Chile, 1960). |
|---|
List of Significant Earthquakes in India
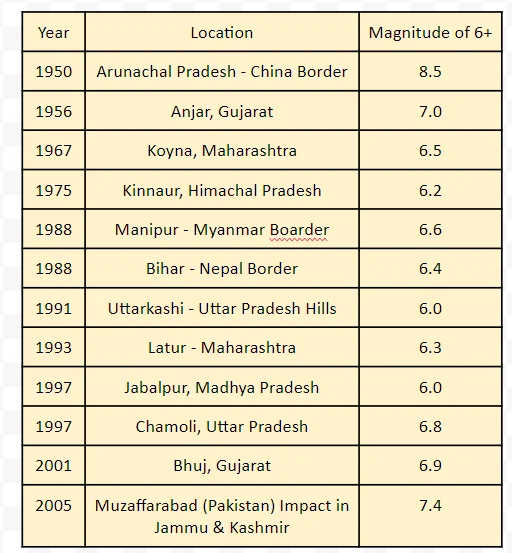
|
Additional Information
|
|---|
|
Do You Know ? New Delhi lie in very high damage risk zone whereas big cities like Mumbai and Chennai are in moderate damage risk zone. |
|---|
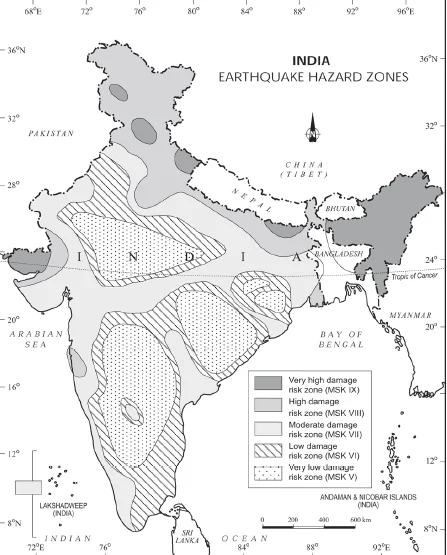
Earthquake Hazard Zones in India
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>