![]() 8 Dec 2023
8 Dec 2023
Since the ancient period, India was one of the seafaring countries. One of the great advantages of water transportation is that it does not require route construction. It is much cheaper because the friction of water transport is far less than that of land. The energy cost of water transportation is lower. They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods. It is fuel-efficient and environment friendly.
Waterways is an important mode of transport for both passenger and cargo traffic in India. It is a fuel-efficient and eco-friendly mode of transport.
The types of water transport are of two types– Oceanic waterways, and Inland waterways.
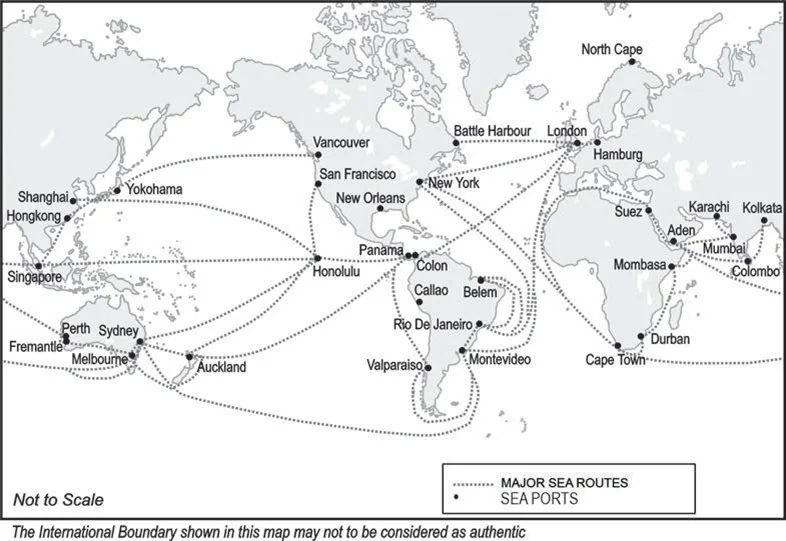
Major Sea Routes and Ports in the World
Also Read: Evolution of Communication System: Drums to Satellites & Connecting the World
<div class="new-fform">
</div>