Pir Panjal Range is a major Western Himalayan mountain system spread across Himachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir. Explore its location, origin, and geology, length and extent, highest peaks like Indrasan, key passes such as Pir Panjal and Banihal, important rivers, tunnels, and its regional importance.

The Pir Panjal mountain system is an important part of the Western Himalayas. It plays a key role in shaping the geography, climate, and movement routes of northern India. This mountain system forms a natural boundary between different regions and supports diverse landscapes. Its valleys, rivers, and passes have influenced trade, travel, and settlement patterns for centuries.
Understanding where is pir panjal range located helps in studying the physical features of the Himalayan region. The range lies between major river systems and connects several states and regions. Due to its height and width, it affects weather patterns and snowfall in surrounding areas.

The Pir Panjal range origin and geology are linked to the massive tectonic movements that created the Himalayas. These mountains consist of young, folded rocks that rose millions of years ago. Its origin and geology show a gradual rise in elevation towards the northwest. This geological structure creates a natural divide between major river systems in the region.
It is situated in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent. If you look at where is pir panjal range located in india map, you will find it in the northwestern corner. It runs from the southeast to the northwest between the Beas and Neelam rivers. To answer where is pir panjal range located in which state, it primarily lies in Himachal Pradesh and the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir. Some parts also extend into territory administered by Pakistan.
The length and extent cover more than 320 kilometers (200 miles). It dissociates from the main Himalayas near the Sutlej River. The length and extent allow it to form a southwestern boundary for the Pir Panjal Valley. This massive wall of rock keeps the valley protected from the hot winds of the southern plains.
The Pir Panjal range states and regions include Himachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir. In these areas, the mountains offer famous hill stations like Gulmarg. The states and regions are also crucial for the local economy due to tourism and apple orchards. These mountains are a key part of the Pir Panjal Valley landscape.
The highest peak of pir panjal range is Indrasan, which stands at 6,221 meters. Another major summit is Deo Tibba, reaching an elevation of 6,001 meters. These represent the pir panjal range highest peak points at the eastern end of the range. Many climbers visit the highest peak of pir panjal range to experience its challenging slopes. For those looking for a list, the top 10 highest peak of pir panjal range include peaks like Indrasan, Deo Tibba, and various unnamed summits above 4,000 meters.
These passes are the only gateways through these tall mountains. Some famous passes include the Rohtang La and the Haji Pir Pass. The most historic one is the Pir Panjal Pass, also known as Peer Ki Gali.
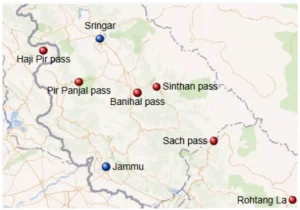
Mountain passes here are vital for connectivity.
The rivers are vital for the people living in the foothills. The range forms a divide between the Ravi and Beas rivers on one side and the Chenab on the other. Many rivers originate from the melting snow of the high peaks. These waters eventually flow into the Jhelum and Chenab systems, providing water for agriculture
Because the passes are often blocked by snow, engineers have built several tunnels. The Jawahar Tunnel and the newer Banihal Qazigund Road Tunnel ensure year-round traffic. The Atal Tunnel under Rohtang Pass is also a world-famous engineering feat. These tunnels have made travel through the mountains much safer and faster for everyone. Modern engineering created tunnels through this mountain system.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
It holds major geographical, geological, and regional importance in the Western Himalayas. Its valleys, rivers, and passes support life, movement, and economic activity across northern India. Understanding its structure helps students gain a clearer view of Himalayan geography.
It continues to shape natural processes and human activity. Its role in climate control, water supply, and regional connectivity makes it a vital mountain system in South Asia.
Ready to boost your UPSC preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, mainly across Himachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir.
Indrasan is the highest peak of the Pir Panjal Range, located in the eastern section of the range.
It is important because it influences the climate, controls river flow, and provides natural routes through mountain passes.
Major passes in the Pir Panjal include Pir Panjal Pass, Banihal Pass, Haji Pir Pass, and Rohtang La.
Several tributaries of the Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, and Beas rivers originate from the Pir Panjal.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>