![]() 23 Jul 2024
23 Jul 2024
Reform and improvement are fundamental to any organisation in order to serve the needs of a changing environment. The UN is no exception. Two basic kinds of reforms faced by the UN: reform of the organisation’s structures and processes; and a review of issues that fall within the jurisdiction of the organisation. Almost everyone agrees that both aspects of reform are necessary. They cannot agree on precisely what is to be done, how it is to be done, and when it is to be done.
Structural and Processual Shifts: The calls for modernization of UN’s traditional structures and procedures have been growing louder.
The UN has seen widespread advocacy for reforms, but arriving at a unanimous decision about the nature of these changes has been challenging. Back in 1992, a landmark resolution by the UN General Assembly pinpointed significant issues with the Security Council:
Over the years, a myriad of criteria have been proposed to determine the eligibility of new members. Suggestions include:
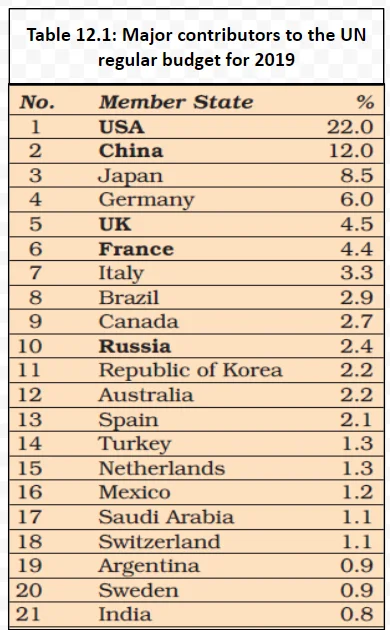
One of the more contentious issues in this debate is how to ensure a fair and diverse representation within the Council:

A significant point of contention in the reform dialogue is the unique veto power vested in the five permanent members:
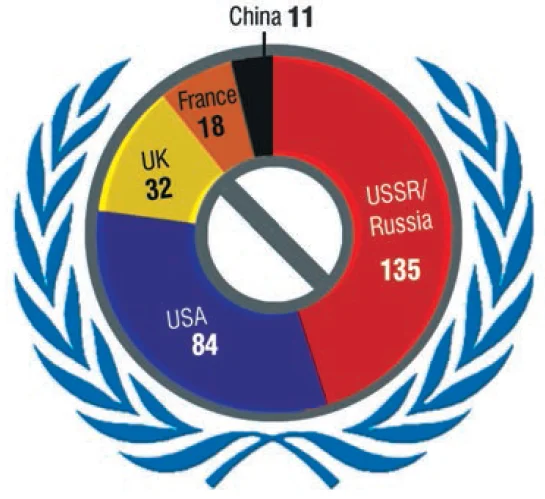
Reflection on Membership and Historical Significance: The UN’s 60th anniversary in September 2005 was a crucial juncture where global leaders convened.
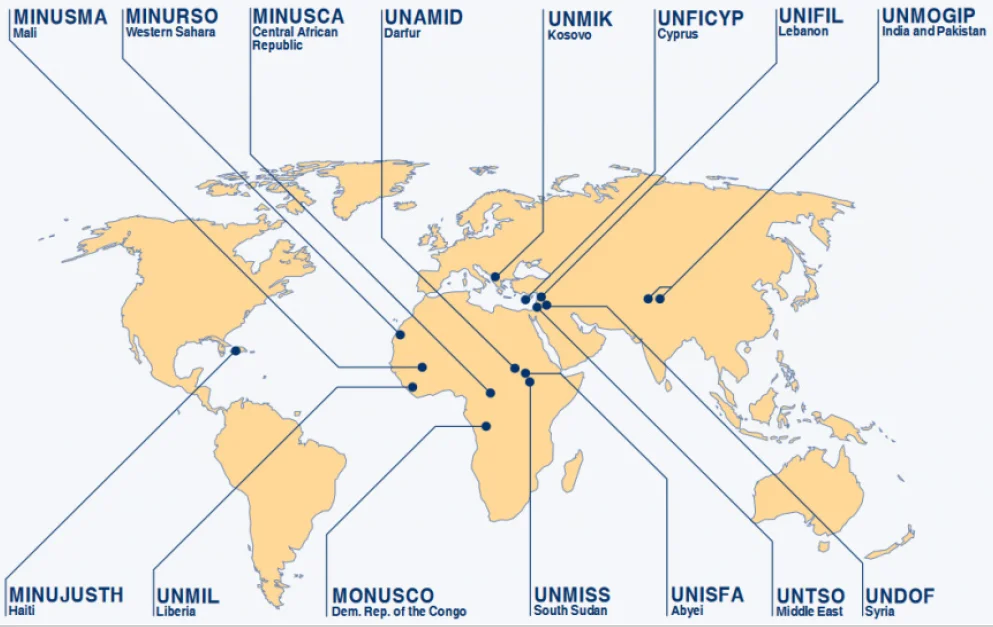

The UN isn’t merely a countermeasure to the US’s might. Instead, it crafts a neutral ground, enabling constructive engagements between the US and the global fraternity.

Over Security Council Structure: The unchanged structure of Security Council, in face of an expanding General Assembly, is a pivotal concern for India.

Standing tall as the world’s largest population and as the beacon of the largest democracy, India aspires to solidify its position with a permanent seat in the Security Council.
Despite India’s strong credentials, its path to permanent membership is riddled with reservations from several countries:
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
The chapter explored the roles and significance of the UN, Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch, the WTO, and IAEA. From Its jurisdiction to balance they offer in a unipolar world, these institutions represent global efforts towards peace, development, and cooperation. The chapter emphasises the crucial role these organisations play in striving for a more equitable and just global order, echoing the initial focus on the challenges faced by the UN.
| Related Articles | |
| 12th General Assembly | WORLD WAR II’S IMPACT |
| ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT | collapse of the Soviet Union |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>