![]() 19 Jul 2024
19 Jul 2024
Hitler was born in Austria in 1889 and spent his youth in poverty. When the First World War broke out in 1914, he enrolled in an army, acted as a messenger in the front, became a corporal, and earned medals for bravery. The German defeat horrified him and the Versailles Treaty made him furious. In 1919, Hitler joined a small group called the German Workers’ Party.

Nazy Party: Hitler subsequently took over the German Workers’ Party and renamed it as National Socialist German Workers’ Party. This party came to be known as the Nazi Party

Dismantling of Democracy: Hitler set out to dismantle the structures of democratic rule. It began with a mysterious fire that broke out in the German Parliament building in February.
Economic Recovery: Economist Hjalmar Schacht was assigned the responsibility of economic recovery by Hitler.
 1933: Hitler pulled out of the League of Nations.
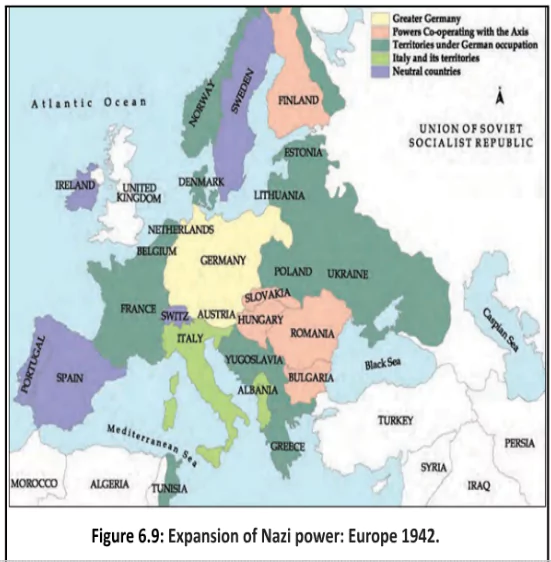
1933: Hitler pulled out of the League of Nations.Germany’s Invasion of the Soviet Union: In June 1941, Hitler attacked the Soviet Union. In this historic blunder, Hitler exposed, German western front to British aerial bombing and the eastern front to the powerful Soviet armies.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Hitler’s Nazi regime radically transformed Germany from a defeated nation to an aggressive, totalitarian state. By manipulating nationalistic fervor and economic hardship, Nazis dismantled democracy, persecuted minorities, and embarked on a path of conquest. This radical transformation ultimately led to World War II, leaving an enduring legacy of destruction and the imperative to prevent such horrors from recurring.
| Related Articles | |
| INDIA GERMANY | Economic Development |
| The Lessons of Hiroshima Must Not Drift Away | Indian Response to First World War & Home Rule Movement |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>