![]() 5 Dec 2023
5 Dec 2023
Urbanization in India refers to the rapid growth and expansion of urban areas within the country. This phenomenon, observed in Urbanization in India, is characterized by the increasing migration of people from rural to urban regions in search of better economic opportunities, improved standards of living, and access to amenities and services.
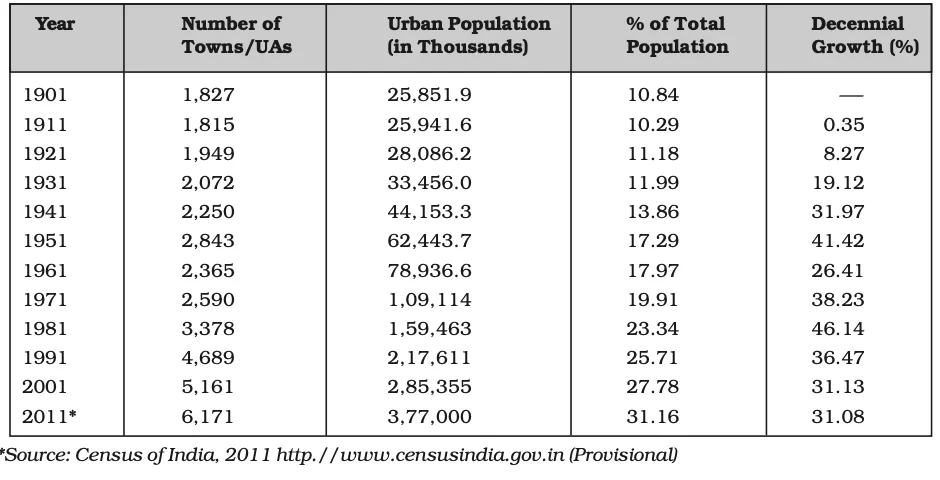
Trends of Urbanisation 1901-2011
Urbanization in India: On the basis of dominant or specialized functions, Indian cities and towns can be broadly classified as follows,
| Type | Description & Examples |
|---|---|
| Administrative | Towns hosting higher-order administrative headquarters. E.g., Chandigarh, New Delhi, Bhopal. |
| Industrial | Dominated by industries. E.g., Mumbai, Jamshedpur, Bhilai, Salem, Coimbatore, Modinagar, Hugli, etc. |
| Transport |
|
| Commercial |
|
| Mining |
|
| Garrison Cantonment |
|
| Educational |
|
| Religious and Cultural |
Haridwar, Ujjain etc. |
| Tourist |
Jaisalmer, Udagamandalam (Ooty), Mount Abu etc. |
Note: Cities, especially the larger ones, tend to be multifunctional. They often evolve and might not fit into a single category due to intertwined functions.
Nurturing Urbanization in India, Progress through the Smart Cities Mission
|
|---|
Glossary:
|
|---|
Also Read: Primary Activities: A Comprehensive Insight into Hunting, Gathering and Commercial Livestock Rearing
<div class="new-fform">
</div>