![]() 18 Dec 2023
18 Dec 2023
Types of Tissue in living organisms represent specialized groups of cells collaborating to perform specific functions essential for the overall well-being of the organism. These types of tissues work in harmony, contributing to the overall structure and function of organs and organ systems in living organisms.
Definition:
Types of Tissues:
Plant- From one of the major types of Tissue:
| Simple Permanent Tissue | Complex Permanent Tissue |
|---|---|
parts that greatly increase the total absorptive surface area.
|
|
Epithelial- From one of the major types of Tissue :
Connective- From one of the major types of Tissue :
Types of Muscles Fibers
Muscular- From one of the major types of Tissue:
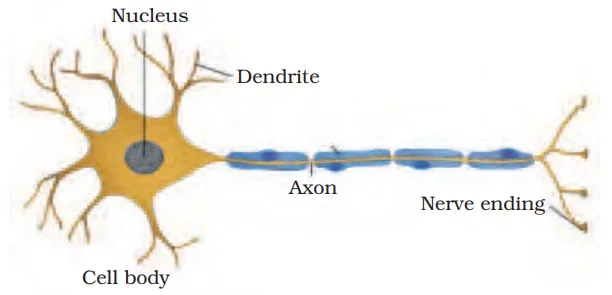
Nervous- From one of the major types of Tissue:
The functional combination of nerve and muscle tissue is fundamental to most animals. This combination enables animals to move rapidly in response to stimuli.
Understanding cells and types of tissues is pivotal in grasping the foundation of life and disease. It offers insights into our biological essence and holds the key to advancements in healthcare and biotechnology. Comprehensive knowledge of cells and types of tissues is indispensable for unraveling the intricacies of life, health, and disease. It forms the cornerstone of medical research, biotechnology, and regenerative medicine, driving progress in diagnostics and therapeutics, and ultimately, improving the quality of human life.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>