Know about full form of POLICE – Public Officer for Legal Investigations and Criminal Emergencies. Learn the meaning of POLICE, COP full form, ranks, duties, eligibility, salary, etc.

The word POLICE full form is more than just a term for law enforcement, it’s an acronym that provides honour with a specific meaning that represents the duties and responsibilities of these protectors of public order. In this informative guidepost, we will know the full form of POLICE, while discovering what each letter stands for and the role it signifies in ensuring safety, justice, and community well-being. Understanding this can provide us with deeper insight into the purpose and commitment of police forces across India.
The full form of “POLICE” is “Public Officer for Legal Investigations and Criminal Emergencies”. It refers to a law enforcement agency responsible for maintaining public order, preventing and investigating crimes, and ensuring the safety and security of the community. Police officers play a vital role in upholding the law, responding to emergencies, conducting investigations, and promoting a sense of safety within society.
| POLICE Full Form | |
|---|---|
| Full Form | Public Officer for Legal Investigations and Criminal Emergencies |
| Role | Maintain law and order, prevent and investigate crimes, ensure public safety. |
| Recruitment | Competitive exams, educational and physical requirements, training at police academies. |
| Authority | Have the authority to make arrests, enforce laws, and maintain public order. |
| Challenges | Deal with dangerous situations, manage stress, maintain work-life balance, address public expectations. |
Eligibility to become a police officer, the requirements can vary depending on the country and jurisdiction. In general, here are some common eligibility criteria that individuals may need to meet to become a police officer:
Becoming a police officer involves several steps, including meeting eligibility requirements, undergoing training, and successfully completing the recruitment process. The exact process can vary based on the country, state, or jurisdiction you’re in. Here’s a general overview of the steps to become a police officer:
Police officers have a wide range of duties and responsibilities aimed at maintaining public safety, enforcing laws, and upholding order within a community. The specific duties can vary based on the jurisdiction, department, and the officer’s rank or specialization. Here are some common duties of police officers:
1. Law Enforcement:
Enforce local, state, and federal laws to prevent and address criminal activities.
2. Patrolling:
Patrol designated areas to deter crime, respond to emergencies, and maintain a visible police presence.
3. Emergency Response:
Respond promptly to emergency calls, accidents, and incidents, and provide assistance as needed.
4. Investigations:
Conduct investigations into criminal activities, gather evidence, interview witnesses, and collect information for case resolution.
5. Arrest and Detainment:
Arrest individuals suspected of committing crimes, take them into custody, and ensure their legal rights are upheld.
6. Traffic Control:
Enforce traffic laws, issue citations, and manage traffic flow to ensure road safety.
7. Conflict Resolution:
Mediate disputes, resolve conflicts, and provide guidance to individuals involved in disagreements.
8. Community Engagement:
Build positive relationships with the community by participating in community events, meetings, and outreach programs.
9. Public Assistance:
Provide assistance to the public, including helping lost individuals, offering directions, and providing information.
10. Crime Prevention:
Identify potential crime risks, implement preventive measures, and educate the public about safety precautions.
11. Protecting Crime Scenes:
Secure and preserve crime scenes to ensure the integrity of evidence for investigations.
12. Testifying in Court:
Prepare and present evidence in court cases as witnesses to support prosecution.
13. Crisis Intervention:
Handle situations involving mental health crises, domestic disputes, and other emergencies with sensitivity and appropriate action.
14. Search and Seizure:
Conduct searches and seizures according to legal procedures and obtain search warrants when necessary.
15. Report Writing:
Document incidents, investigations, and interactions in accurate and detailed reports.
16. Crime Analysis:
Analyze crime trends and data to identify patterns, make informed decisions, and allocate resources effectively.
The following information provides an overview of the POLICE along with their corresponding departments:
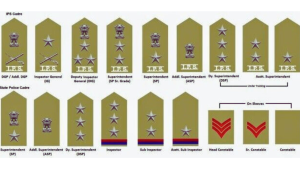
The insignia on police officers’ shoulders holds significant meaning and plays a crucial role in conveying their rank and authority within the law enforcement hierarchy. These symbols, often referred to as “STARS,” represent the responsibilities and leadership that officers at various ranks hold. Let’s discuss the roles of these STARS on police officers’ shoulders:
Assistant Superintendent of Police (ASP):
ASPs often have one star on their shoulder insignia.
Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP):
DSPs may have one or two stars on their insignia.
Superintendent of Police (SP) / Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP):
SPs and SSPs are typically identified by three stars on their insignia.
Deputy Inspector General (DIG):
DIGs may have three stars along with additional embellishments or symbols.
Inspector General (IG):
IGs often have three stars on their shoulder insignia, accompanied by other distinctive elements.
Additional Director General (ADG):
ADGs are identified by three stars along with other specific symbols that signify their higher position.
Director General of Police (DGP):
DGPs usually have three stars on their shoulder insignia, often accompanied by other design elements that distinguish their top leadership role.
Assistant Sub-Inspector (ASI) and Sub-Inspector (SI):
These ranks typically have one to three chevrons (V-shaped symbols) on their shoulder insignia. ASIs and SIs are often responsible for supervising constables, assisting with investigations, and maintaining order within their jurisdictions.
Inspector and Police Inspector (PI):
The insignia for these ranks often features one to three stars. Inspectors and Police Inspectors are tasked with overseeing investigations, managing cases, and ensuring law enforcement activities are carried out effectively.
The STARS on police officers’ shoulders signify not only their rank but also their roles and responsibilities within the law enforcement hierarchy. They help establish a clear chain of command, facilitate effective communication, and convey the level of authority an officer holds. As officers progress through their careers and take on greater responsibilities, the STARS serve as visible markers of their leadership within the police force.
Joining the police force comes with a range of benefits, both intrinsic and extrinsic, that make it an attractive career choice for many individuals. Here are some benefits of joining the police:
1. Serving the Community: One of the most fulfilling aspects of a police career is the opportunity to serve and protect your community. Police officers play a vital role in ensuring public safety, maintaining order, and helping people during times of crisis.
2. Job Security: Law enforcement is a stable and essential field, offering long-term job security. Society will always need police officers to maintain law and order.
3. Variety of Roles: Police departments offer a wide range of roles and specializations, from patrol officers to detectives, K-9 handlers, traffic control, cybercrime experts, and more. This diversity allows officers to find a niche that aligns with their skills and interests.
4. Career Advancement: Police departments often have clear career paths and opportunities for advancement. With experience and further training, officers can progress to higher ranks and leadership positions.
5. Training and Skill Development: Police officers undergo extensive training in various areas, including law enforcement tactics, self-defense, communication, crisis management, and community relations. These skills are not only valuable in the job but also transferable to other fields.
6. Health Benefits: Many police departments offer comprehensive health and medical benefits for officers and their families, ensuring access to healthcare services.
7. Stable Income: Police officers receive a stable salary with potential overtime pay and allowances, ensuring financial stability.
8. Respect and Authority: Police officers are respected members of society who hold authority to enforce laws and protect citizens. This authority can be empowering and personally fulfilling.
9. Challenging and Rewarding Work: The dynamic nature of police work means that no two days are the same. The challenges and successes that come with the job can be highly rewarding.
“POLICE” की फुल फॉर्म “Public Officer for Legal Investigations and Criminal Emergencies” होती है, और भारतीय पुलिस अधिकारी खाकी वर्दी पहनते हैं, जो कि उनकी पहचान होती है। पुलिस समाज में सुरक्षा और कानून-व्यवस्था की महत्वपूर्ण श्रेणी में आती है। पुलिस संगठन समाज की सुरक्षा और व्यवस्था की रक्षा करने के लिए संकल्पित होता है, और वार्तालापिक सहयोग से आपसी विश्वास और भरोसे की बढ़ाता है। पुलिसकर्मी उच्च मानकों को पालन करते हुए समाज में न्याय, समानता और सुरक्षा की दिशा में योगदान करते हैं।
पुलिसकर्मियों की कई भिन्न भूमिकाएं होती हैं, जैसे कि पैट्रोलिंग, जांच और अनुसंधान, विशेषज्ञ इकाइयाँ जैसे कि विपणन, कानूनी अधिकारी, और साइबरक्राइम विशेषज्ञता में। पुलिसकर्मियों की शिक्षा, प्रशिक्षण और अनुभव उन्हें उनके करियर में उनकी वृद्धि और नौकरी की उन्नति के लिए महत्वपूर्ण उपकरण प्रदान करते हैं।
The salary of a police officer in India varies depending on factors such as location, rank, and experience. Starting salaries generally range from INR 2.5 LPA to 3 LPA, with potential for significant growth over time. With experience and enhanced skills, officers can earn salaries that increase progressively. At the senior-most levels, such as the Deputy Inspector General (DIG), the salary can reach up to INR 24.50 LPA. The salary criteria also depend and may differ across states due to variations in the cost of living and government policies.
Here is a table which illustrates the salary progression of a police officer in India:
| Salary of a Police Officer in India | |
|---|---|
| Rank/Level | Average Salary (INR) |
| Starting Level (Entry-level officer) | 2.5 LPA to 3 LPA |
| Mid-level (Sub-Inspector, Inspector) | 5 LPA to 8 LPA |
| Senior-level (Deputy SP, Assistant Commissioner) | 10 LPA to 15 LPA |
| Top-level (Deputy Inspector General) | Up to 24.5 LPA |
| Related Articles Links | |
|---|---|
| GATT Full Form | State PCS Full Form |
| APMC Full Form | RBI Full Form |
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
The police play a vital role in maintaining law and order, preventing and investigating crimes, protecting citizens, and ensuring public safety.
The police force has various ranks, including constable, sub-inspector, inspector, superintendent, deputy commissioner, and director general, among others.
To become a police officer, one usually needs to meet educational and physical fitness requirements, clear competitive exams conducted by police departments or civil service commissions, and undergo training at police academies.
Constables are entry-level officers responsible for general law enforcement duties, while inspectors are higher-ranking officers involved in investigations, supervising cases, and managing units.
Detectives are specialized officers responsible for investigating and solving complex crimes, gathering evidence, interviewing witnesses, and building cases for prosecution.
पुलिस का फुल फॉर्म “Public Officer for Legal Investigations and Criminal Emergencies” होता है। इसका अर्थ है कानून-व्यवस्था बनाए रखने और अपराधों की जांच करने वाली संस्था।
PI का मतलब Police Inspector, PET का मतलब Physical Endurance Test, BPF का मतलब Border Protection Force, और GD का मतलब General Duty होता है। ये सभी पुलिस भर्ती और रैंकों से जुड़े महत्वपूर्ण शब्द हैं।
In policing, COP stands for “Constable On Patrol.” It is often used to describe patrolling officers responsible for community safety, monitoring activities, and responding to incidents.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>