![]() 8 Dec 2023
8 Dec 2023
The economic strength of a country is measured by the development of secondary activities which mainly encompasses manufacturing industries. Secondary activities are those activities which transform raw materials into finished and valuable products. Hence they add value to natural resources as the raw materials become more valuable and can be used for making finished goods.
While all the economic activities like primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary obtain and utilise resources necessary for our survival, secondary activities specifically deal with manufacturing, processing and construction (infrastructure) industries.
In this article, analysis of these manufacturing activities will be discussed in detail.
Manufacturing Industry
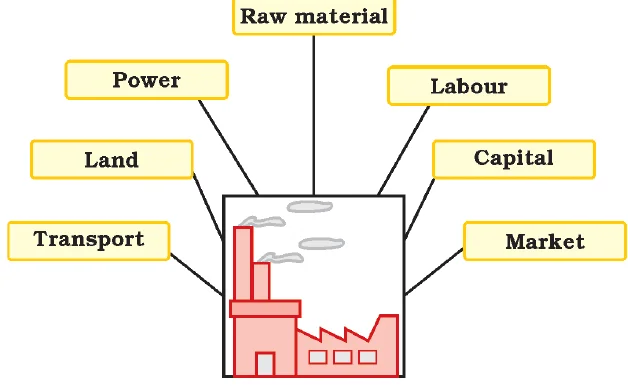
Locational factors for industries
Also Read: Industrial Location: Analyzing Factors and Strategies Shaping Manufacturing Centers
<div class="new-fform">
</div>