Light reflection is the phenomenon where light waves encounter a surface and bounce back. This fundamental process shapes our perception of the world, enabling visibility. Reflection of light is crucial in various fields, from optics to daily experiences, impacting how we see objects and interpret our surroundings.
These optical principles naturally involve reflection of light.
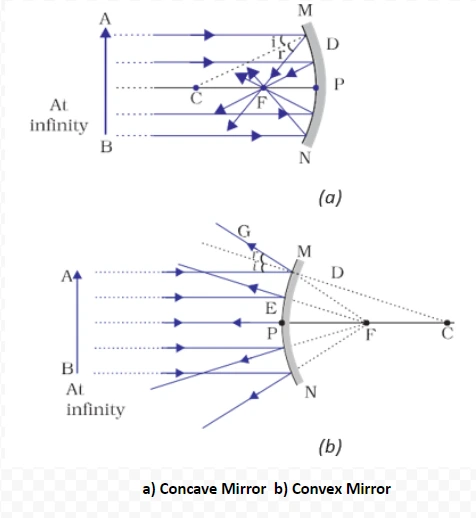
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
