2024
Question 1
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which one of the following is the largest source of sulphur dioxide emissions?
(a) Locomotives using fossil fuels
(b) Ships using fossil fuels
(c) Extraction of metals from ores
(d) Power plants using fossil fuels
ExplanationAns: d
Exp:
Emissions that lead to high concentrations of SO2 generally also lead to the formation of other SOx. The largest sources of SO2 emissions are from fossil fuel combustion at power plants and other industrial facilities. EPA’s national ambient air quality standards for SO2 are designed to protect against exposure to the entire group of sulfur oxides (SOx). SO2 is the component of greatest concern and is used as the indicator for the larger group of gaseous sulfur oxides (SOx). Other gaseous SOx (such as SO3) are found in the atmosphere at concentrations much lower than SO2.
Question 2
Consider the following statements:
Statement I: India does not import apples from the United States of America.
Statement II: In India, the law prohibits the import of Genetically Modified food without the approval of the competent authority.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I.
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I.
(c) Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect.
(d) Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct.
ExplanationAns: d
Exp:
Statement-I is Incorrect: Apples are one of the major imports from the USA. After India removed “retaliatory import duty” on US apples in September, imports of American apples have surged 40 times in three months, while traders are hopeful of regaining market share. In 2017-18, the import of US apples was a record of over 7 million boxes, which dropped to 50,000 boxes in the 2022–23.
Statement-II is correct: In India, the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, prohibits import, manufacture, use or sale of GM food without FSSAI’s approval.
Question 3
The organisms “Cicada, Froghopper, and Pond skater” are :
(a) Birds
(b) Fish
(c) Insects
(d) Reptiles
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
“Cicada, Froghopper, and Pond Skater” comes under the category of Insects.
Cicada: Cicada is a family of more than 3,000 species of sound-producing insects. They are found in tropical and temperate areas worldwide and occur in deserts, grasslands, and forests. Cicadas have long been used in folk medicines, as religious and monetary symbols, and as an important source of food for humans and many other organisms.
Froghopper: Froghopper are species of small hopping insects which are worldwide in distribution and they produce a frothy substance known as spittle. The whitish nymph secretes a fluid through the anus that is mixed with a secretion from the abdominal glands. Air bubbles are introduced through a special valve on the abdomen to create a spittle that protects the larva from enemies and desiccation.
Pond Skater: Pond skaters are a truly remarkable group of insects that have evolved unique adaptations to thrive in aquatic environments. These small creatures, also known as water striders, can be found gliding effortlessly across the surface of ponds, lakes, and even slow-moving streams.
Question 4
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Many chewing gums found in the market are a source of environmental pollution.
Statement-II: Many chewing gums contain plastic as gum base.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
ExplanationAns: a
Exp:
Chewing gum is known for its stress-relieving qualities as well as its ability to keep our mouths fresh. Soon, ‘chewing gum’ will be included as part of the drug delivery mechanism. Unfortunately, it has had some negative consequences. Modern chewing gum is made of non-biodegradable hydrophobic polymers together with artificial sweeteners and flavours. So, chewing this sort of synthetic material over a long time could produce some adverse effects. Each year, chewing gum generates more than 105 tonnes of “plastic” garbage. Thus, the discarded non-biodegradable residue of the gum produces plastic pollution. Every year, enormous sums of money are spent to clean up the abandoned gum from the streets. Again, it has a high potential to trap bacteria inside. Therefore, this widespread habit causes an additional nuisance in this pandemic situation. Hence, Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
Question 5
Consider the following pairs:
| Country | Animal found in its natural habitat | |
| 1. | Brazil | Indri |
| 2. | Indonesia | Elk |
| 3. | Madagascar | Bonobo |
How many of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
ExplanationAns: d
Exp:
Pair 1 is incorrectly matched: The Indri is endemic to the island country of Madagascar, specifically inhabiting the eastern rainforests. The unique geographical features and climate of Madagascar have facilitated the evolution of numerous species found nowhere else on Earth, including the Indri.
Pair 2 is incorrectly matched: Elk is the largest and most advanced subspecies of red deer, found in North America and in the high mountains of Central Asia. It is a member of the deer family. Recent genetic studies suggest that the “red deer” may have three species:
Pair 3 is incorrectly matched: Bonobos and chimpanzees look very similar and both share 98.7% of their DNA with humans—making the two species our closest living relatives. Bonobos are usually a bit smaller, leaner, and darker than chimpanzees. They are found only in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Their discontinuous range extends from the Lualaba River in the east to the Kasai/Sankuru Rivers in the south and as far as the Congo River in the west and around Lake Tumba/Lake Mai-Ndombe.
Question 6
Consider the following statements :
1. Lions do not have a particular breeding season.
2. Unlike most other big cats, cheetahs do not roar.
3. Unlike male lions, male leopards do not proclaim their territory by scent marking.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Exp:
Statement 1 is correct: Both Males and Females of the Lions are polygamous and breed throughout the year, but females are usually restricted to one or two adult males of their pride. In captivity, lions often breed every year, but in the wild, they usually breed no more than once in two years. Females are receptive to mating for three or four days within a widely variable reproductive cycle.
Statement 2 is correctly matched: There are four big cats that can roar: lion, tiger, leopard and jaguar – all of which belong to the genus Panthera. In these species, the epihyal bone, part of the voice box, is replaced by a ligament. This can be stretched, creating a larger sound-producing passage and thus a wider range of pitch. The bones of the cheetah’s voice box form a fixed structure, with divided vocal cords that vibrate with both in and out breaths. This structure is the same for all the ‘small’ cats. While this design enables these cats to purr continuously, it limits the range of other sounds and prevents them from being able to roar.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Leopards are known for their solitary nature and impressive hunting abilities. They are skilled predators that primarily hunt at night, using their incredible agility and stealth to catch a variety of prey. Their diet includes bugs, fish, antelope, monkeys, rodents, and more. Leopards are considered opportunistic hunters, adapting and targeting different species based on availability and their specific habitat. To avoid competition and conflicts, leopards establish their own territories, marking them with scent and claw marks on trees. Male leopards will fiercely defend their territories if they overlap with other males.
Question 7
Consider the following:
1. Battery storage
2. Biomass generators
3. Fuel cells
4. Rooftop solar photovoltaic units
How many of the above are considered “Distributed Energy Resources”?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
ExplanationAns: d
Exp:
Distributed energy resources, or DER, are small-scale energy systems that power a nearby location. DER can be connected to electric grids or isolated, with energy flowing only to specific sites or functions. DER include both energy generation technologies and energy storage systems. When energy generation occurs through distributed energy resources, it is referred to as distributed generation. Examples of distributed energy resources that can be installed include:
Question 8
Which one of the following shows a unique relationship with an insect that has coevolved with it and that is the only insect that can pollinate this tree?
(a) Fig
(b) Mahua
(c) Sandalwood
(d) Silk cotton
ExplanationAns: a
Exp:
The banyan fig tree Ficus microcarpa is famous for its aerial roots, which sprout from branches and eventually reach the soil. Aerial roots are roots above the ground that are found in diverse plant species like mangroves, banyan figs and orchids. The tree also has a unique relationship with a wasp that has coevolved with it and is the only insect that can pollinate it. Figs are known to sustain at least 1,200 bird and mammal species. Fig trees were among the earliest domesticated crops and appear as sacred symbols in Hinduism, Buddhism and other spiritual traditions.
Question 9
Consider the following:
1. Butterflies
2. Fish
3. Frogs
How many of the above have poisonous species among them?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
Butterflies: Hybrid Heliconius butterflies are Poisonous in nature. In nature, these butterflies are rare. Heliconius melpomene and Heliconius cydno are both highly poisonous, having evolved to produce their own cyanide, and predators have learned exactly what both of these toxic insects look like.
Fish: “Venomous” fish are those that can inject their toxic venom into victims, whereas “poisonous” fish are those that cause toxic symptoms only if they are eaten. For example: Lionfish, red-bellied piranha etc.
Frogs: Frogs are amphibians which can survive both on land and water. Some of them can be poisonous also. Poison dart frogs are small, brightly colored amphibians that live on tropical rainforest floors across Central and South America. Poison dart frogs are named for the toxins they secrete from their skin, which have traditionally been used to tips of hunters’ weapons. For example, the Emberá and Noanamá Indigenous people in western Colombia have used the skin of golden poison frogs (Phyllobates terribilis) to tip blowgun darts for hundreds of years.
Question 10
With reference to perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) that are used in making many consumer products, consider the following statements:
1. PFAS are found to be widespread in drinking water, food and food packaging materials.
2. PFAS are not easily degraded in the environment.
3. Persistent exposure to PFAS can lead to bioaccumulation in animal bodies.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Exp:
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a large, complex group of synthetic chemicals that have been used in consumer products around the world since about the 1950s.
Question 11
Consider the following:
1. Carabid beetles
2. Centipedes
3. Flies
4. Termites
5. Wasps
Parasitoid species are found in how many of the above kind of organisms?
(a) Only two
(b) Only three
(c) Only four
(d) All five
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
Many animals are predators, parasites or parasitoids, using other animals as food. They use a great diversity of hunting strategies and behaviours to capture or feed on their prey. Invertebrate predators, parasites and parasitoids play an important role in keeping many animal populations under control.
Question 12
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: The Indian Flying Fox is placed under the “vermin” category in the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972.
Statement-II: The Indian Flying Fox feeds on the blood of other animals.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
(c) Statement -I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
Statement 1 is correct: The Indian Flying Fox is placed under the “vermin” category in the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 due to its destructive tendencies towards fruit farms.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Bats are the only flying mammals in the world, and the Indian Flying Fox is one of the largest. The species, Pteropus giganteus , also called the Great Indian Fruit Bat, it eats fruits, feeding on the juice, and helps in seed dispersion and pollination, making them an integral part of the ecosystem.
Question 13
Consider the following materials:
1. Agricultural residues
2. Corn grain
3. Wastewater treatment sludge
4. Wood mill waste
Which of the above can be used as feedstock for producing Sustainable Aviation Fuel?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4 only
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
Sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), hydrogen and electric all have a role to play in the decarbonization of aviation. SAF is vitally important as it can address decarbonization of fuel over its lifecycle, and this is now available to be used in all turbine engines including in mid and long-range aircraft. Therefore, understanding the feedstock landscape as well as the technology pathways is integral to maximising the production and supply of SAF. The production of SAF starts with one of five main families of raw materials:
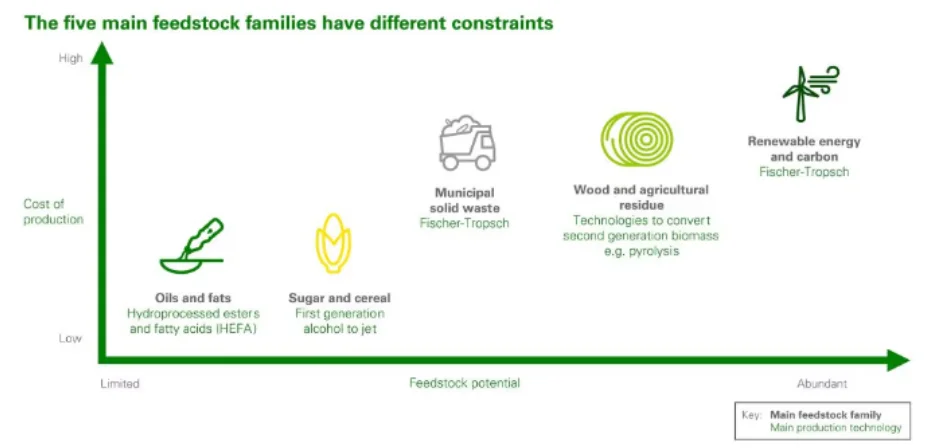
2023
Question 1
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: India, despite having uranium deposits, depends on coal for most of its electricity production.
Statement-II: Uranium, enriched to the extent of at least 60%, is required for the production of electricity.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect Statement-II is correct
Ans: c
Exp:
Statement-I is correct: Although India has significant uranium deposits, its reliance on coal for electricity production is higher compared to uranium. It constitutes 55% of the nation’s energy requirements.
Statement-II is not correct: For electricity generation, uranium enrichment to a level of 3 to 5 percent of the U235 isotope is necessary. Research reactors utilise uranium enriched to a minimum concentration of 20%. Uranium enriched to at least 90% is classified as weapons-grade uranium.
Question 2
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Marsupials are not naturally found in India.
Statement-II: Marsupials can thrive only in montane grasslands with no predators.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Ans: c
Exp:
Statement-I is correct: Marsupials can be observed in regions spanning Australia, Papua New Guinea, and South America. They are not naturally found in India. Examples of marsupials include kangaroos, wallabies, wombats, opossums, bandicoots, and koalas.
Statement-II is not correct: These creatures predominantly inhabit arid and semi-arid areas, and they are not restricted solely to montane grasslands
Question 3
Invasive Species Specialist Group’ (that develops the Global Invasive Species Database) belongs to which one of the following organisations?
(a) The International Union for Conservation of Nature
(b) The United Nations Environment Programme
(c) The United Nations World Commission for Environment and Development
(d) The World Wide Fund for Nature
Ans: a
Exp:
The Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG) is a global network of scientific and policy experts on invasive species, organised under the auspices of the Species Survival Commission (SSC) of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The ISSG fosters and enables the worldwide exchange of knowledge and information concerning invasive species. It also ensures the linkage between knowledge, practice, and policy to ensure that decisions are based on well-informed insights.
Question 4
Consider the following fauna:
1. Lion-tailed Macaque
2. Malabar Civet
3. Sambar Deer
How many of the above are generally nocturnal or most active after sunset?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
ExplanationAns: b
Exp:
Option 1 is not correct: Lion-tailed Macaque also referred to as the wanderoo, inhabits the upper canopy of tropical evergreen rainforests and monsoon forests across various elevations. This species is endemic to the Western Ghats. They are diurnal. Conservation Status in India:
Option 2 is correct: Malabar Civet is endemic to the Western Ghats of India. It is listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List. The Malabar civet is considered nocturnal and so elusive that little is known about its biology and ecology apart from habitat use.
Option 3 is correct: The sambar is a large deer native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia that has been listed as a vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List since 2008. Sambar are nocturnal or crepuscular animals and rest during the day under the cover of heavy forest. The males live alone for
much of the year, and the females live in small herds of up to 16 individuals.
Question 5
Which of the following organisms perform waggle dance for others of their kin to indicate the direction and the distance to a source of their food?
(a) Butterflies
(b) Dragonflies
(c) Honey Bees
(d) Wasps
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
Honeybees reside in colonies managed by a single queen overseeing the entire hive. Worker honeybees, all of which are females, constitute the only bees
typically observed flying outside the hive by the general populace. Bees perform two distinct types of dances: The Round Dance and The Tail-wagging or Waggle Dance. The waggle dance of honeybees has long been recognized as a behaviour that communicates information about resource location from a foraging worker to her nest mates.
Question 6
Consider the following statements:
1. Some mushrooms have medicinal properties.
2. Some mushrooms have psychoactive properties
3. Some mushrooms have insecticidal properties.
4. Some mushrooms have bioluminescent properties.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
ExplanationAns: d
Exp:
Statement 1 is correct: Mushrooms possess antibacterial properties, enhance the immune system, and aid in lowering cholesterol levels. Moreover, they serve as significant reservoirs of bioactive compounds. Consequently, certain mushroom extracts are utilised to support human health and are available in the form of dietary supplements.
Statement 2 is correct: Psychoactive properties refer to substances that influence brain function, resulting in alterations in mood, awareness, cognition, emotions, or behaviour. Psilocybin is a hallucinogenic compound found in specific mushrooms commonly known as magic mushrooms.
Statement 3 is correct: In recent times, there has been a growing discovery of insecticidal compounds within mushrooms.
Statement 4 is correct: Bioluminescence refers to the generation and release of light by living organisms. Panellus stipticus stands out as one of the most luminous bioluminescent mushrooms found on our planet. The newly discovered species, designated as Roridomyces phyllostachydis found in Meghalaya, now joins the ranks of the 97 recognised types of bioluminescent fungi worldwide.
Question 7
Consider the following statements regarding the Indian squirrels:
1. They build nests by making burrows in the ground.
2. They store their food materials like nuts and seeds in the ground.
3. They are omnivorous.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
Statement 1 is correct: Tree squirrels typically live in wooded areas since they prefer to live in trees. Flying squirrels make their homes in tree holes or nests
that are built into the crooks of branches. Ground squirrels live up to their names. They dig burrows, a system of tunnels underground, to live in. Some
squirrels also hibernate in burrows during the winter to keep warm.
Statement 2 is correct: Nuts serve as the primary food source for these creatures year-round, especially during the winter months when they are preparing for hibernation. They store nuts by burying them underground, enabling retrieval during the winter season.
Statement 3 is correct: Squirrels are omnivores. Their diet primarily consists of nuts and fruits, although they will also consume seeds, insects, small mammals, reptiles, eggs, and occasionally even bird chicks.
Question 8
Consider the following statements:
1. Some microorganisms can grow in environments with temperature above the boiling point of water.
2. Some microorganisms can grow in environments with temperature below the freezing point of water.
3. Some microorganisms can grow in highly acidic environment with a pH below 3.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
Microorganisms are classified into three primary groups on the basis of their preferred range of temperature:
Statement 1 is correct: Thermophiles are able to survive at temperatures up to 122°C. Thermophile. Hyperthermophiles induce the production of heat
shock proteins (HSPs), which are standard proteins responsible for responding to heat stress and safeguarding against cellular damage.
Statement 2 is correct: In Psychrophiles, the lowest temperature limit for life seems to be around −20 °C, which is the value reported for bacteria living in permafrost soil and in sea ice. The antifreeze proteins (AFPs) have the ability to bind to ice crystals through a large complementary surface and thereby create thermal hysteresis and lower the temperature at which an organism can grow.
Statement 3 is correct: pH 6.5-7 (neutral range) is best suited for bacterial growth. However some bacteria can grow at an acidic pH below 4 and are
called acidophiles. While some bacteria prefer an alkaline pH (8-9), are called alkalophiles. Molds and yeasts (fungus) require an optimum pH of about 5 to 6 for growth.
Question 9
Which one of the following makes a tool with a stick to scrape insects from a hole in a tree or a log of wood?
(a) Fishing cat
(b) Orangutan
(c) Otter
(d) Sloth bear
ExplanationAns: b
Exp:
Orangutans have been known for making and using tools such as sticks for fishing out bugs from bark. Orangutan (genus Pongo) is any of three species of
Asian great apes found in rainforests on the Southeast Asian islands of Sumatra and Borneo. The Bornean orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus) inhabits large portions of Borneo, whereas the Sumatran orangutan (P.abelii) and the Tapanuli orangutan (P. tapanuliensis) are limited to northern Sumatra. Orangutans possess cognitive abilities comparable to those of the gorilla and the chimpanzee, which are the only primates more closely related to humans.
Question 10
Consider the following:
1. Aerosols
2. Foam agents
3. Fire retardants
4. Lubricants
In the making of how many of the above are hydrofluorocarbons used?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
ExplanationAns: d
Exp:
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) are a climate “Super- Pollutant” – Greenhouse gases with hundreds to thousands of times the heat-trapping power of carbon dioxide (CO). HFCs are synthetic gases used in air conditioning systems, aerosol propellants, foam-blowing agents, solvents, lubricants, and flame retardants. These gases were first developed as alternatives to ozone-depleting chemicals, but after their rollout, it was learned that their release to the atmosphere during manufacturing processes and leakage during use, servicing, and retirement/ replacement of equipment poses a grave threat to our climate.
Question 11
Consider the following:
1. Aerosols
2. Foam agents
3. Fire retardants
4. Lubricants
In the making of how many of the above are hydrofluorocarbons used?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
Statement I is correct: Carbon markets are trading systems in which carbon credits are sold and bought. Companies or individuals can use carbon markets to compensate for their greenhouse gas emissions by purchasing carbon credits from entities that remove or reduce greenhouse gas emissions. One tradable carbon credit equals one tonne of carbon dioxide or the equivalent amount of a different greenhouse gas reduced, sequestered or avoided.
Statement II is not correct: Carbon markets are trading systems in which carbon credits are sold and bought. There is no transfer of resources from the
private sector to the state.
Question 12
Consider the following infrastructure sectors:
1. Affordable housing
2. Mass rapid transport
3. Health care
4. Renewable energy
On how many of the above does the UNOPS Sustainable Investments in Infrastructure and Innovation (S3i) initiative focus for its investments?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
The UNOPS Sustainable Investments in Infrastructure and Innovation (S3i) initiative was introduced in 2015 as a pilot project to investigate inventive approaches to financing sustainable infrastructure endeavours in developing nations. The initiative sought to capitalise on UNOPS’ proficiency and track record in providing infrastructure solutions that align with the requirements and ambitions of individuals and communities. The S3i initiative provides initial funding for significant projects in affordable housing, renewable energy, and health infrastructure. It does not emphasise investments in mass rapid transport infrastructure. Hence only Statements 1, 3 and 4 are correct.
Question 13
Consider the following statements regarding mercury pollution:
1. Gold mining activity is a source of mercury pollution in the world.
2. Coal-based thermal power plants cause mercury pollution.
3. There is no known safe level of exposure to mercury.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
Statement 1 is correct: Mercury is used in Artisanal Small-Scale Gold Mining (ASGM). The majority of the mercury emissions associated with the ASGM sector come from the burning of mercury-gold amalgam, which is responsible for 38% of all anthropogenic mercury emissions to the atmosphere.
Statement 2 is correct: Mercury is released into the atmosphere via the burning of coal and other fossil fuels. Because coal has far higher mercury content than other fossil fuels, coal-fired power stations frequently produce more mercury pollution than power plants that burn other fossil fuels.
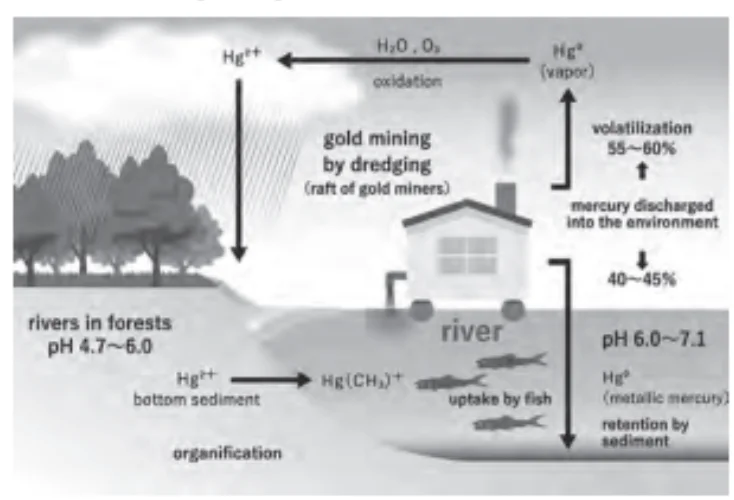
Statement 3 is correct: There is no known safe level of exposure to mercury due to its extreme toxicity. The ideal level of mercury in the body is zero because it has no physiological advantages for either children or adults.
Question 14
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: According to the United Nations’ World Water Development Report, 2022’, India extracts more than a quarter of the world’s groundwater withdrawal each year.
Statement-II: India needs to extract more than a quarter of the world’s groundwater each year to satisfy the drinking water and sanitation needs of almost 18% of the world’s population living in its Territory.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Ans: c
Exp:
Statement-I is correct: According to the United Nations’ World Water Development Report 2022, India extracts more than a quarter of the world’s groundwater withdrawal each year. This indicates that India has a significant reliance on groundwater resources for various purposes, including irrigation, drinking water, and industrial use.
Statement-II is not correct: Approximately 89% of India’s groundwater is utilised for irrigation purposes. The primary portion of the total groundwater extracted in India serves irrigation needs rather than being allocated for drinking and sanitation purposes.
Question 15
Consider the following statements:
1. In India, the Biodiversity Management Committees are key to the realisation of the objectives of the Nagoya Protocol.
2. The Biodiversity Management Committees have important functions in determining access and benefit sharing, including the power to levy collection fees on the access of biological resources within its jurisdiction.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
As per the Biodiversity Act of 2002, Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs) are constituted at the local level. The act implements India’s obligations
outlined in the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) of 1992. BMCs play a crucial role in preparing peoples’ biodiversity registers (PBRs), containing comprehensive information on local biological resources and associated traditional knowledge. They also oversee access and benefit-sharing (ABS) and have the authority to impose collection fees on biological resource access within their jurisdiction. BMCs are essential for fulfilling the objectives of the Nagoya Protocol (2010), negotiated within the CBD, ensuring benefits from genetic resources andtraditional knowledge accrue to indigenous and local communities on agreed terms. Hence, both statement 1 and statement 2 are correct.
Question 16
Consider the following statements:
Once the Central Government notifies an area as a ‘Community Reserve’.
1. The Chief Wildlife Warden of the State becomes the governing authority of such forest.
2. Hunting is not allowed in such area.
3. People of such areas are allowed to collect non-timber forest produce.
4. People of such areas are allowed traditional agricultural practices.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
ExplanationAns: c
Exp:
Community Reserves fall under protected areas, along with marine protected areas, national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and conservation reserves, according to the Wild Life (Protection) Act (WLPA), 1972. These protected area categories were first introduced in the Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Act of 2002.
Statement 1 is correct: Under Section 33 of the Wildlife Protection Act (WLPA), upon the Centre’s notification of an area as a community reserve, the Chief Wildlife Warden of the state assumes authority over the forest. All decisions regarding the area necessitate the consent of this governing authority.
Statement 2 is correct: Following the designation of a forest as a community reserve, hunting is strictly prohibited in these areas.
Statement 3 is correct: In a Community Reserve, the collection of non-timber forest produce by the local communities is subject to the specific rules and regulations governing the Community Reserve. It may be regulated or restricted to ensure sustainable use and conservation of resources.
Statement 4 is incorrect: After a forest has been made into a community reserve, people cannot use it for agricultural practices, leave alone jhum cultivation.
2022
Question 1
Which of the following are nitrogen-fixing plants?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 3 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3, 5 and 6 only
(c) 2, 4, 5 and 6 only
(d) 1, 2, 4, 5 and 6
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Nitrogen fixation
Option (a) is the correct answer: Alfalfa, Chickpea and Clover are nitrogen-fixing plants.
Nitrogen-fixation:
Question 2
Among the following crops, which one is the most important anthropogenic source of both methane and nitrous oxide?
(a) Cotton
(b) Rice
(c) Sugarcane
(d) Wheat
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Agriculture and Greenhouse gases
Option (b) is the correct answer: Rice is one of the most important anthropogenic sources of both methane and nitrous oxide.
Agriculture and Greenhouse gases:
|
NOTE: Climate Smart Agriculture and GHG Emissions was very much in news, hence the question. Therefore, it is very important to holistically cover both the static and current affairs for UPSC Pre and Mains. |
Question 3
“System of rice Intensification” of cultivation, in which alternate wetting and drying of rice fields is practised, results in:
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: System of Rice Intensification
Option (d) is the correct answer: All of the given results come from the System of Rice Intensification.
System of Rice Intensification:
| Advantages of SRI | In situ Conservation |
|
|
Question 4
In the context of WHO Air Quality Guidelines, consider the following statements:
1. The 24-hour mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 15 ug/m3 and annual mean of 5 should not exceed 5 ug/m3.
2. In a year, the highest levels of ozone pollution occur during the period of inclement weather.
3. PM10 can penetrate the lung barrier and enter the bloodstream.
4. Excessive ozone in the air can trigger asthma.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 3 and 4
(b) 1 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1 and 2 only
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Air quality
Statement 1 is correct: The 24-hour ceiling mean of PM 2.5 used to be 25 micrograms but has now dropped to 15.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Ozone at ground level is formed by the reaction with sunlight (photochemical reaction) of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) from vehicle and industry emissions and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by vehicles, solvents and industry. As a result, the highest levels of ozone pollution occur during periods of sunny weather and not during inclement weather.
Statement 3 is incorrect: PM is a common proxy indicator for air pollution. It affects more people than any other pollutant. While particles with a diameter of 10 microns or less, (≤ PM10) can penetrate and lodge deep inside the lungs, the even more health-damaging particles are those with a diameter of 2.5 microns or less, (≤ PM2.5). PM2.5 can penetrate the lung barrier and enter the blood system.
Statement 4 is correct: Excessive ozone in the air can have a marked effect on human health. It causes breathing problems, triggers asthma, reduces lung function and causes lung diseases. Ozone triggers asthma because it is very irritating to the lungs and airways.
Question 5
Consider the following:
Excess of which of the above in the environment is/ are cause(s) of acid rain?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 4 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Air Pollution
Option (b) is the correct answer: Nitrous oxide and Sulphur dioxide cause Acid rain.
→ Acid Rain (HNO3 + H2SO4)
Common Air Pollutants and Their Effects
| Pollutant | Sources | Effects |
|
Particulate matter (PM) |
Vehicles, power plants, construction activities, oil
refinery, railway yard, industries, etc. |
Cardiovascular diseases, reduces visibility (haze) |
| Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) | Emissions from combustion processes | Can aggravate respiratory diseases, acid rain, Hazy weather |
|
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) |
Burning of fossil fuels, power plants, metals processing
and smelting facilities, vehicles |
Affects respiratory system & functions of the lungs. causes irritation of the eyes, chronic bronchitis, Acid rain |
|
Ozone (O3) |
Results from photochemical reactions b/w NOx & VOCs in presence of sunlight. | Affect the lungs, the respiratory tract, and the eyes, lung cancer |
NOTE: This particular straightforward question is repeated verbatim from 2013.
Question 6
Which one of the following has been constituted under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986?
(a) Central Water Commission
(b) Central Ground Water Board
(c) Central Ground Water Authority
(d) National Water Development Agency
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Environment (Protection) Act, 1986/ Central Ground Water Authority Central Ground Water Authority:
Environment (Protection) Act, 1986:
Question 7
With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 only
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Wildlife Protection Important Provisions of Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972:
Statement 1 is incorrect: As per the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972, every Wild Animal shall be the property of the State Government, and, where such animal is hunted in a sanctuary or National Park declared by the Central Government, such animal or any animal article, trophy, uncured trophy or meat [derived from such animal, or any vehicle, vessel, weapon, trap or tool used in such hunting] shall be the property of the Central Government.
Hunted animals are the sole property of the Government.
Statement 2 is correct: The law governing the subject of wildlife, the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, provides for equal protection for wild animals irrespective of where they are found. It does not discriminate between animals found in protected areas and outside.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Mere apprehension or fear that a wild animal could endanger human life is not a ground for capture or killing. As per Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, only if the wild animal becomes a danger to human life or is deceased or disabled beyond recovery can it be allowed to be captured or killed by the competent authority, the Chief Wildlife Warden of the State.
Question 8
The “Miyawaki method” is well known for the:
(a) Promotion of commercial farming in arid and semi-arid areas
(b) Development of gardens using genetically modified flora
(c) Creation of mini forests in urban areas
(d) Harvesting wind energy on coastal areas and on sea surfaces
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Miyawaki Method of Urban Afforestation
Option (c) is the correct answer: Miyawaki method is a method of urban afforestation by turning backyards into mini-forests. It includes planting trees as close as possible in the same area which not only saves space, but the planted saplings also support each other in growth and block sunlight from reaching the ground, thereby preventing the growth of weeds. Thus the saplings become maintenance-free (self- sustainable) after the first three years. It helps to create a forest in just 20 to 30 years while through conventional methods it takes anywhere between 200 to 300 years.
Miyawaki Process
Question 9
Consider the following pairs:
Wetland/Lake – Location
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) Only one pair
(b) Only two pairs
(c) Only three pairs
(d) All four pairs
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Wetlands
Option (b) is correct:
| Wetlands | Location and Significance |
| Hokera Wetland | Jammu and kashmir.
A perennial natural wetland that is part of the Jhelum basin. |
| Renuka Wetland |
|
| Lake Rudijala/ Rudrasagar Lake |
|
| Sasthamkotta |
|
Question 10.
“If rainforests and tropical forests are lungs of the Earth, then surely wetlands function as its kidneys.” Which one of the following functions of wetlands best reflects the above statements?
(a) The water cycle in wetlands involves surface runoff, subsoil percolation and evaporation.
(b) Algae form the nutrient base upon which fish, crustaceans, molluscs, birds, reptiles and mammals thrive.
(c) Wetlands play a vital role in maintaining sedimentation balance and soil stabilisation.
(d) Aquatic plants absorb heavy metals and excess nutrients.
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Wetland Conservation
Option (d) is the correct answer: Natural wetlands have often been referred to as “earth’s kidneys” because of their high and long-term capacity to filter pollutants from the water that flows through them. Hence, Aquatic plants absorb heavy metals and excess nutrients.
Functions of Kidney and Wetland
Question 11.
With reference to “Gucchi” sometimes mentioned in the news, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Species and their habitat
Option (c) is the correct answer: Guchhi Mushroom is a Species of Fungus cultivated in Himalayan Forests.
Statement 1 is correct: Guchhi mushroom is a species of fungus in the family Morchellaceae of the Ascomycota.
Statement 2 is correct: It is grown in the foothills of Himalayas mostly in the temperate forests of Himachal Pradesh, Uttaranchal, and Jammu and Kashmir.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The mushrooms cannot be cultivated commercially and grow in conifer forests across temperate regions.
Question 12
Which of the following is not a bird?
(a) Golden Mahseer
(b) Indian Nightjar
(c) Spoonbill
(d) White Ibis
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Freshwater Species
Golden Mahseer (freshwater fish)
Option (a) is the correct answer: Golden Mahseer is also known as the tiger of Indian rivers. It is a species of the genus Tor. The Golden Mahseer, the longest-living freshwater fish, is native to mountain and sub-mountain regions found in the Himalayan Rivers (Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra). The Pong Dam reservoir, around 250 km from state capital Shimla and 190 km from Chandigarh, supports an ample population of the golden Mahseer. Conservation Status: IUCN: Endangered.
2021
Question 1
In nature, which of the following is/are most likely to be found surviving on a surface without soil?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Biodiversity/Ecosystem
Option (c) is the correct answer: Lichen and Moss can survive on a surface without soil.
Bryophytes:
Statement 1 is incorrect: There are four particular types of habitats that ferns are found in: moist, shady forests; crevices in rock faces, especially when sheltered from the full sun; acid wetlands including bogs and swamps; and tropical trees, where many species are epiphytes.
Statement 2 is correct: Lichens are generally found on rock, tree bark, soil, houses, tombstones, cars, old farm equipment, etc. Thus, lichen can be found surviving on surfaces without soil.
Statement 3 is correct: Mosses are nonvascular plants. They do not need soil to survive, instead they have a rhizoid multi-cell anchoring structure that is used to climb and grip over rocky surfaces. Moss thrives in moist and shady areas.
Statement 4 is incorrect: A mushroom is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically grows above ground, on soil, etc.
Question 2
Consider the following kinds of organisms:
Which of the above are primary producers in the food chains of oceans?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 3 and 4
(d) 1 and 4
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Food chain
Option (b) is the correct answer: Cyanobacteria and Diatoms are primary producers in the food chains of oceans.
Copepods:
Cyanobacteria:
Diatoms:
Foraminifera:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Free-living copepods form a crucial link in the food chain and are often assigned the role of “primary consumers”.
Statement 2 is correct: Cyanobacteria, also called blue-green algae, are microscopic organisms found naturally in all types of water. These organisms use sunlight to make their own food.
Statement 3 is correct: Diatoms are photosynthesising algae. They are found in almost every aquatic environment including fresh and marine waters. They are primary producers in oceanic food chain.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Foraminifera are found in all marine environments, they may be planktic or benthic in their mode of life. Foraminifera are recorded as feeding chiefly upon bacteria, small diatoms, and nanoplankton in a wide variety of marine environments.
Question 3
Which of the following are detritivores?
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 3 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Food Chain
Option (c) is the correct answer: Earthworms, Millipedes and Woodlice are Detritivores.
Question 4
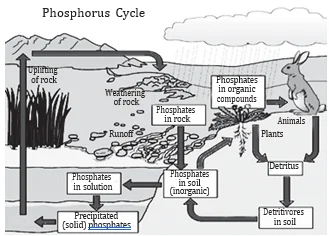
In which one of the following biogeochemical cycles, the weathering of rocks is the main source of release of nutrients to enter the cycle?
(a) Carbon cycle
(b) Nitrogen cycle
(c) Phosphorus cycle
(d) Sulphur cycle
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Biogeochemical Cycles
Option (c) is the correct answer: Phosphate ions and other minerals gradually leak out of rocks as a result of weathering and rain.
Phosphorus Cycle:
Question 5
Which of the following have species that can establish a symbiotic relationship with other organisms?
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Species Interaction
Option (d) is the correct answer: All species can establish a symbiotic relationship with other organisms.
Symbiotic Relationship:
Option 1 is correct: The relationship between cnidarians and dinoflagellate algae is termed “symbiotic” because both the animal host and the algae are benefiting from the association. It is a mutualistic interaction.
Option 2 is correct: Two common mutualistic relationships involving fungi are mycorrhiza (fungi and plant roots) and lichen (fungi and either cyanobacteria or green algae).
Option 3 is correct: Protozoa mostly represent a close mutualistic association between a protozoan and unicellular symbiont such as bacteria, cyanobacteria or/and unicellular algae or protozoans and a multicellular organisms such as ruminants, lower termites, wood-eating cockroaches, plants.
Question 6
With reference to the water on the planet Earth, consider the following statements:
1. The amount of water in the rivers and lakes is more than the amount of groundwater.
2. The amount of water in polar ice caps and glaciers is more than the amount of groundwater.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 Only
(b) 2 Only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Water Conservation
Water Resources:

|
NOTE: This question is repeated from 2013. Also, it is a direct question from Class 7 NCERT (Geography). |
Question 7
Which one of the following is used in preparing a natural mosquito repellent?
(a) Congress grass
(b) Elephant grass
(c) Lemongrass
(d) Nut grass
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Biodiversity/Everyday Science
Option (c) is the correct answer: Lemongrass is used in preparing a natural mosquito repellent.
Question 8
The vegetation of savannah consists of grassland with scattered small trees, but extensive areas have no trees. The forest development in such areas is generally kept in check by one or more or a combination of some conditions. Which of the following are such conditions?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 4 and 5
(c) 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 5
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Biomes
Savannah Biome:
Geographical Location:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The savannah biome relies on their herd numbers and speed for survival, as the vast open areas provide little means of escape from quick predators.
Statement 2 is correct: The combination of high temperatures and little precipitation makes savannahs perfect areas for grass and brush fires during their dry seasons.
Statement 3 is correct: Many of the savannah biome animals are grazing herbivores that migrate through the region.
Statement 4 is correct: Savannah regions have two distinct seasons – a wet season and a dry season. There is very little rain in the dry season. In the wet season vegetation grows, including lush green grasses and wooded areas.
Statement 5 is incorrect: Soil properties influence the type of savannah and its vegetation but don’t contribute to checking it once formed.
Question 9
How is permaculture farming different from conventional chemical farming?
1. Permaculture farming discourages monocultural practices but in conventional chemical farming, monoculture practices are predominant.
2. Conventional chemical farming can cause an increase in soil salinity but the occurrence of such a phenomenon is not observed in permaculture
3. Conventional chemical farming is easily possible in semi-arid regions but permaculture farming is not so easily possible in such regions.
4. Practice of mulching is very important in permaculture farming but not necessarily so in conventional chemical farming.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 1, 2 and 4
(c) 4 only
(d) 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Sustainable Agriculture
Statement 1 is correct: Permaculture is a totally integrated design system that’s modelled on nature. Permaculture farming promotes multi-cropping and integrated farming systems. While chemical farming is more suitable for monoculture cropping due to the use of crop- specific inputs like irrigation, chemical fertiliser and harvesting methods.
Statement 2 is correct: Conventional farming usually alters the natural environment, increases soil salinity, and eliminates biodiversity. Such problems are not seen in permaculture farming as it relies on organic fertilizers.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Chemical farming is based on the intense use of inputs like chemical fertilizers and irrigation that make the soil less fertile over time, thus restricting its practice in semi-arid regions. Thus, conventional farming is not suitable for semi-arid regions. Permaculture involves well-designed systems that don’t produce waste and permaculture tries to imitate well-designed systems. Thus, it can work in arid climates as well.
Statement 4 is correct: Mulching is an important component of Permaculture systems for promoting maximum efficiency.
Question 10
In the context of India’s preparation for Climate-Smart Agriculture, consider the following statements:
1. The ‘Climate-Smart Village’ approach in India is a part of a project led by the Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), an international research programme.
2. The project of CCAFS is carried out under the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) headquartered in France.
3. The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in India is one of the CGIAR’s research centres.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Agriculture and Environment
Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA):
Statement 1 is correct: The Climate-Smart Village project in India is a CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS).
Statement 2 is correct: Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCFAS) is carried out under CGIAR (formerly the Consultative Group for International Agricultural Research).
Statement 3 is correct: ICRISAT is a CGIAR Research Center. It is a non-profit, non-political public international research organization that conducts agricultural research for development in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa with a wide array of partners throughout the world.
Question 11
Why is there a concern about copper smelting plants?
1. They may release lethal quantities of carbon monoxide into the environment.
2. The copper slag can cause the leaching of some heavy metals into the environment.
3. They may release sulphur dioxide as a pollutant.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Industrial Pollution
Copper Smelting:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Copper smelting does not release lethal quantities of carbon monoxide into the environment.
Statement 2 is correct: Some smelting processes can also produce large quantities of solid waste, known as slag. This slag may leach heavy metals (arsenic, cadmium, lead or mercury depending on the composition of the ore) into groundwater reservoirs.
Statement 3 is correct: Smelting processes are known to emit high quantities of air pollutants such as hydrogen fluoride, sulphur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, offensive and noxious smoke fumes, vapours, gases, and other toxins.
Question 12
With reference to furnace oil, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Air Pollution/Emissions
Furnace oil:
Applications of Furnace oil:
Statement 1 is correct: Furnace oil or fuel oil is a dark viscous residual product of crude-oil distillation. It is used as a fuel in different types of combustion equipment.
Statement 2 is correct: Marine engines and slow speed engines for power generation use Furnace oil.
Statement 3 is correct: The emissions of oxides of sulphur are a direct result of the sulphur content of the fuel oil.
Question 13
Magnetite par ticles, suspected to cause neurodegenerative problems, are generated as environmental pollutants from which of the following?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Industrial Pollution
Option (b) is the correct answer: Brakes of motor vehicles, engines of motor vehicles, and power plants are sources of Magnetic Particles.
Magnetite particles:
Option 1 is correct: Vehicle brake systems are the major source of airborne magnetite at the roadside.
Options 2 and 4 are correct: Petrol and diesel- engine exhaust and power plants are also a source of airborne magnetite.
Options 3 and 5 are incorrect: There is no adequate evidence supporting the generation of magnetite particles from sources like microwave Stoves within homes and telephone lines.
Question 14
The ‘Common Carbon Metric’, supported by UNEP, has been developed for
(a) Assessing the carbon footprint of building operations around the world
(b) Enabling commercial farming entities around the world to enter carbon emission trading
(c) Enabling governments to assess the overall carbon footprint caused by their countries
(d) Assessing the overall carbon foot-print caused by the use of fossil fuels by the world in a unit time
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Air Pollution/Carbon Emission Option (a) is the correct answer: The carbon footprint of building operations is assessed through ‘Common Carbon Metric’.
Question 15
What is blue carbon?
(a) Carbon captured by oceans and coastal ecosystems
(b) Carbon sequestered in forest biomass and agricultural soils
(c) Carbon contained in petroleum and natural
(d) Carbon present in atmosphere
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Carbon Sink
Blue Carbon:
Blue Carbon Initiative:
It also comprises:
Question 16
Consider the following animals:
To reduce the chance of being captured by predators, which of the above organisms rolls up/roll up and protects/protects its/their vulnerable parts?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Food Chain/Species
Statement 1 is correct: Hedgehogs are small mammals with short limbs and a body low to the ground. Their most distinctive characteristic is the thousands of stiff, sharp spines – harder and sharper than those of a porcupine – that cover the animal’s back and sides, like a pincushion filled with needles. If attacked they will curl into a prickly and unappetizing ball that deters most predators. IUCN Red List Status: Least concern
Statement 2 is incorrect: Marmot are any of 14 species of giant ground squirrels found primarily in North America and Eurasia. Marmots are well suited for life in cold environments and have small fur-covered ears, short, stocky legs, and strong claws for digging. Due to the absence of scales or spines, they do not roll up and protect their vulnerable parts. IUCN Red Listed as: Least Concern.
Statement 3 is correct: Pangolin, also called scaly anteaters because of their preferred diet, pangolins are the most trafficked mammal in the world. If touched or grabbed it will roll up completely into a ball, while the sharp scales on the tail can be used to lash out.
Question 17
Which one of the following is a filter feeder?
(a) Catfish
(b) Octopus
(c) Oyster
(d) Pelican
Ans: (c)
Sub-Theme: Species
Option (c) is the correct answer: Oyster is a Filter Feeder.
Filter feeders are a subgroup of suspension feeding animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water, typically bypassing the water over a specialised filtering structure. Clams, krill, sponges, oysters, baleen whales, and numerous fish are among the creatures that rely on this way of feeding (including some sharks). Filter feeders include some birds like flamingos and several varieties of duck. Filter feeders are regarded as ecosystem engineers since they might be crucial in the clarification of water. They serve as indicator organisms and are crucial in bioaccumulation.
Question 18
With reference to ‘palm oil’, consider the following statements:
1. The palm oil tree is native to Southeast Asia.
2. Palm oil is a raw material for some industries producing lipstick and perfumes.
3. The palm oil can be used to produce biodiesel.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Species
Palm Oil (Native to Africa)
Statement 1 is incorrect: Oil palm trees are native to Africa but were brought to South-East Asia over 100 years ago as an ornamental tree crop.
Statement 2 is correct: Non-food applications of Palm oil are Cosmetics, toiletries, soaps and detergents. Oleochemical industry, as a base material for laundry detergents, household cleaners and cosmetics.
Statement 3 is correct: Palm oil can be used to produce biodiesel, which can be used in compression ignition engines, i.e., diesel engines without any modifications.
Applications of Palm Oil
| Food-based applications | Cooking oil, substitute for butter, vanaspati/ vegetable ghee, margarine, confectionery and bakery fats, ice cream, coffee creamers, emulsifiers, vitamin E supplements among others. |
| Non-food applications | Cosmetics, toiletries, soaps and detergents. Oleochemical industry, as a base material for laundry detergents, household cleaners and cosmetics. Also, Palm oil can be used to produce biodiesel. |
|
NOTE: Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi has announced this new national initiative on palm oil and in August, 2021, Environmental activists and politicians have expressed concerns over the centre’s proposal to promote palm oil cultivation in the Northeastern states and in the Andaman and Nicobar islands. Hence, the question!! |
Question 19
Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4 and 5
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 5
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Species
Statement 1 is incorrect: Moringa is a fast- growing, drought-resistant tree native to the Indian subcontinent. Found in the wild in the sub- Himalayan regions of Northern India and now grown worldwide in the tropics and sub-tropics.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Tamarind is a leguminous tree bearing edible fruit that is indigenous to tropical Africa.
Statements 3 and 4 are correct: In India most of the Tamarind is collected as Minor Forest Produce with Minimum Support Price. Tamarind is also actively exported from India.
Statement 5 is correct: Biodiesel is derived from the tamarind seed through the transesterification process as potential alternative feedstock for the diesel engine.
|
NOTE: Recently, the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) has been supporting private entities in creating the necessary infrastructure to promote Moringa products exports from India. Hence, the question! |
2020
Question 1
What are the advantages of fertigation in agriculture?
1. Controlling the alkalinity of irrigation water is possible.
2. Efficient application of Rock Phosphate and all other phosphatic fertilizers is possible.
3. Increased availability of nutrients to plants is possible.
4. Reduction in the leaching of chemical nutrients is possible.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c)1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Agriculture and Environment
Fertigation:
Statement 1 is correct: Drip irrigation also avoids water spillage on the field which could have promoted weed growth or increased soil alkalinity due to water logging. So, fertigation also helps control weed growth and cut down alkalinity.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Rock phosphate is not soluble and thus not suitable for fertigation.
Statement 3 is correct: Accurate placement of nutrient, where the water goes the nutrient goes as well. Thus, increased nutrient absorption by plants.
Statement 4 is correct: Reduction of fertiliser, chemicals, and water. It leads to reduction in the leaching of chemicals into the water supply.
Question 2
What is/are the advantage/ advantages of zero tillage in agriculture?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Sustainable Agriculture Benefits/Advantages of Zero tillage or No-till farming:
Statement 1 is correct: Zero tillage is the process where the crop seed will be sown through drillers without prior land preparation and disturbing the soil where previous crop stubbles are present.
Statement 2 is correct: Direct Seeded Rice (DSR) is a viable option to reduce the unproductive water flows, with increasing shortage of water, dry-DSR with minimum or zero tillage further enhances the benefits of this technology by saving labour.
Statement 3 is correct: No-till farming has been claimed to increase soil organic matter, and thus increase carbon sequestration.
Question 3
In the context of India, which of the following is/ are considered to be practice(s) of eco-friendly agriculture?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme:Climate Smart Agriculture
Statement 1 is correct: The Climate-Smart Village project in India is a program of CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS). The CCAFS started piloting the Climate-Smart Village in 2012 in Africa (Burkina Faso, Ghana, Mali, Niger, Senegal, Kenya, Ethiopia, Tanzania, and Uganda) and South Asia (Bangladesh, India, and Nepal).
Statement 2 is correct: Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCFAS) is carried out under CGIAR (formerly the Consultative Group for International Agricultural Research). Headquarter of CGIAR is in Montpellier, France. CGIAR is a global partnership that unites international organizations engaged in research about food security.
Statement 3 is correct: International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) is a CGIAR Research Center. ICRISAT is a non-profit, non-political public international research organization that conducts agricultural research for development in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa with a wide array of partners throughout the world.
Question 4
What is the use of biochar in farming?
1. Biochar can be used as a part of the growing medium in vertical farming.
2. When biochar is a part of the growing medium, it promotes the growth of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms.
3. When biochar is a part of the growing medium, it enables the growing medium to retain water for longer time.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Environment and Agriculture
Biochar:
Benefits:
Statement 1 is correct: The use of biochar in vertical farming can increase output significantly.
Statement 2 is correct: Using biochar in the soil promotes the growth of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms.
Statement 3 is correct: Biochar is hygroscopic. Thus, it is a desirable soil material in many locations due to its ability to attract and retain water.
Question 5
Which of the following are the reasons/factors for exposure to benzene pollution?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Air pollution
Option (a) is the correct answer: Automobile exhaust, tobacco smoke, and wood burning are the major factors for exposure to benzene pollution.
Benzene
Sources and Uses:
Question 6
According to India’s National Policy on Biofuels, which of the following can be used as raw materials for the production of biofuels?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 5 and 6 only
(b) 1, 3, 4 and 6 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Eco-Engineering
National Policy on Biofuels 2018:
|
NOTE 1: Though all six of the given materials can be used for preparing biofuel, but the question is specific and asked about ‘India’s National Policy on Biofuels’. NOTE 2: Earlier, UPSC has asked questions on ‘Eco-Engineering’ and specifically on ‘Biofuel’ in 2017. Also, we need to achieve the SDG goal and INDC by 2030. Therefore, it underlines the importance of the theme. Please refer to PYQ for a detailed explanation of Biofuel. |
Question 7
Which one of the following statements best describes the term ‘Social Cost of Carbon’?
It is a measure, in monetary value, of the:
(a) Long-term damage done by a tonne of CO2 emissions in a given year.
(b) Requirement of fossil fuels for a country to provide goods and services to its citizens, based on the burning of those fuels.
(c) Efforts put in by a climate refugee to adapt to live in a new place.
(d) Contribution of an individual person to the carbon footprint on the planet Earth.
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Air Pollution/Carbon Pricing/ Carbon Emission
Option (a) is the correct answer: Social cost of Carbon is best described as the measure of monetary value of long-term damage done by a tonne of CO2 emissions in a given year.
Social Cost Of Carbon:
Social Cost:
Question 8
Consider the following statements:
1. Coal ash contains arsenic, lead and mercury.
2. Coal-fired power plants release sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen into the environment.
3. High ash content is observed in Indian coal.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Air Pollution/Coal Ash
Statement 1 is correct: Coal ash contains contaminants like mercury, cadmium and arsenic. Without proper management, these contaminants can pollute waterways, groundwater, drinking water, and the air.
Statement 2 is correct: This statement is direct from NCERT Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 (Environmental Chemistry), Pg. 410. Burning of fossil fuels (which contain sulphur and nitrogenous matter) such as coal and oil in power stations and furnaces or petrol and diesel in motor engines produce sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which leads to ‘acid rain’.
Statement 3 is correct: Indian Coal has comparatively higher ash content than imported coal due to the drift theory of the formation of coal deposits in India. Coal seams formed due to drift theory contain higher ash as compared to the in-situ theory of formation
Question 9
If a particular plant species is placed under Schedule VI of The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, what is the implication?
(a) A licence is required to cultivate that plant.
(b) Such a plant cannot be cultivated under any circumstances.
(c) It is a Genetically Modified crop plant.
(d) Such a plant is invasive and harmful to the ecosystem.
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Environmental Laws
Option (a) is the correct answer: The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 has six schedules. Schedule VI has following provisions:
| NOTE: In 2017 a similar question came from the same topic, therefore, please refer to the solution of that question for a detailed explanation of Schedules under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. |
Question 10
Steel slag can be the material for which of the following?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Government Policies
Steel Slag
Statement 1 and 3 are correct: Steel slag is used as a base course material, the material under the surface layer of an asphalt road, track or surface. Also produce portland slag cement.
Statement 2 is correct: Steel slag can be used in the agricultural sector due to its ability to correct soil acidity. In fact, developed countries like Japan, the USA have taken the lead in making fertilisers using steel-making slag.
|
NOTE: In Nov, 2019 the Ministry of Steel issued a new Steel Scrap Recycling Policy, hence, the question featured and underlines the importance of reading the daily newspaper. |
Question 11
In rural road construction, the use of which of the following is preferred for ensuring environmental sustainability or to reduce carbon footprint?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 4 and 5 only
(d) 1 and 5 only
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Green Technologies
Statement 1 is correct: Copper slag is a by- product obtained during smelting and refining of copper. The use of copper slag in cement and concrete provides potential environmental as well as economic benefits.
Statement 2 is correct: Cold mix asphalt is produced by mixing unheated mineral aggregate with either emulsified bitumen or foamed bitumen. It is suitable for light to medium trafficked roads when used in base and surface courses.
Statement 3 is correct: Government has allowed the use of coir based geotextiles for construction of rural roads under the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana in 2020.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) is a combination of approximately 95% stone, sand, or gravel bound together by asphalt cement, a product of crude oil. The wide use of hot mix technology leads to environmental pollution as these plants emit a huge amount of greenhouse gases.
Statement 5 is incorrect: Portland cement is a major CO2 emitter.
|
NOTE: There was news on PMGSY new technology guidelines, where the government encourages the use of “Green Technologies” and non-conventional materials for constructing rural roads under Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY). Therefore, thorough newspaper reading is very crucial both in terms of UPSC Pre and Mains. |
Question 12
Consider the following statements:
1. 36% of India’s districts are classified as “overexploited” or “critical” by the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA).
2. CGWA was formed under the Environment (Protection) Act.
3. India has the largest area under groundwater irrigation in the world.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Major Environmental Organization/ Groundwater
Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA):
Statement 1 is incorrect: 256 of our approximately 700 districts have groundwater levels which are “critical” or “over-exploited” as per the latest data from the Central Ground Water Board (2017).
Statement 2 is correct: Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA) constituted under Section 3(3) of ‘The Environment (Protection) Act, (1986)’ regulates the extraction of groundwater through guidelines which are updated regularly.
Statement 3 is correct: FAO research paper shows the countries with the largest extent of areas equipped for irrigation with groundwater, in absolute terms, are India (39 million ha), China (19 million ha) and the USA (17 million ha)
Question 13. With reference to India’s Desert National Park, which of the following statements are correct?
1. It is spread over two districts.
2. There is no human habitation inside the park.
3. It is one of the natural habitats of the Great Indian Bustard.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: National Parks/Biosphere Reserve
Desert National Park, Rajasthan(Jaisalmer and Barmer, Rajasthan)
Statement 1 is correct: Desert National Park is situated in the west Indian state of Rajasthan and spreads over the districts of Jaisalmer and Barmer.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Normally human activities are not allowed in National Park but many villagers lived inside Desert National park, and they did not have access to even basic facilities like road, electricity and water.
Statement 3 is correct: The Thar desert harbours a wide array of flora and faunal species. It is the only place where Rajasthan State Bird, Great Indian Bustard are found naturally.
Question 14
Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”?
(a) Corbett
(b) Ranthambore
(c) Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
(d) Sunderbans
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: National Parks/Biosphere Reserve
Option (c) is the correct answer: Nagarjunsagar- Srisailam is the largest tiger reserve in India having a Core/ Critical Tiger Habitat of 3721 Sq. Km. The tiger reserve spans five districts in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. The Nallamala Hills make up the majority of the region. The reserve is home to the multifunctional reservoirs Srisailam and Nagarjunasagar. This reserve’s basin is bisected by the Krishna River.
Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
Question 15
Which one of the following protected areas is well- known for the conservation of a sub-species of the Indian swamp deer (Barasingha) that thrives well on hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous?
(a) Kanha National Park
(b) Manas National Park
(c) Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
(d) Tal Chhapar Wildlife Sanctuary
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: National Parks/Biosphere Reserve
Option (a) is the correct answer: Kanha National Park is located in Madhya Pradesh’s Mandla and Balaghat districts, covering an area of 940 square kilometres. There were two sanctuaries in the modern-day Kanha region: Hallon and Banjar. Kanha National Park was established in 1955, and the Kanha Tiger Reserve was established in 1973. The largest national park in Central India is Kanha National Park. It is the first tiger reserve in India to officially introduce a mascot, “Bhoorsingh the Barasingha”.
Kanha National Park (Mandla and Balaghat districts, Madhya Pradesh)
Question 16
Which of the following are the most likely places to find the musk deer in its natural habitat?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1 and 4 only
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: National Parks/Biosphere Reserve
Option (a) is the correct answer: To safeguard the critically endangered Musk Deer and its environment, the Askot Musk Deer Sanctuary was created in 1986. The refuge is sometimes referred to as “Green Paradise on Earth.” It is situated in Askot, a tiny village in the Pithoragarh district of Uttarakhand. Fauna:Snow leopard, Himalayan black bear, Himalayan tahr, blue sheep, musk deer, loong, monal, kalij pheasant, and cheer pheasant are some examples of the local fauna.
Gangotri National Park was founded in 1989 and is located in Uttarkashi, Uttrakhand, in the Bhagirathi River’s upper watershed. The Ganga River’s source, Gaumukh in Gangotri Glacier, is situated inside the park. The park area effectively connects Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary and Govind National Park. The park is completely surrounded by temperate coniferous forests.The typical vegetation includes chirpine, deodar, fir, spruce, oak, and rhododendron. The park is home to a number of rare and endangered animals, including the snow leopard, musk deer, Himalayan monal, Himalayan snowcock, and blue sheep (also known as bharal).
Question 17
With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements:
1. The leader of an elephant group is a female.
2. The maximum gestation period can be 22 months.
3. An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only.
4. Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4 only
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Species
Asian Elephants:
Asian elephants come in three subspecies: Indian, Sumatran, and Sri Lankan.
The majority of the continent’s remaining elephants belong to the Indian subspecies, which has the largest range.
Statement 1 is correct: The leader of a group is the oldest female. She guides the herd in their search for food and water sources. These matriarchal units can occasionally divide into smaller, temporary groups.
Statement 2 is correct: The gestation period lasts for 22 months, yielding a single baby.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Although sexually mature in their early teens, elephants generally only start to mate at about 20 years and stop bearing calves at about 50.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Recent census showed Kerala as having 5,706 elephants, while Karnataka with 6049 elephants.
Question 18
With reference to India’s biodiversity, Ceylon frogmouth, Coppersmith barbet, Gray-chinned minivet and White-throated redstart are
(a) Birds
(b) Primates
(c) Reptiles
(d) Amphibians
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Species Diversity
Option (a) is the correct answer: Ceylon frogmouth, Coppersmith barbet, Gray- chinned minivet and White-throated redstart are Birds.
White-throated redstart is a species of bird in the family Muscicapidae. It can be found in northeastern India, Nepal, Bhutan, central China, and the far northern reaches of Myanmar. From Pangolakha Wildlife Sanctuary, East Sikkim, India in alpine snowy meadows. IUCN Red List: Least Concern
2019
Question 1
In India, the use of carbofuran, methyl parathion, phorate and triazophos is viewed with These chemicals are used as
(a) pesticides in agriculture
(b) preservatives in processed foods
(c) fruit-ripening agents
(d) moisturizing agents in cosmetics
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Pesticides in Agriculture
Option (a) is the correct answer: Carbofuran, Methyl Parathion, Phorate and Triazophos are used as Pesticides.
Pesticides
Question 2
In the context of which one of the following are the terms ‘pyrolysis and plasma gasification’ mentioned?
(a) Extraction of rare earth elements
(b) Natural gas extraction technologies
(c) Hydrogen fuel-based automobiles
(d) Waste-to-energy technologies
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Waste Management
Option (d) is the correct answer: Pyrolysis and Plasma Gasification are associated with Waste-to-energy technologies.
Question 3
Why is there a great concern about the ‘microbeads’ that are released into the environment?
(a) They are considered harmful to marine ecosystem.
(b) They are considered to cause skin cancer in children.
(c) They are small enough to be absorbed by crop plants in irrigated fields.
(d) They are often found to be used as food adulterants.
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Water Pollution
Option (a) is the correct answer: Microbeads (Harmful to Marine Ecosystem)
Question 4
Which of the following statements are correct about the deposits of ‘methane hydrate’?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Methane Emission
Methane Hydrate:
Statement 1 is correct: Owing to the melting of ice, global warming might trigger the release of methane gas from these deposits hence having a significant impact in climate change.
Statement 2 is correct: Sediment and sedimentary rock units below Arctic permafrost have the temperature and pressure conditions suitable for the formation and stability of methane hydrate.
Statement 3 is correct: Methane is relatively short-lived in the atmosphere; a molecule of methane is oxidised to water and carbon dioxide within a decade or so, mainly by reaction with other trace gases.
Question 5
Consider the following:
Which of the above are released into the atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Air Pollution
Option (d) is the correct answer: All the given gases are result of Stubble Burning:
Effects of Stubble Burning:
Question 6
In the context of which of the following do some scientists suggest the use of cirrus cloud thinning technique and the injection of sulphate aerosol into the stratosphere?
(a) Creating the artificial rains in some regions
(b) Reducing the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones
(c) Reducing the adverse effects of solar wind on the Earth
(d) Reducing the global warming
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Geoengineering
Option (d) is the correct answer: Geoengineering is used for Reducing global warming.
Question 7
Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Climate Change and Agriculture Option (d) is the correct answer: All statements about Climate Change and Agriculture are correct.
Statement 1 is correct: Agricultural soils are the largest single source of nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions.
Statement 2 is correct: Cattle account for 80% of the ammonia production.
Statement 3 is correct: Poultry industry recorded an excretion of reactive nitrogen compounds of 0.415 tonnes in 2016.
Question 8
In the context of proposals to the use of hydrogen- enriched CNG (H-CNG) as fuel for buses in public transport, consider the following statements:
1. The main advantage of the use of H-CNG is the elimination of carbon monoxide emissions.
2. H-CNG as fuel reduces carbon dioxide and hydrocarbon emissions.
3. Hydrogen up to one-fifth by volume can be blended with CNG as fuel for buses.
4. H-CNG makes the fuel less expensive than CNG.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Mitigating Vehicular Emissions Option (b) is the correct answer: Advantages of use of hydrogen-enriched CNG (H-CNG) as fuel.
Hydrogen-enriched CNG (H-CNG)
Advantages
Statement 1 is incorrect: HCNG doesn’t eliminate but reduces emissions of CO up to 70%. Statement 2 is correct: It can be used in place of gasoline, diesel fuel and propane (C3H8) / LPG and its combustion produces fewer undesirable gases.
Statement 3 is correct: The blending of hydrogen with CNG provides a blended gas termed as HCNG. Statement 4 is incorrect: Current cost of Hydrogen is more than the cost of Natural Gas. So, HCNG’s cost is more than CNG.
Question 9
In India, ‘extended producer responsibility’ was introduced as an important feature in which of the following?
(a) The Bio-medical Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 1998
(b) The Recycled Plastic (Manufacturing and Usage) Rules, 1999
(c) The e-Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011
(d) The Food Safety and Standard Regulations, 2011
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: E-Waste Management
Option (c) is the correct answer: Laws to manage e-waste have been in place in India since 2011 under The e-Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011, which was amended in 2016 as E-waste (Management) Rules, 2016 recognises producers’ liability for recycling and reducing e-waste in the country.
| Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
• It is a policy approach under which producers are given a significant responsibility – financial and/or physical– for the treatment or disposal of post- consumer products. • The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has been given the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) authorisation under the new e-waste rules. |
Question 10
Consider the following statements:
1. As per law, the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority exists at both National and State levels.
2. People’s participation is mandatory in the compensatory afforestation programmes carried out under the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Act, 2016.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Environmental Policies and Initiatives
Compensatory Afforestation Fund Act (Campa Act), 2016
Statement 1 is correct: As per the Act, the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) is set up at both central and state levels for expeditious and transparent utilisation of funds released for forest land diverted for non-forest purposes.
Statement 2 is incorrect: There is no such provision in the act, also the term “participation” does not occur in the said Act.
Question 11
Consider the following statements:
The Environment Protection Act, 1986 empowers the Government of India to:
1. State the requirement of public participation in the process of environmental protection, and the procedure and manner in which it is sought
2. Lay down the standards for emission or discharge of environmental pollutants from various sources
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Major Environmental Laws
ENVIRONMENT (PROTECTION) ACT, 1986
Statement 1 is incorrect: Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 doesn’t contain any provision related to public participation.
Statement 2 is correct: Clearly, the Central Government lays down the standards for emission or discharge of environmental pollutants from various sources
Question 12
As per the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016 in India, which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Waste generators have to segregate waste into five categories.
(b) The Rules are applicable to notified urban local bodies, notified towns and all industrial townships only.
(c) The Rules provide for exact and elaborate criteria for the identification of sites for landfills and waste processing facilities.
(d) It is mandatory on the part of the waste generator that the waste generated in one district cannot be moved to another district.
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Solid Waste Management
Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016
Question 13
Which one of the following National Parks lies completely in the temperate alpine:
(a) Manas National Park
(b) Namdapha National Park
(c) Neora Valley National Park
(d) Valley of Flowers National Park
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: National Parks/Biosphere Reserve
Option (d) is the correct answer: Valley of Flowers National Park was established in 1982.
Located in Chamoli, in the state of Uttarakhand, between 3352 and 3658 metres above sea level, it is renowned for its meadows of indigenous alpine flowers and the variety of vegetation. The park is entirely inside the temperate alpine region. It is located close to Joshimath in the Garhwal area, tucked in the upper reaches of the Bhyundar Ganga river’s Pushpawati river valley. The Asiatic black bear, snow leopard, musk deer, brown bear, red fox, and blue sheep are among the rare and endangered species that call this area home. Himalayan monal pheasants and other high-altitude birds can also be seen in the park.
Question 14
Which of the following are in Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve?
(a) Neyyar, Peppara and Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuaries; and Kalakad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve
(b) Mudumalai, Sathyamangalam and Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuaries; and Silent Valley National Park
(c) Kaundinya, Gundla Brahmeswaram and Papikonda Wildlife Sanctuaries; and Mukurthi National Park
(d) Kawal and Sri Venkateswara Wildlife Sanctuaries; and Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: National Parks/Biosphere Reserve
Option (a) is the correct answer: Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve was established in 2001. It is located near the southernmost tip of the Western Ghats, straddling the boundary between the districts of Pathanamthitta, Kollam, and Thiruvananthapuram in Kerala and Tirunelveli and Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu, South India. It includes the following wildlife sanctuaries: Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuary, Peppara Wildlife Sanctuary, and Neyyar Wildlife Sanctuary. It comprises the tropical wet evergreen forests of India, the moist deciduous forests of the South Western Ghats, the montane rain forests of the South Western Ghats, and Shola. The Kanikaran tribe, one of the oldest extant ancient tribes in the world, is also found in Agasthyamalai. In March 2016, it was added to the World Network of Biosphere Reserves of UNESCO.
Question 15
Consider the following statements:
1. Asiatic lions are naturally found in India only.
2. Double-humped camels are naturally found in India only.
3. One-horned rhinoceros is naturally found in India only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Species
Statement 1 is correct: Asiatic lions were once distributed to the state of West Bengal in the east and Rewa in Madhya Pradesh, in central India. At present Gir National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary is the only abode of the Asiatic lion. IUCN Red List: Endangered
Statement 2 is incorrect: Double-humped Camel or Bacterian Camel is native to the steppes of Central Asia, restricted to the Gobi and Gashun Gobi deserts of northwest China and Mongolia, and Ladakh in India.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Only the Great One- Horned Rhino is found in India, while the other four species spread across Africa, Java and Sumatra. IUCN Red List: Vulnerable. Indian Rhino Vision 2020 (IRV 2020) was launched in 2005 by the Forest Department, Government of Assam, in partnership with WWF India, the International Rhino Foundation, and several other organisations. It aimed to raise the rhino population in Assam to 3,000. Four Protected Areas in Assam have rhinos: Pabitora Wildlife Reserve, Rajiv Gandhi Orang National Park, Kaziranga National Park, and Manas National Park.
Question 16
Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Species Diversity
Statement 1 is correct: Unlike other members of its family, such as the hawksbill sea turtle, the green sea turtle is mostly herbivorous.
Statement 2 is correct: Surgeonfish and Parrotfish are algae eaters, other herbivores include the Japanese angelfish, yellow blotch- rabbitfish, and tilapia.
Statement 3 is correct: Manatees and dugongs are the only herbivores among marine mammals.
Statement 4 is correct: Boa constrictors and green anacondas are two examples of viviparous snakes, meaning they give birth to live young with no eggs involved at any stage of development.
Question 17
Consider the following pairs:
Wildlife Naturally found in
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Species Habitat
Pair 1 is correctly matched: Blue Finned Mahseer is found in the Mula-Mutha River close to the Indian city of Pune, a part of the Krishna River basin. It is also found in other rivers of the Deccan Plateau and we know the deccan plateau has three principal rivers: the Godavari, the Krishna, and the Cauvery. It is a freshwater fish. It is also known as Deccan Mahseer or Tor Khudree. IUCN Status: Least Concern (LC).
Pair 2 is incorrectly matched: Irrawaddy Dolphin’s habitat extends from the Bay of Bengal to New Guinea and the Philippines. Also found in three rivers namely The Irrawaddy (Myanmar), the Mahakam (Indonesian Borneo) and the Mekong. The highest single lagoon population of dolphins is considered to be found in Chilika Lake. IUCN: Endangered.
Pair 3 is correctly matched: Rusty Spotted Cat was observed in eastern Gujarat’s Gir National Park, in Maharashtra’s Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve and along India’s Eastern Ghats.
2018
Question 1
Which of the following leaf modifications occur(s) in the desert areas to inhibit water loss?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: (d)
Sub-Theme: World Biome/Adaptation
Option (d) is the correct answer: Hard and waxy leaves, Tiny leaves and Thorns instead of leaves are the modifications that occur in the desert areas to inhibit water loss.
Desert Biome:
Question 2
Which of the following statements best describes “carbon fertilization”?
(a) Increased plant growth due to increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
(b) Increased temperature of Earth due to increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
(c) Increased acidity of oceans as a result of increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
(d) Adaptation of all living beings on Earth to the climate change brought about by the increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
ExplanationAns: (a)
Sub-Theme: Agriculture and Environment
Carbon fertilisation
Impact on agriculture:
Question 3
With reference to agricultural soils, consider the following statements:
1. A high content of organic matter in soil drastically reduces its water holding capacity.
2. Soil does not play any role in the sulphur cycle.
3. Irrigation over a period of time can contribute to the salinization of some agricultural lands.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Agriculture and Environment
Statement 1 is incorrect: Soil water holding capacity is the amount of water that a given soil can hold for crop use. Soil texture and organic matter are the key components that determine soil water holding capacity. Organic matter influences the physical conditions of a soil in several ways.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Sulphur is one of three nutrients that are cycled between the soil, plant matter and the atmosphere. The sulphur cycle describes the movement of sulphur through the atmosphere, mineral and organic forms, and through living things.
Statement 3 is correct: Salinization is a major problem associated with irrigation, because deposits of salts build up in the soil and can reach levels that are harmful to crops.
|
NOTE: Again, same story!! Carefully observe the extreme keyword ‘drastically’ and ‘any’ in statements 1 and 2 respectively. Not all but most of the time these extreme statements happen to be wrong. |
Question 4
With reference to the circumstances in Indian agriculture, the concept of “Conservation Agriculture” assumes significance. Which of the following fall under the Conservation Agriculture?
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 3 and 4
(b) 2, 3, 4 and 5
(c) 2, 4 and 5
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 5
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Agriculture and Environment
Conservation Agriculture (CA):
According to FAO’s website there are three principles of Conservation of Agriculture:
Question 5
Which of the following is/are the possible consequence/s of heavy sand mining in river beds?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Sand Mining (Environmental Issues)
Pollution of groundwater and Lowering of the water-table are consequences of heavy sand mining in river beds.
Statement 1 is incorrect: It may also lead to saline-water intrusion from the nearby sea.
Statement 2 is correct: The amount of suspended particles in the water at the excavation site and downstream increases due to increased riverbed and bank erosion. Aquatic ecosystems and water users may be negatively impacted by suspended particles.
Statement 3 is correct: The groundwater table drops leaving the drinking water wells on the embankments of these rivers dry.
Sand mining
Impact of Sand Mining on Rivers
Question 6
How is the National Green Tribunal (NGT) different from the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)?
1. The NGT has been established by an Act whereas the CPCB has been created by an executive order of the Government.
2. The NGT provides environmental justice and helps reduce the burden of litigation in the higher courts whereas the CPCB promotes cleanliness of streams and wells, and aims to improve the quality of air in the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Environmental Laws
NATIONAL GREEN TRIBUNAL (NGT) ACT, 2010
CENTRAL POLLUTION CONTROL BOARD (CPCB):
Statement 1 is incorrect: Both the NGT and CPCB were established by an Act – NGT Act, 2010 and Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974. Respectively.
Statement 2 is correct: The objective of NGT is to provide effective & expeditious disposal (within 6 months of appeal) of the environmental cases and to help reduce the burden of litigation in the higher courts.
Question 7
With reference to the ‘Global Alliance for Climate- Smart Agriculture (GACSA)’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Sustainable Agriculture
Global Alliance for Climate-Smart Agriculture (GACSA)
Statement 1 is incorrect: the concept of Climate- Smart Agriculture (CSA) was originally developed by FAO and officially presented and at the Hague Conference on Agriculture, Food Security and Climate Change in 2010, through the paper “Climate-Smart Agriculture: Policies, Practices and Financing for Food Security, Adaptation and Mitigation”. In 2014 an alliance was set up with this issue as its focal point: the GASCA (Global Alliance for Climate-Smart Agriculture).
Statement 2 is correct: Membership in the Alliance does not create any binding obligations and each member individually determines the nature of its participation.
Statement 3 is incorrect: India is just a signatory and had no instrumental role in the creation of GACSA.
Question 8
The Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE), a UN mechanism to assist countries transition towards greener and more inclusive economies, emerged at
(a) The Earth Summit on Sustainable Development 2002, Johannesburg
(b) The United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development 2012, Rio de Janeiro
(c) The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate change 2015, Paris
(d) The World Sustainable Development Summit 2016, New Delhi
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Major Environmental Organizations and their mechanism
Option (b) is correct: Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE) is a direct response to the Rio+20 Declaration, The Future We Want i.e. The United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development 2012, Rio de Janeiro. PAGE serves as a framework to coordinate UN efforts in the green economy and to help nations meet and track the upcoming Sustainable Development Goals, particularly SDG 8: Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for everyone.
PAGE brings together the experts from five UN agencies:
NOTE: UPSC has repeatedly asked such questions directly from the website of various Environmental Organization’s ‘About Us’ pages. This highlights the importance of basic knowledge of various environmental organisations, at least the major ones.
Question 9
“Momentum for Change: Climate Neutral Now” is an initiative launched by
(a) The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
(b) The UNEP Secretariat
(c) The UNFCCC Secretariat
(d) The World Meteorological Organization
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Major Environmental Organizations
Option (c) is correct: The Climate Neutral Now programme, created by the UNFCCC secretariat in 2015, aims to encourage and support a climate-neutral world by the middle of the century, as outlined in the Paris Agreement approved the same year. In order to achieve climate neutrality, the effort calls on businesses, organisations, governments, and individuals to reduce their climate footprint using a straightforward three-step process:
Question 10
In which one of the following States is Pakhui Wildlife Sanctuary located?
(a) Arunachal Pradesh
(b) Manipur
(c) Meghalaya
(d) Nagaland
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: National Parks/Biosphere Reserve
Option (a) is the correct answer: Another name of Pakke Tiger Reserve is “Pakhui Tiger Reserve”, In the northeastern Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh’s Pakke Kessang district, there is a Project Tiger reserve. The Eastern Himalayas Biodiversity Hotspot includes it. The Pakke Wildlife Sanctuary is located in Arunachal Pradesh in the undulating, hilly Eastern Himalayan foothills. In the west, north, and east, it is bordered by the Bhareli or Kameng River, and by the Pakke River. It is renowned for its incredible encounters with four local hornbill species. For its Hornbill Nest Adoption Program, this Tiger Reserve received the 2016 India Biodiversity Award in the category of “Conservation of vulnerable species.”
Question 11
Why is a plant called Prosopis juliflora often mentioned in the news?
(a) Its extract is widely used in cosmetics.
(b) It tends to reduce the biodiversity in the area in which it grows.
(c) Its extract is used in the synthesis of pesticides.
(d) None of these
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Invasive Species
Option (b) is the correct answer: Prosopis Juliflora is a shrub or small tree in the family Fabaceae. It is native to Mexico, South America and the Caribbean. It was initially introduced in India during colonial times, since then it has become an invasive species. It’s an aggressive coloniser, a common weed of wastelands, scrublands and degraded forests.
2017
Question 1
The term ‘M-STrIPES’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of
(a) Captive breeding of Wild Fauna
(b) Maintenance of Tiger Reserves
(c) Indigenous Satellite Navigation System
(d) Security of National Highways
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Technology in wildlife protection Option (b) is the correct answer: M-STrIPES stands for Monitoring system for Tigers –Intensive Protection and Ecological Status.
M-STrIPES:
Question 2
Due to some reasons, if there is a huge fall in the population of species of butterflies, what could be its likely consequence/consequences?
Select the correct using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Biotic Interaction
Pollination:
Statement 1 is correct: This is basic knowledge that Bees, butterflies and other biotic agents play a vital role in the pollination of plants and the production of crops by transporting pollen grains from one place to another.
Statement 2 is incorrect: There is no credible source or research behind this and moreover the extreme keyword ‘drastic’ in the statement makes it more absurd and irrelevant.
Statement 3 is correct: These are some of the common predators of butterflies: wasps, ants, parasitic flies, birds, snakes, toads, rats etc. The decline in the butterfly population would therefore adversely affect the food chain
|
NOTE: if we observe statement 2 carefully, the examiner used the word “drastic increase” which is extreme and absolute. It also connotes all of sudden change in the present situation. So, elimination of statement 2 left us with option (a) and option (c). Now it is common understanding that decline in butterfly population would adversely affect the food chain, so the reduction in other dependent species such as wasps, spiders and birds. So, statement 3 is correct. |
Question 3
Which of the following statements can help in water conservation in agriculture?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Agriculture and Environment
Question 4
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a standard criterion for:
(a) Measuring oxygen levels in blood
(b) Computing oxygen levels in forest ecosystems
(c) Pollution assay in aquatic ecosystems
(d) Assessing oxygen levels in high altitude regions
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Water Pollution
Option (c) is the correct answer: Pollution assay in aquatic ecosystems is based on Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) criterion.
NOTE: This is an easy and straight question from NCERT Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 (Environmental Chemistry), though the non- science graduates may not find interest in reading class 11 and 12 science NCERTs this particular chapter is very important for the environment and ecology.
Question 5
In the context of solving pollution problems, what is/are the advantage/advantages of bioremediation technique?
1. It is a technique for cleaning up pollution by enhancing the same biodegradation process that occurs in nature.
2. Any contaminant with heavy metals such as cadmium and lead can be readily and completely treated by bioremediation using
3. Genetic engineering can be used to create microorganisms specifically designed for
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: (c)
Sub-Theme: Eco-Engineering
Benefits of Bioremediation:
Statement 1 is correct: Bioremediation uses naturally occurring organisms to break down hazardous substances into less toxic or non-toxic substances.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Not all contaminants are easily treated by bioremediation using microorganisms. For eg. Heavy metals such as cadmium and lead are not readily absorbed or captured by microorganisms.
Statement 3 is correct: The use of genetic engineering to create organisms specifically designed for bioremediation has great potential. For e.g. Alcanivorax, a bacteria with oil-eating abilities, can be used to create species that are much more capable of cleaning oil spills.
|
NOTE: UPSC asks standard conceptual questions on Eco-engineering every year. Bioremediation, biofuels, and genetic engineering are some such standard concepts. Hence, conceptual clarity of this particular topic is very important. Also, always be cautious of extreme statements and words such as ‘readily’ (quickly) and ‘completely’. |
Question 6
It is possible to produce algae-based biofuels, but what is/are the likely limitation(s) of developing countries in promoting this industry?
1. Production of algae-based biofuels is possible in seas only and not on continents.
2. Setting up and engineering the algae-based biofuels production requires high level of expertise/technology until the construction is
3. Economically viable production necessitates the setting up of large-scale facilities which may raise ecological and social concerns.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Eco-Engineering
Biofuels
Statement 1 is incorrect: Algaculture (farming algae) can be initiated on land unsuitable for agriculture or saline water or wastewater.
Statement 2 is correct: Producing algae for biofuels (excluding simple seaweed production) requires significant capital investments, which may be a significant barrier in developing countries that have a weak investment climate.
Statement 3 is correct: Using the land allotted to food crops to algal biofuel reduces the amount of food available for humans, resulting in an increased cost for both the food and the fuel produced. This is an ecological as well as economic concern.
Question 7
In the context of mitigating the impending global warming due to anthropogenic emissions of carbon dioxide, which of the following can be potential sites for carbon sequestration?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Global warming mitigation/Carbon sequestration
Option (d) is the correct answer: All are potential sites for carbon sequestration.
Carbon Sequestration:
Types of CO2 Sequestration:
Statement 1 is correct: Uneconomic coal seams can be used to store CO2 because the CO2 molecules attach to the surface of coal.
Statement 2 is correct: CO2 is sometimes injected into declining oil fields to increase oil recovery.
Statement 3 is correct: Other potential sites are gas reservoirs, saline formations and shale formations with high organic content.
|
NOTE: UPSC has asked about “potential sites”. If we see options, all the given options could be potential sites for carbon sequestration. It is always advisable to stay focused while reading questions and try to identify such keywords from the given questions. |
Question 8
In India, if a species of tortoise is declared protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, what does it imply?
(a) It enjoys the same level of protection as the tiger.
(b) It no longer exists in the wild, a few individuals are under captive protection; and not it is impossible to prevent its extinction.
(c) It is endemic to a particular region of India.
(d) Both (b) and (c) stated above are correct in this context.
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Environmental Laws
Schedule I covers endangered species that need rigorous protection. The species are granted protection from poaching, killing, trading etc. It enjoys the same level of protection as the Bengal tiger.
Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972:
Question 9
According to the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, which of the following animals cannot be hunted by any person except under some provisions provided by law?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Environmental Laws
Option (d) is the correct answer: All are Scheduled I species.
“Schedules and Species under the Act”
| Schedules | Parameters | Species | ||
|
Schedule I |
• It covers endangered species that need rigorous protection. The species are granted protection from poaching, killing, trading etc.
• A person is liable to the harshest penalties for violation of the law under this Schedule. • Species under this Schedule are prohibited to be hunted throughout India, except under threat to human life or in case of a disease that is beyond recovery. |
The Black Buck; Bengal Tiger; Clouded Leopard; Snow Leopard; Swamp Deer; Himalayan Bear; Asiatic Cheetah; Kashmiri Stag; Fishing Cat; Lion-tailed Macaque; Musk Deer; Rhinoceros; Brow Antlered Deer; Wild Buffalo; Chinkara (Indian Gazelle); Capped Langur; Golden Langur; Hoolock Gibbon; Gharials; Dugong; Great Indian Bustard; Indian Wild Ass; etc. | ||
|
Schedule II |
• Animals under this list are also accorded high protection with the prohibition on their trade.
• They cannot be hunted except under threat to human life or if they are suffering from a disease/ disorder that goes beyond recovery. |
Assamese Macaque, Pig Tailed Macaque, Stump Tailed Macaque, Bengal Hanuman langur, Himalayan Black Bear, Himalayan Newt/ Salamander, Jackal, Flying Squirrel, Giant Squirrel, Sperm Whale, Indian Cobra, King Cobra | ||
|
Schedule III & IV |
• Species that are not endangered are included under Schedule III and IV.
• This includes protected species with hunting prohibited but the penalty for any violation is less compared to the first two schedule. • These animals can be hunted. |
|||
|
Schedule III |
Chital (spotted deer), Bharal (blue
sheep), Hyena, Nilgai, Sambhar (deer), Sponges |
|||
|
Schedule IV |
Flamingo, Hares, Falcons, Kingfishers, Magpie, Horseshoes Crabs | |||
|
Schedule V |
• This schedule contains animals that are considered as vermin (small wild animals that carry disease and destroy plants and food). | Common Crows, Fruit Bats, Rats, Mice |
|
Schedule VI |
• It provides for regulation in cultivation of a specified plant and restricts its possession, sale and transportation.
• Both cultivation and trade of specified plants can only be carried out with prior permission of competent authority. |
Beddomes’ cycad (Native to India), Blue Vanda (Blue Orchid), Red Vanda (Red Orchid), Kuth (Saussurea lappa), Slipper orchids (Paphiopedilum spp.), Pitcher plant (Nepenthes khasiana) |
Question 10
With reference to ‘Global Climate Change Alliance’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. It is an initiative of the European union.
2. It provides technical and financial support to targeted developing countries to integrate climate change into their development policies and budgets.
3. It is coordinated by World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Global Climate Finance Architecture
Global Climate Change Alliance (GCCA)
Statement 1 is correct: The Global Climate Change Alliance (GCCA) is an initiative of the European Union.
Statement 2 is correct: It was launched to strengthen dialogue and cooperation on climate change between the European Union (EU) and developing countries most vulnerable to climate change, in particular, Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and Small Island Developing States (SIDS), which are hardest hit by the adverse effects of climate change.
Statement 3 is incorrect: There is no mention of WRI and WBCSD on the official page of GCCA, even though a lot of other institutions are mentioned like FAO, UNDP etc.
Question 11
Consider the following statements:
1. Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) to Reduce Short Lived Climate Pollutants is a unique initiative of G2O group of countries.
2. The CCAC focuses on methane, black carbon and hydrofluorocarbons.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Global Climate Finance Architecture
Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC):
Statement 1 is incorrect: The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the governments of Bangladesh, Canada, Ghana, Mexico, Sweden, and the United States joined forces in 2012 to launch initiatives to handle short-lived climate pollutants as an urgent and collective concern.
Statement 2 is correct: Short-Lived Climate Pollutants include black carbon, methane, tropospheric ozone, and hydro-fluorocarbons.
NOTE: UPSC usually puts such “about us” page questions not with the primary desire of getting correct answers from the aspirants, but rather to eliminate candidates. Now with a calm and composed mind we can make some intelligent guesses to reach the correct answer. Though it’s a bit risky but still if we consider ‘unique’ as an extreme word with G20 then the first statement becomes wrong. And the second statement looks like a factual one with no extreme word like ‘only’, not all but in most cases such type of question ought to be right. Please use due diligence while attempting this method.
Question 12
Consider the following statements in respect of Trade Related Analysis of Fauna and Flora in Commerce (TRAFFIC):
1. TRAFFIC is a bureau under the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
2. The mission of TRAFFIC is to ensure that trade in wild plants and animals is not a threat to the conservation of nature.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Conservation Agencies/Schemes
/Initiatives
Statement 1 is incorrect: The TRAFFIC, the Wildlife Trade Monitoring Network, is a non- governmental organisation which works to monitor the wildlife trade in the context of both biodiversity conservation and sustainable development. Headquarters: Cambridge, United Kingdom. The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the International Union for Conservation of Nature collaborate on this programme (IUCN).
Statement 2 is correct: It is working globally on the Wildlife trade monitoring network. It specialises in investigating and analysing wildlife trade trends, patterns, impacts and drivers to provide the leading knowledge base on trade in wild animals and plants.
TRAFFIC and India:
|
NOTE: Conservation agencies/schemes/ initiatives esp. WWF is the favourite topic of UPSC, one example being Earth hour asked in PYQ. Hence, try to cover WWF, TRAFFIC and related websites comprehensively to answer such questions. Reading Shankar will help you to solve this question without much trouble. |
Question 13
From the ecological point of view, which one of the following assumes importance in being a good link between the Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats?
(a) Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
(b) Nallamala Forest
(c) Nagarhole National Park
(d) Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: National Parks/Biosphere Reserve
Option (a) is the correct answer: Sathyaman- galam Tiger Reserve (STR) is situated where the Western and Eastern Ghats converge. This region is home to a sizable tiger population and is adjacent to other landscapes dedicated to protecting tigers, including BRT, Bandipur, Mudumalai, and Nagarahole. The Nilgiri-Eastern Ghats Elephant Reserve includes this area as well. Due to its position, it contains a wide variety of vegetation and animals.
NOTE: UPSC has the habit of picking up options from questions in its previous year’s papers and asking new questions after improvising them. Nallamala Forest, Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve, etc. are some examples. Hence, it underlines the importance of solving and analysing PYQs.
Question 14
If you want to see gharials in their natural habitat, which one of the following is the best place to visit?
(a) Bhitarkanika Mangroves
(b) Chambal River
(c) Pulicat Lake
(d) Deepor Beel
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Species (Fauna)
Option (a) is incorrect: Gharials inhabit deep freshwater habitats, not both freshwater and saltwater habitats as inhabited by crocodile species. It is the home of saltwater crocodiles.
Option (b) is correct: The most important surviving populations of Gharials are within four tributaries of the Ganges River – Girwa, Son, and Chambal Rivers in India and the Rapti- Narayani River in Nepal. The most significant breeding population is within the Chambal River, which spans the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh.
Option (c) is incorrect: Pulicat Lake is the second largest brackish water lake or lagoon in India after Chilika Lake. It is located on the border of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu with over 96% of it in Andhra Pradesh and 4% in Tamil Nadu situated on the Coromandel Coast in South India. The lake encompasses Pulicat Lake Bird Sanctuary. The Buckingham Canal, a navigation channel, is part of the lagoon on its western side.
Option (d) is incorrect: Deepor Beel is one of the largest freshwater lakes in Assam and the State’s only Ramsar site besides being an Important Bird Area by Birdlife International. Till date no such credible information has been found in terms of Gharial population in Deepor beel.
2016
Question 1
‘Gadgil Committee Report’ and ‘Kasturirangan Committee Report’, sometimes seen in the news, are related to
(a) constitutional reforms
(b) Ganga Action Plan
(c) linking of rivers
(d) protection of Western Ghats
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Disaster Management
Option (d) is the correct answer: ‘Gadgil Committee Report’ and ‘Kasturirangan Committee Report’, are related to protection of Western Ghats.
GADGIL COMMITTEE REPORT, 2011:
KASTURIRANGAN COMMITTEE REPORT, 2013:
Question 2
Which of the following best describe/ describes the aim of the ‘Green India Mission’ of the Government of India?
1. Incorporating environmental benefits and costs into the Union and State Budgets thereby implementing the ‘green accounting’
2. Launching the second green revolution to enhance agricultural output so as to ensure food security to one and all in the future
3. Restoring and enhancing forest cover and responding to climate change by a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Conservation/Environmental pollution
Green India Mission:
Objectives of the Mission:
Statement 1 and 2 are incorrect: Both the statements are irrelevant to Green India Mission.
Statement 3 is correct: The mission intends to increase forest/tree cover; improve/enhance ecosystem services and increase the forest-based livelihood income of about 3 million households.
Question 3
In the cities of our country, which among the following atmospheric gases are normally considered in calculating the value of the Air Quality Index?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Air Pollution
Option (b) is the correct answer: CO2 , CO and SO2 are normally considered in calculating the value of the Air Quality Index.
Question 4
The term ‘Intended Nationally Determined Contributions’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of
(a) Pledges made by the European countries to rehabilitate refugees from the war-affected Middle East
(b) Plan of action outlined by the countries of the world to combat climate change
(c) Capital contributed by the member countries in the establishment of Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
(d) Plan of action outlined by the countries of the world regarding Sustainable Development Goals
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Climate Change/Global Warming
Intended Nationally Determined Contributions: Plan of action outlined by the countries of the world to Combat Climate Change
Question 5
What is ‘Greenhouse Gas Protocol’?
(a) It is an international accounting tool for government and business leaders to understand, quantify and manage greenhouse gas emissions.
(b) It is an initiative of the United Nations to offer financial incentives to developing countries to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to adopt eco-friendly technologies
(c) It is an inter-governmental agreement ratified by all the member countries of the United Nations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to specified levels by the year 2022
(d) It is one of the multilateral REDD+ initiatives hosted by the World Bank
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Global Warming
Option (a) is the correct answer: ‘Greenhouse Gas Protocol’ is an International Accounting Tool for Government and Business Leaders
GHG Protocol:
Question 6
With reference to the Agreement at the UNFCCC Meeting in Paris in 2015, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. The Agreement was signed by all the member countries of the UN and it will go into effect in 2017.
2. The Agreement aims to limit greenhouse gas emissions so that the rise in average global temperature by the end of this century does not exceed 2 degrees C or even 1.5 degrees C above pre-industrial levels.
3. Developed countries acknowledged their historical responsibility in global warming and committed to donate $1000 billion a year from 2020 to help developing countries to cope with climate change.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Summits and Conventions
Statement 1 is incorrect: It was only “agreed” by 195 nations in Paris at the conference. The agreement will enter into force only after 55 countries that account for at least 55% of global emissions have deposited their instruments of ratification.
Statement 2 is correct: Paris Summit COP21 aims to limit global warming to well below 2, preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial levels. It requires all parties to put forward their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) which are voluntary in nature.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Developed countries will work to define a clear roadmap on ratcheting up climate finance to USD 100 billion (not USD 1000 billion) by 2020.
Paris Summit COP21:
|
NOTE: Following basic information about COP21 from any newspaper/monthly magazine was enough to solve this rather difficult question. Observe statement 3 carefully, the examiner has just made his efforts to mention “USD100Bn as USD1000Bn” to make the statement incorrect and confuse aspirants. If we eliminate option 3, we get the correct answer i.e. only 2.
The key takeaway from the above question is to read numbers very carefully and cautiously. |
Question 7
Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a collection of 17 global goals designed to be a “blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all”
The SDGs are a part of UN Resolution 70/1, the 2030 Agenda, which was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015.
They are known as “Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development” in official documents.
Statement 1 is incorrect: In 1972, the Club of Rome’s first major Report, ‘The Limits to Growth’ was published.
Statement 2 is correct: In 2015, the United Nations General Assembly approved 17 goals with 169 associated targets. They became effective from 1/1/2016 and were to be achieved by 2030.
Question 8
What is/are the importance/ importances of the ‘United Convention to Combat Desertification’?
1. It aims to promote effective action through innovative national programmes and supportive international partnerships
2. It has a special/particular focus on South Asia and North Africa regions, and its Secretariat facilitates the allocation of major portions of financial resources to these regions.
3. It is committed to a bottom-up approach, encouraging the participation of local people in combating the desertification.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Major Conventions
UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION TO COMBAT
DESERTIFICATION (UNCCD):
Statement 1 is correct: Its 197 Parties aim, through partnerships, to implement the Convention and achieve the Sustainable Development Goals. The end goal is to protect the land from overuse and drought, so it can continue to provide food, water and energy.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Convention addresses specifically the arid, semi-arid and dry sub-humid areas, known as the drylands, where some of the most vulnerable ecosystems and peoples can be found.
Statement 3 is correct: The UNCCD is particularly committed to a bottom-up approach, encouraging the participation of local people in combating desertification and land degradation.
Question 9
Consider the following pairs:
Terms sometimes seen in the news : Their origin
1. Annex-I Countries : Cartagena Protocol
2. Certified Emissions Reductions : Nagoya Protocol
3. Clean Development Mechanisms : Kyoto Protocol
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Major Conventions
Classification of Parties and their commitments under Kyoto Protocol:
|
Annex I |
Developed countries [US, UK, Russia etc.] + Economies in transition (EIT) [Ukraine, Turkey, some eastern European countries etc.] |
|
Annex II |
Developed countries (Annex II is a subset of Annex I).
Required to provide financial and technical support to the EITs and developing countries to assist them in reducing their greenhouse gas emissions. |
|
Annex B |
Annex I Parties with first or second- round Kyoto greenhouse gas emissions targets.
The first-round targets apply over the years 2008–2012 and the second- round Kyoto targets, apply from 2013 to 2020. Compulsory binding targets to reduce GHG emissions. |
|
Non-Annex I |
Parties to the UNFCCC are not listed in Annex I of the Convention (mostly low-income developing countries).
No binding targets to reduce GHG emissions. |
|
LDCs |
Least-developed countries
No binding targets to reduce GHG emissions. |
Options 1 and 2 are incorrect: Terms in these options are associated with the Kyoto Protocol.
Option 3 is correct: Clean Development Mechanism is associated with the Kyoto Protocol.
Question 10
With reference to an initiative called ‘The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB)’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. It is an initiative hosted by UNEP, IMF and World Economic Forum.
2. It is a global initiative that focuses on drawing attention to the economic benefits of biodiversity.
3. It presents an approach that can help decision- makers recognize, demonstrate and capture the value of ecosystems and biodiversity.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Major Environmental Conventions/ Environmental Policies and Initiatives
The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB)
Statement 1 is incorrect: It is an international initiative, launched by Germany and the European Commission.
Statement 2 is correct: It is an international initiative to draw attention to the global economic benefits of biodiversity.
Statement 3 is correct: Its objective is to highlight the growing cost of biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation and to draw together expertise from the fields of science, economics and policy to enable practical actions.
Question 11
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Proper design and effective implementation of UN- REDD+ Programme can significantly contribute to:
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Environmental Conventions/ Environmental Policies and Initiatives
The UN-REDD Programme has identified the following three topics for supporting national REDD+ governance structures:
UN REDD+
Question 12
With reference to ‘Agenda 21’, sometimes seen in the news, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Sustainable Development Goals
Rio Declaration on Environment and Development:
Agenda 21:
Question 13
The FAO accords the status of ‘Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System (GIAHS)’ to traditional agricultural systems.
What is the overall goal of this initiative?
1. To provide modern technology, training in modern farming methods and financial support to local communities of identified GIAHS so as to greatly enhance their agricultural productivity.
2. To identify and safeguard eco-friendly traditional farm practices and their associated landscapes, agricultural biodiversity and knowledge systems of the local communities.
3. To provide Geographical Indication status to all the varieties of agricultural produce in such identifies GIAHS.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Major Environmental Organizations
Statement 1 is incorrect: Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) was started by the FAO to safeguard and support the world’s agricultural heritage systems.
Statement 2 is correct: The initiative intends to safeguard the social, cultural, economic and environmental goods and services of these heritage systems.
Statement 3 is incorrect: There is no such provision. GI is accorded to products from a certain origin (e.g. Hyderabadi Biryani) and not to all traditional agricultural systems.
|
NOTE: The central theme of the question is “Heritage System”. Statement 1 talks about “modern technology, training in modern farming” which is in contradiction to the given question, so this can be marked as incorrect. Statement 3 is also incorrect as FAO has no role in accordance with GI status. In India, GI status is governed by the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 (GI Act) in India. Geographical Indications protection is granted through the TRIPS Agreement. |
Question 14
What is/are unique about ‘Kharai camel’, a breed found in India?
Select the correct answer using the code given
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Species (Fauna)
Statement 1 is correct: Kharai camels have a special ability to swim in seawater and feed on saline plants and mangroves, which is how they get their name, Kharai. Recognized as a separate breed a few years ago by the National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources (NBAGR), the Kharai camel is probably the only domesticated breed of camel that lives in dual ecosystems. There are two camel breeds in Kutch, a coastal region of Gujarat that is also a sizable desert territory. IUCN Red List: Endangered
Statement 2 is correct: Kharai camels are known to feed on mangroves on the island offshore. And to eat this salty marine food, they sometimes swim for hours.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Given the breed’s ability to survive both on land and sea, this particular statement is highly unlikely.
NOTE: Observe the extreme keyword ‘cannot’ in statement 3, it makes the statement a bit absurd from the other two statements. Hence, by eliminating this single statement you can easily reach the correct answer.
Question 15
With reference to ‘Red Sanders’, sometimes seen in the news, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Species (Flora)
Statement 1 is correct: Red Sanders is an Indian endemic tree species, with a restricted geographical range in the Eastern Ghats. It is endemic to a distinct tract of forests in Andhra Pradesh. Red Sanders usually grow in the rocky, degraded and fallow lands with Red Soil and hot and dry climate. IUCN Red List: Endangered.
Statement 2 is incorrect: It occurs in the forest formation which is classified as “Southern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests”.
Threats: Illicit felling for smuggling, forest fires, cattle grazing and other anthropogenic threats. The tree is known for their rich hue and therapeutic properties, are high in demand across Asia, particularly in China and Japan, for use in cosmetics and medicinal products as well as for making furniture, woodcraft and musical instruments.
Question 16
In which of the following regions of India are you most likely to come across the ‘Great Indian Hornbill’ in its natural habitat?
(a) Sand deserts of northwest India
(b) Higher Himalayas of Jammu and Kashmir
(c) Salt marshes of western Gujarat
(d) Western Ghats
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Species – Fauna
Great Indian Hornbill (Western Ghats, Nilgiris)
Option (d) is the correct answer: The great hornbill (Buceros bicornis) also known as the great Indian hornbill or great pied hornbill, is one of the larger members of the hornbill family. A large majority of their population is found in India with a significant proportion in the Western Ghats and the Nilgiris. They also occur in Myanmar, islands in the Mergui archipelago, southern China, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, peninsular Malaysia and in Sumatra, Indonesia.
2015
Question 1
Which one of the following is the best description of the term ‘ecosystem’?
(a) A community of organisms interacting with one another
(b) That part of the Earth which is inhabited by living organisms
(c) A community of organisms together with the environment in which they live
(d) The flora and fauna of a geographical area
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Ecosystem
Option (c) is the correct answer: Ecosystem can be defined as a community of organisms together with the environment in which they live.
Ecosystem:
Question 2
What can be the impact of excessive/inappropriate use of nitrogenous fertilizers in agriculture?
1. Proliferation of nitrogen fixing microorganisms in soil can occur.
2. Increase in the acidity of soil can take place.
3. Leaching of nitrate to the groundwater can occur.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Soil Pollution
Impact of Excessive/inappropriate use of nitrogenous fertilizers:
Statement 1 is incorrect: More nitrogen in the soil leads to less need for nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Statement 2 and 3 are correct: Excessive/ inappropriate use of nitrogenous fertilizers increases the acidity of soil and the leaching of nitrate into the groundwater.
NOTE: Excessive or inappropriate use of anything will have a negative impact on the environment, there should be a balance in everything. Now, look at the extreme keyword in the first statement. ‘Proliferation’ which means ‘rapid increase’, think logically, is it possible that the use of excessive nitrogenous fertilizer will proliferate the nitrogen-fixing microorganisms in soil? Having said that, it is also advisable to read this topic thoroughly as it is very important and high yielding both in terms of prelims and mains.
Question 3
Which one of the following is associated with the issue of control and phasing out of the use of ozone- depleting substances?
(a) Bretton Woods Conference
(b) Montreal Protocol
(c) Kyoto Protocol
(d) Nagoya Protocol
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer
Montreal Protocol
Option (a) is incorrect: Bretton Woods Conference established the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Option (b) is correct: Montreal Protocol is a protocol to the Vienna Convention and it deals with the substances that deplete the Ozone Layer (ozone-depleting substance-ODS).
Option (c) is incorrect: Kyoto Protocol deals with the reduction of Greenhouse gas.
Option (d) is incorrect: Nagoya Protocol is a supplementary agreement to the 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) on “Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization”.
Question 4
What is the Rio+20 Conference, often mentioned in the news?
(a) It is the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development
(b) It is a Ministerial Meeting of the World Trade Organization
(c) It is a Conference of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
(d) It is a Conference of the Member Countries of the Convention on Biological Diversity.
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Major Environment Conventions, Conference, etc.
Question 5
The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee is constituted under the
(a) Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006
(b) Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999
(c) Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
(d) Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Genetically Modified Crops
Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee
NOTE: There are recurrent and repeated questions on “Genetic Engineering” either in science-tech or environment. It is advisable to prepare this topic thoroughly and holistically.
Question 6
With reference to an organisation known as ‘BirdLife International’, which of the following statements is/ are correct?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Major Conservation Organizations
BirdLife International
Statement 1 is correct: BirdLife International is a global partnership of conservation organisations that strives to conserve birds, their habitats, and global biodiversity, working with people towards sustainability in the use of natural resources.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The idea of Biodiversity Hotspots was first put forward by Norman Myers in 1988.
Statement 3 is correct: It identifies the sites known/referred to as ‘Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas’.
Question 7
With reference to the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resource (IUCN) and the Convention of International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. IUCN is an organ of the United Nations and CITES is an international agreement between
2. IUCN runs thousands of field projects around the world to better manage natural environments.
3. CITES is legally binding on the States that have joined it, but this Conventional does not take the place of national laws.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Major Environmental Conventions
Statement 1 is incorrect: IUCN is an NGO, founded in October 1948 as the International Union for the Protection of Nature (or IUPN) following an international conference in Fontainebleau, France. Later the name was changed to International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN). CITES on the other hand is an intergovernmental treaty, concluded under the aegis of the United Nations Environment Programme.
Statement 2 is correct: IUCN supports scientific research, manages field projects globally and brings governments, non-government organisations, United Nations agencies, companies and local communities together to develop and implement policy.
Statement 3 is correct: CITES is legally binding but does not take the place of national laws.
|
NOTE: Only knowing the names of UN specialised agencies is enough for solving this question. With this knowledge, we can eliminate option 1 and get the correct answer. Most of the time the examiner connects two different statements in which one is correct and the other is incorrect. It is advisable to ascertain the correctness of both connected statements and don’t rush after only reading a partial statement. |
Question 8
Which of the following statements regarding ‘Green Climate Fund’ is/are correct?
1. It is intended to assist developing countries in adaptation and mitigation practices to counter climate change.
2. It is founded under the aegis of UNEP, OECD, Asian Development Bank and World Bank.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Global Climate Finance Architecture
Green Climate Fund (GCF)
Statement 1 is correct: Green Climate Fund aims to make an ambitious contribution to attaining the mitigation and adaptation goals of the international community to counter climate change.
Statement 2 is incorrect: GCF was discussed in Cancun Summit 2010 of UNFCCC and finally adopted in Durban Summit 2011.
Question 9
Which of the following National Parks is unique in being a swamp with floating vegetation that supports a rich biodiversity?
(a) Bhitarkanika National Park
(b) Keibul Lamjao National Park
(c) Keoladeo Ghana National Park
(d) Sultanpur National Park
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: National Parks/ Tiger Reserve/ Biosphere Reserve/Wildlife Sanctuary/Wetland
Option (b) is the correct answer: Keibul Lamjao National Park in the Bishnupur district of the Indian state of Manipur is the only floating park in existence and is a crucial component of Loktak Lake, which lies in North East India. Locally known as “Phumdi,” the national park is distinguished by floating decaying plant matter. It was established in 1966 as a wildlife sanctuary to protect the Eld’s deer’s natural habitat, which is in risk of extinction (Cervus eldi eldi). It was declared a national park in 1977. The park is unique in that it is “too shallow to be a lake, too deep to be marsh.”
Flora: The park offers a diverse array of aquatic, wetland, and terrestrial ecosystems and is mostly made up of damp, semi-evergreen forests.
Fauna found in the park include the brow- antlered deer (Cervus eldi eldi), which is its emblematic species, as well as the Asian Golden Cat, Marbled Cat, Malayan Bear, Hog Deer, Himalayan Black Bear, and others.
Question 10
Which one of the following National Parks has a climate that varies from tropical to subtropical, temperate and arctic?
(a) Khangchendzonga National Park
(b) Nanda Devi National Park
(c) Neora Valley National Park
(d) Namdapha National Park
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: National Parks/ Tiger Reserve/ Biosphere Reserve/Wildlife Sanctuary/Wetland
Option (d) is the correct answer: The Namdapha National Park is located 27° N of the equator. It is located at the international border between India and Myanmar (Burma) in Changlang District, Arunachal Pradesh in northeast India. Geographically, Namdapha National Park is in the sub-tropical zone because it is 27° N of the equator, but because its altitude ranges from 200 m to 4571 m, its climate changes and it also experiences a lot of rain. There are different types of climates, such as tropical, subtropical, temperate, and arctic. For instance, the Namdapha National Park’s mountainous region has a mountain climate, whereas the low-lying plains and valleys experience a tropical climate. It was established as the 15th Tiger Reserve of India by the Government in 1983.
Question 11
With reference to ‘dugong’, a mammal found in India, which of the following statements is/are correct?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 only
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Marine Species
Statement 1 is correct: Sea Cow or Dugong is one of the four surviving species in the Order Sirenia and it is the only existing species of herbivorous mammal that lives exclusively in the sea including in India.
Statement 2 is incorrect: They are found in over 30 countries and in India are seen in the Gulf of Mannar, Gulf of Kutch, Palk Bay, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Statement 3 is correct: It gives legal protection under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
Question 12
Which one of the following is the national aquatic animal of India?
(a) Saltwater crocodile
(b) Olive ridley turtle
(c) Gangetic dolphin
(d) Gharial
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Marine Species
Option (c) is the correct answer: Gangetic River Dolphin, also called ‘susu’ is the National Aquatic Animal of India.
Gangetic Dolphin
Habitat:
Features:
2014
Question 1
Which of the following are some important pollutants released by steel industry in India?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1, 3 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Industrial Pollution
Option (d) is the correct answer: All the above are major pollutants released by the steel industry in India.
The environmental impact of steel production:
Emissions to Air:
Emissions to water:
Waste:
Question 2
There is some concern regarding the nanoparticles of some chemical elements that are used by the industry in the manufacture of various Why?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Industrial Pollution
Use of Nanoparticles:
Impact of Nanoparticles:
Statement 1 is correct: A matter particle with a dimension ranging from 1 to one 100 nanometers (nm) is referred to as a nanoparticle. They can accumulate in the environment, contaminate water and soil.
Statement 2 is correct: They enter into the food chains.
Statement 3 is correct: They also trigger the production of free radicals.
Question 3
Brominated flame retardants are used in many household products like mattresses and upholstery. Why is there some concern about their use?
1. They are highly resistant to degradation in the environment.
2. They are able to accumulate in humans and animals.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: (c)
Sub-Theme: General Environment
Brominated Flame Retardants (BFRs):
Concerns:
Statement 1 is correct: They don’t degrade easily in fact they are highly resistant to degradation in the environment.
Statement 2 is correct: Some brominated flame retardants were identified as persistent, bioaccumulative, and toxic to both humans and the environment and were suspected of causing neurobehavioral effects and endocrine disruption.
Question 4
The scientific view is that the increase in global temperature should not exceed 2°C above the pre- industrial level. If the global temperature increases beyond 3°C above the pre-industrial level, what can be its possible impact/impacts on the world?
1. Terrestrial biosphere tends toward a net carbon source.
2. Widespread coral mortality will occur.
3. All the global wetlands will permanently disappear.
4. Cultivation of cereals will not be possible anywhere in the world.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Effects of Global Warming
Statement 1 is correct: If the global temperature increases beyond 3°C above the pre-industrial level, the terrestrial biosphere tends toward a net carbon source. Taiga and temperate forests act as an important carbon sink; these forests would turn into a carbon source.
Statement 2 is correct: As temperatures rise, mass coral bleaching events occur. If the temperature keeps on rising, widespread coral mortality will occur.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The temperate regions can still survive if the temperature increases. The temperate zones are where the widest seasonal changes occur. The vegetation can survive there.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The weather should be warm and moist during the early stage of the growth of cereals. Therefore, the cultivation of cereals would still be possible if the temperature rises.
Question 5
What are the significances of a practical approach to sugarcane production known as ‘Sustainable Sugarcane Initiative’?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable Sugarcane Initiative:
The Sustainable Sugar Initiative (SSI) was launched jointly by International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) and by ICRISAT and World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF).
Aims: Cultivating sugarcane mainly by changing the way the inputs and methods are used, such as less use of seeds ,less use of water, optimum utilization of fertilizers and land, aims at reducing the input cost.
Statement 1 is correct: It majorly aims at reduction of the input cost compared to the conventional method of cultivation. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
Statements 2 and 4 are correct: SSI provides ample scope for intercropping and the drip irrigation method.
Statement 3 is incorrect: There is an application of both Inorganic and organic fertilizers such as Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium (NPK) fertilizers.
|
NOTE: here, the topic in question is the “Sustainable” Sugarcane Initiative (SSI). Statement 2 talks about Drip-irrigation which is sustainable irrigation practice, that complies and is in conformity with SSI. Statement 1 talks about low input cost which is also in confirmation of sustainable practices. However, statement 3 endorses that “there is no application of chemical/ inorganic fertilizers at all” which sounds extreme. So statement 3 can be eliminated to get the correct answer. |
Question 6
Consider the following international agreements:
Which of the above has/have a bearing on biodiversity?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: International efforts to protect biodiversity/Laws and Legislations
Objectives:
United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD):
World Heritage Convention:
NOTE: Question on the same theme earlier has been asked in 2011 i.e provisions bearing on biodiversity. It is advisable to go through provisions of the Indian constitution bearing upon the environment and its conservation.
Question 7
Consider the following statements regarding ‘Earth Hour’
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: UNEP/ Major Programmes of the UNEP
Earth Hour:
Significance: The urgent need to address global climate change is highlighted in this hour. Additionally, it raises public awareness of environmental issues.
Statement 1 is incorrect: Earth Hour is a global movement for environmental conservation, started by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) in 2007.
Statement 2 is correct: It is an annual event that takes place on the last Saturday of March. Millions of people in over 180 countries and territories participate in it by turning off their lights.
Statement 3 is correct: It showcases the need to take action on the pressing issue of global climate change. Further, it promotes awareness about environmental issues on a public platform.
Question 8
If a wetland of international importance is brought under the ‘Montreux Record’, what does it imply?
(a) Changes in ecological character have occurred, are occurring or are likely to occur in the wetland as a result of human interference.
(b) The country in which the wetland is located should enact a law to prohibit any human activity within five kilometres from the edge of the wetland.
(c) The survival of the wetland depends on the cultural practices and traditions of certain communities living in its vicinity and therefore the cultural diversity therein should not be destroyed.
(d) It is given the status of ‘World Heritage Site’
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Wetland Conservation
Option (a) is the correct answer: ‘Montreux Record’ is a register of wetlands on the List of Wetlands of International Importance where ecological character changes have occurred, are occurring, or are anticipated to occur due to technological advancements, pollution, or other human influence.
Wetlands:
Ramsar Convention:
Ramsar Convention is not a regulatory regime.
|
NOTE: This is a straightforward question from Montreux Record under Ramsar Convention. Also, these are high yielding topics and to attempt this type of question aspirants are requested to go through all the National Parks/Wildlife Sanctuary/ Biosphere Reserve/Wetlands including their locations (map), and geographical features, important flora and fauna if any. |
Question 9
With reference to a conservation organisation called ‘Wetlands International’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. It is an intergovernmental organisation formed by the countries which are signatories to the Ramsar convention.
2. It works at the field level to develop and mobilise knowledge, and use the practical experience to advocate for better policies.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Wetland Conservations
Wetlands International:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Wetlands International is an independent, not-for-profit, global organization, supported by government and NGO members from around the world.
Statement 2 is correct: Wetlands International does work at the field level to develop and mobilise knowledge and use the practical experience to advocate for better policies.
|
NOTE: These are high yielding topics and to attempt this type of question aspirants are requested to go through all the National Parks/Wildlife Sanctuary/Biosphere Reserve/ Wetlands including their locations (map), geographical features, important flora and fauna if any. |
Question 10
Consider the following pairs:
Wetlands Confluence of Rivers
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Wetland Conservation/Map Based
Harike Wetland
Keoladeo National Park
Kolleru Lake
Pair 1 is correct: The Harike Wetland is located downstream of the confluence of the Beas and Sutlej rivers just south of Harike village.
Pair 2 is incorrect: The Keoladeo National Park is situated at the confluence of the Gambhira and the Banganga rivers.
Pair 3 is incorrect: Kolleru Lake is located between Krishna and Godavari deltas.
Question 11
With reference to ‘Global Environment Facility’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
(a) It serves as a financial mechanism for ‘Convention on Biological Diversity’ and ‘United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change’.
(b) It undertakes scientific research on environmental issues at global level.
(c) It is an agency under OECD to facilitate the transfer of technology and funds to underdeveloped countries with specific aims to protect their environment.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Climate Change Organization/ Global Environmental Facility
Option (a) is the correct answer: The GEF serves as financial mechanism for the following Conventions:
GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT FACILITY (GEF)
Question 12
Consider the following statements:
1. Animal Welfare Board of India was established under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
2. The National Tiger Conservation Authority is a statutory body.
3. The National Ganga River Basin Authority is chaired by the Prime Minister.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Environmental Organizations and Institutions in India.
Statement 1 is incorrect: Animal Welfare Board of India was established in 1962 under Section 4 of the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960.
Statement 2 is correct: National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change.
Statement 3 is correct: The National Ganga Council (Earlier National Ganga River Basin Authority) is chaired by the Prime Minister. The National Ganga Council was established in accordance with the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. The National Ganga River Basin Authority was replaced (NGRBA). It is in charge of overseeing the restoration of the River Ganga Basin, including Ganga and its tributaries, and the prevention of pollution.
Animal Welfare Board of India
National Tiger Conservation Authority
Question 13
With reference to Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS), consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Major Conservation Organizations
Statement 1 is incorrect: BNHS is one of the largest non-governmental organisations in India engaged in conservation and biodiversity research.
Statement 2 is correct: It supports many research efforts through grants and publishes the Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society. It has been classified as a “Scientific and Industrial Research Organization” by the Department of Science and Technology.
Statement 3 is correct: It organises and conducts nature trails and camps for the general public.
BNHS
Question 14
With reference to ‘Eco-Sensitive Zones’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Eco-Sensitive Zones
Statement 1 is incorrect: ESZs are notified by MoEFCC, Government of India under Environment Protection Act 1986.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The basic aim is to regulate certain activities around National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries so as to minimise the negative impacts of such activities on the fragile ecosystem encompassing the protected areas.
Activities in ESZs:
|
Prohibited activities |
Commercial mining, sawmills, industries that pollute the environment (air, water, soil, noise, etc.), the construction of large hydroelectric projects (HEP), the use of wood for commercial purposes, tourism-related activities like hot-air balloon flights over national parks, the discharge of effluents or any solid waste, or the manufacture of hazardous materials. |
|
Regulated activities |
Tree cutting, the construction of hotels and resorts, the exploitation of natural water for commercial purposes, the installation of electricity lines, a radical transformation of agriculture, such as the use of heavy machinery, pesticides, etc., and road widening. |
|
Permitted activities |
The ongoing horticultural or agricultural techniques, the use of renewable energy sources, organic farming, rainwater harvesting, and the implementation of green technology across all sectors. |
Question 15
The most important strategy for the conservation of biodiversity together with traditional human life is the establishment of:
(a) Biosphere reserves
(b) Botanical gardens
(c) National parks
(d) Wildlife sanctuaries
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: National Parks/Tiger Reserve/ Biosphere Reserve/Wildlife Sanctuary/Wetland
Option (a) is the correct answer: Biosphere reserves are legally protected regions where people and the environment can coexist while honouring each other’s needs. These areas might be terrestrial, coastal, or a combination of both. They are recognised under UNESCO’s MAB programme and nominated and established by the relevant nations. Hence, the most important strategy for the conservation of biodiversity together with traditional human life is the establishment of Biosphere Reserve.
Zonation Of Biosphere Reserve:
| Core Areas |
The central portions of biosphere reserves are strictly protected zones, which are frequently publicly owned lands that are subject to legal protection, such as a previously established national park, wilderness area, or wildlife refuge. The core region, however, could be privately held or be a part of non- governmental groups. |
| Buffer Zones |
Facilities for education, training, tourism, and recreation may be located nearby the core area(s). In many biosphere reserves, the buffer zone is viewed as a region where scientific study is conducted and human use is less intense than what might be found in the transition zone. |
| Transition Areas |
The most remote area where a society supports socioculturally and environmentally sound economic and human activity. |
| NOTE: This is again a high yielding topic w.r.t. Environment and Ecology. To solve this type of question, aspirants need to have a clear concept regarding various conservation efforts. Hence, it is advisable that aspirants should read and understand this topic thoroughly. |
Question 16
With reference to Neem tree, consider the following statements:
1. Neem oil can be used as a pesticide to control the proliferation of some species of insects and mites.
2. Neem seeds are used in the manufacture of biofuels and hospital detergents.
3. Neem oil has applications in the pharmaceutical industry.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Tree Species
Statement 1 is correct: Neem oil and neem barks are used as an insect repellent.
Statement 2 is incorrect: No such relevant and strong reference has been found.
Statement 3 is correct: Neem oil has multiple applications in the pharmaceutical industry.
Question 17. Other than poaching, what are the possible reasons for the decline in the population of Ganges River Dolphins?
1. Construction of dams and barrages on rivers
2. An increase in the population of crocodiles in rivers
3. Getting trapped in fishing nets accidentally
4. Use of synthetic fertilisers and other agricultural chemicals in crop-fields in the vicinity of rivers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Marine Species
Statement 1 is correct: Gangetic dolphins live in the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu river systems of Nepal, India, and Bangladesh. The Ganges river dolphin can only live in freshwater. They are essentially blind. They are also called ‘susu’. Construction of dams and other irrigation-related projects make them susceptible to inbreeding and more vulnerable to other threats because they cannot move to new areas.
Statement 2 is incorrect: An increase in the population of crocodiles in rivers is not a threat to Gangetic dolphins.
Statement 3 is correct: Dolphins die as a result of accidentally being caught in fishing nets, also known as bycatch.
Statement 4 is correct: Industrial, agricultural, and human pollution is another serious cause of habitat degradation.
Question 18
If you walk through countryside, you are likely to see some birds stalking alongside the cattle to seize the insects disturbed by their movement through grasses.
Which one of the following is/are such bird/birds?
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Species(Avifauna)
Common Myna
Statement 1 is incorrect: Painted storks forage in flocks in shallow waters along rivers or lakes. IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
Statement 2 is correct: Common Myna is an opportunistic feeder on insects, disturbed by grazing cattle.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The habitat of Black- necked Crane is in the high altitude wetlands of the Tibetan plateau, Sichuan (China), and eastern Ladakh (India). Therefore, it is highly unlikely it can be seen in the countryside. IUCN Red List: Near Threatened.
2013
Question 1
With reference to the food chains in ecosystems, which of the following kinds of organism is/are known as decomposer organism/organisms?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Biotic Components
Option (b) is the correct answer: Fungi and Bacteria, are known as decomposers.
Decomposer:
Question 2
In the grasslands, trees do not replace the grasses as a part of an ecological succession because of:
(a) Insects and fungi
(b) Limited sunlight and paucity of nutrients
(c) Water limits and fire
(d) None of the above
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Ecological Succession
Option (c) is the correct answer: Water limits and Fire restrict trees to replace the grasses as a part of an ecological succession.
Grassland Ecosystem:
Question 3
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of ecosystems in the order of decreasing productivity?
(a) Oceans, lakes, grasslands, mangroves
(b) Mangroves, oceans, grasslands, lakes
(c) Mangroves, grasslands, lakes, oceans
(d) Oceans, mangroves, lakes, grasslands
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Energy Flow
Option (c) is correct:
Productivity:
Question 4
With reference to food chains in ecosystems, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Food Chain
Food Chain:
Statement 2 is incorrect: Food chains are found within the populations of a species but not among all species (Man won’t eat man).
Statement 3 is incorrect: A food web illustrates the numbers of each organism which are eaten by others, not the food chain.
Question 5
Which one of the following terms describes not only the physical space occupied by an organism but also its functional role in the community of organisms?
(a) Ecotone
(b) Ecological niche
(c) Habitat
(d) Home range
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Ecological community
Option (b) is the correct answer: Ecological niche describes not only the physical space occupied by an organism but also its functional role in the community as well.
Ecological Niche:
Option (a) is incorrect: Ecotone is a zone of transition between two ecosystems such the mangrove forests represent an ecotone between marine and terrestrial ecosystems, etc.
Option (b) is correct: Ecological niche subsumes all of the interactions between a species and the biotic and abiotic environment, and thus represents a very basic and fundamental ecological concept.
Option (c) is incorrect: A habitat is a place where an organism makes its home also it meets all the environmental conditions an organism needs to survive.
Option (d) is incorrect: A home range is an area in which an animal lives and moves on a daily or periodic basis (a little bigger than habitat – home
→ office → home).
Question 6
On the planet earth, most of the freshwater exists as ice caps and Out of the remaining freshwater, the largest proportion:
(a) is bound in atmosphere as moisture and clouds
(b) is found in freshwater lakes and rivers
(c) exists as groundwater
(d) exists as soil moisture
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Water Conservation
Option (c) is the correct answer: Ground has the largest portion of freshwater after freshwater that exists as ice caps and glaciers.
Water Resources:
|
NOTE: This is a basic, easy and direct question from NCERT. Also, same question was repeated in Pre 2021. |
Question 7
Which of the following can be found as pollutants in the drinking water in some parts of India?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 3 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
ExplanationAns: c
b-Theme: Water Pollution
Option (c) is the correct answer: Arsenic, Fluoride and Uranium are found as pollutants in the drinking water.
Water Pollution:
Options 1, 3 and 5 are correct: Arsenic, Fluoride, Iron, Uranium, Nitrate, Salinity are some major groundwater pollutants in India.
Option 2 is incorrect: Sorbitol is a sugar alcohol found in fruits and plants with diuretic, laxative and cathartic properties.
Option 4 is incorrect: Formaldehyde is used to preserve fish longer. The use of this chemical is banned in fresh floods by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India.
Question 8
Due to improper/indiscriminate disposal of old and used computers or their parts, which of the following are released into the environment as e-waste?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
(b) 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6 only
(c) 2, 4, 5 and 7 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Explanation
Ans: b
Sub-Theme: Waste Management
E-WASTE:
| E-waste Sources | Constituents |
| PCBs, glass panels, and Computer monitors | Lead |
| Resistors & Semiconductors | Cadmium |
| Relays and switches, & PCBs | Mercury |
| Galvanised steel plates & decorator or hardener | Chromium |
| Cabling, Computer & housing | Plastics & PVC |
| Electronic equipments & circuit boards | Brominated flame-
retardants |
| Front panels of CRTs | Barium, Phosphorus & Heavy metals |
| Copper wires, PCB tracks | Copper |
| Nickel Cadmium batteries | Nickel |
| Lithium-ion battery | Lithium |
| Motherboards | Beryllium |
Options 1,2,3,5 and 6 are correct: All elements in these options are the harmful constituents that are released into the environment due to improper disposal of e-waste.
Option 4 is incorrect: Heptachlor is used as pesticides and also comes under the 12 initial POPs under the Stockholm Convention.
Option 7 is incorrect: Plutonium is a radioactive material.
Question 9
Acid rain is caused by the pollution of environment by
(a) Carbon dioxide and nitrogen
(b) Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide
(c) Ozone and carbon dioxide
(d) Nitrous oxide and sulphur dioxide
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Air Pollution
Option (d) is the correct answer: Nitrous oxide and Sulphur dioxide cause Acid rain.
Common Air Pollutants and their Sources
| Pollutant | Sources |
|
Particulate matter (PM) |
Vehicles, power plants, construction activities, oil refinery, railway yard, industries, etc. |
| Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) | Emissions from combustion processes |
| Sulphur dioxide (SO2) | Burning of fossil fuels, power plants, metals processing and smelting facilities, vehicles |
|
Ozone (O3) |
Results from photochemical reactions b/w NOx & VOCs in presence of sunlight. |
Question 10
Photochemical smog is a resultant of the reaction among
(a) NO2, O3 and peroxyacetyl nitrate in the presence of sunlight
(b) CO, O2 and peroxyacetyl nitrate in the presence of sunlight
(c) CO, CO2 and NO2 at low temperature
(d) High concentration of NO2, O3 and CO in the evening
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Air Pollution
Option (a) is the correct answer: NO2, O3 and peroxyacetyl nitrate react in the presence of sunlight and Photochemical Smog (summer smog) is formed.
Question 11
Improper handling and storage of cereal grains and oilseeds result in the production of toxins known as aflatoxins which are not generally destroyed by the normal cooking process. Aflatoxins are produced by:
(a) bacteria
(b) protozoa
(c) moulds
(d) viruses
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: General Science
Option (c) is the correct answer: Fungi (moulds) produce Aflatoxins.
Question 12
With reference to the usefulness of the by products of the sugar industry, which of the following statements is/are correct?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Byproduct of Sugar Industry
Bagasse and Molasses
| Introduction | Uses | |
|
Bagasse |
• The remnant left after extracting the juice of the sugarcane or sorghum is known as bagasse. It is a dry pulpy fibrous material. | • It is used for the generation of heat energy and electricity. Ethanol produced from it is also used as a popular fuel in some countries.
• It substitutes wood to produce pulp, paper, and board. • As a cattle feed when mixed with molasses and enzymes and then fermenting. |
|
Molasses |
• It is the thick syrup that results from the refining of sugarcane or sugar beets into sugar.
• It contains a good amount of Vitamin B6 and minerals like calcium, manganese, iron and magnesium. |
• Sweetening and flavouring foods.
• In the production of fine commercial brown sugar. • In baking and cooking. • Producing ethanol and is the prime ingredient in the distillation of few alcoholic beverages. • As a cattle feed. |
Statement 1 is correct: Bagasse can be used for the generation of heat energy and electricity.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Molasses is not used for the production of chemical fertilizers.
Statement 3 is correct: Molasses can be used for the production of ethanol and it is also used as the prime ingredient in the distillation of a few alcoholic beverages.
Question 13
Consider the following fauna and India:
Which of the above is/are endangered?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Species
Option (c) is the correct answer: All the above- mentioned species are endangered. Gharials, sometimes called gavials, are a type of Asian crocodilian distinguished by their long, thin snouts.
India has three species of Crocodilians namely:
IUCN- Vulnerable.
Question 14
Consider the following:
Which of the above are naturally found in India?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Species
Statements 1, 2 and 3 are correct: Star tortoise, Monitor lizard and Pygmy hog are naturally found in India.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Spider Monkey is found in the tropical forests of Central and South America. It is critically endangered as per the IUCN Red List.
Question 15
Consider the following animals:
Which of the above is/are mammal/mammals?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Species Diversity
Statements 1 and 3 are correct: Both the Sea Cow or Dugong and Sea Lion are mammals. Dugong also called ‘Sea Cow’ is the only existing species of herbivorous mammal that lives exclusively in the sea including in India. Dugongs are an important part of the marine ecosystem and their depletion will have effects all the way up the food chain. They are found in over 30 countries and in India are seen in the Gulf of Mannar, Gulf of Kutch, Palk Bay, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. IUCN Red List status: Vulnerable. Sea Lion belongs to the family Otariidae of class Mammalia. They are carnivorous aquatic mammals, hence the name Sea Lion.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Sea Horse is a bony fish (Osteichthyes). Seahorses are mainly found in shallow tropical and temperate saltwater throughout the world, from about 45°S to 45°N. They live in sheltered areas such as seagrass beds, estuaries, coral reefs, and mangroves. Four species are found in Pacific waters from North America to South America.
Question 16
Consider the following organisms:
Which of the above is/are used as biofertilizer/ biofertilizers?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Species helps in agriculture
Statement 1 is incorrect: Bio-fertilizers are living or biologically active products or microbial inoculants of bacteria, algae and fungi (separately or in combination) which are able to enrich the soil with nitrogen, phosphorus, organic matter etc. Agaricus is a genus of mushrooms containing both edible and poisonous species, it is not a biofertilizer.
Statement 2 is correct: Nostoc fixes atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which may then be used or converted to a form suitable for plant growth. Thus demonstrating Nostoc’s potential as a sustainable biofertilizer.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Spirogyra is not generally used as a biofertilizer, instead if you use it; it would compete with the plants.
Question 17
In which of the following States is lion-tailed macaque found in its natural habitat?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Species
Option (a) is the correct answer: Lion-tailed Macaque is endemic to the Western Ghats in the states of Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
Although the species has a relatively wide range, its area of occupancy is small and severely fragmented. Primarily diurnal arboreal, it prefers the upper canopy of primary tropical evergreen rainforest. It can also be found in monsoon forests in hilly country and in disturbed forest.
2012
Question 1
The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment describes the following major categories of ecosystem services— provisioning, supporting, regulating, preserving and cultural.
Which one of the following is a supporting service?
(a) Production of food and water
(b) Control of climate and disease
(c) Nutrient cycling and crop pollination
(d) Maintenance of diversity
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme:
Option (c) is the correct answer: Nutrient cycling and crop pollination are supporting services under Millennium Ecosystem Assessment.
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA):
Question 2
What would happen if phytoplankton of an ocean is completely destroyed for some reason?
1. The ocean as a carbon sink would be adversely affected.
2. The food chains in the ocean would be adversely affected.
3. The density of ocean water would drastically decrease.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Food Chain
Statement 1 is correct: Phytoplankton prefer iron and iron pulls carbon out of the atmosphere during photosynthesis, thus the complete destruction of phytoplankton would certainly affect the carbon sinking mechanism of the ocean.
Statement 2 is correct: In a balanced ecosystem, phytoplankton provide food for a wide range of sea creatures, thus Phytoplankton are considered the primary producers in the marine food chain, they are called the ‘grass of the sea’. Thus, the destruction of phytoplankton will certainly have an adverse effect on the marine food chain.
Statement 3 is incorrect: First of all the use of extreme words like ‘drastically’ in the statement is itself a red flag. Now coming to the main part of the statement, if the phytoplankton of an ocean is completely destroyed for some reason, then it may affect the marine food chain because when the phytoplankton disappeared, that affects the zooplankton, which then affects the small fish that ate the zooplankton, and the large fish that ate the small fish. So it’s like dominoes falling. Phytoplankton and macroalgae → zooplankton → small fish → large fish. Therefore, it may hardly affect the density of water.
Question 3
How does the National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) help in protecting Indian Agriculture?
1. NBA checks the biopiracy and protects the indigenous and traditional genetic resources.
2. NBA directly monitors and supervises the scientific research on genetic modification of crop
3. Application for Intellectual Property Rights related to genetic/biological resources cannot be made without the approval of NBA.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Conservation Effort National Biodiversity Authority(NBA):
Statements 1 and 3 are correct:
Statement 2 is incorrect: Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) monitors and supervises the scientific research on genetic modification of crop plants.
Question 4
Consider the following agricultural practices:
In the context of global climate change, which of the above helps/help in carbon sequestration/storage in the soil?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None of them
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Agriculture practices
Option (b) is the correct answer: Zero Tillage helps in carbon sequestration/storage in the soil. Zero Tillage:
Contour bundling:
Relay Cropping:
Question 5
Consider the following statements:
Chlorofluorocarbons, known as ozone-depleting
substances, are used:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Ozone Depleting Substances Ozone Depleting Substances: Chlorofluorocarbons, Hydrochlorofluorocarbons, Carbon tetrachloride, Methyl chloroform, Methyl chloroform, Halons, Methyl bromide, etc.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs):
Statements 1,3 and 4 are correct: Chlorofluoro- carbons, known as ozone-depleting substances, are used in the production of plastic foams, in cleaning electronic components, and as pressurising agents in aerosol cans.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Tubeless tyre is basically a clincher tyre inflated onto a rim with no inner tube. Instead of an inner tube holding the air pressure, an airtight chamber is created with a tubeless-specific tyre, developed with a special (commonly carbon) bead, and a compatible rim.
Question 6
The increasing amount of carbon dioxide in the air is slowly raising the temperature of the atmosphere, because it absorbs
(a) The water vapour of the air retains its
(b) The ultraviolet part of the solar
(c) All the solar
(d) The infrared part of the solar
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Global Warming
Option (d) is the correct answer: The increasing amount of carbon dioxide in the air is slowly raising the temperature of the atmosphere because it absorbs the infrared part of the solar radiation.
Infrared Radiation:
Greenhouse Effect:
Question 7
Which of the following can be threats to the biodiversity of a geographical area?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Biodiversity Loss
Option (a) is the correct answer: Global Warming, Habitat Loss/Fragmentation and Invasive Alien Species threats to the biodiversity of a geographical area.
Options 1,2 and 3 are correct: Global Warming, Fragmentation of Habitat, Invasion of Alien Species, Co- extinctions are the potential threats to biodiversity.
Option 4 is incorrect: Promotion of vegetarianism can’t be a cause for the loss or threat of biodiversity.
Question 8
The National Green Tribunal Act, 2010 was enacted in consonance with which of the following provisions of the Constitution of India?
1. Right to healthy environment, construed as a part of Right to life under Article 21.
2. Provision of grants for raising the level of administration in the Scheduled Areas for the welfare of Scheduled Tribes under Article 275(1).
3. Powers and functions of Gram Sabha as mentioned under Article 243(a).
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Option (b) is the correct answer: National- Green Tribunal (NGT) Act, 2010 was enacted for ensuring a healthy environment, construed as a part of Right to life under Article 21.
National-Green Tribunal (NGT) Act, 2010
Statement 1 is correct: The National Green Tribunal Act, 2010, draws inspiration from India’s constitutional provision of (Constitution of India/ Part III) Article 21 Protection of life and personal liberty, which assures the citizens of India the right to a healthy environment.
Statements 2 and 3 are incorrect: These statements have no relation to NGT.
Question 9
Consider the following protected areas:
Which of the above are declared Tiger Reserves?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: National Parks/ Tiger Reserve/ Biosphere Reserve/Wildlife Sanctuary/Wetland
Option (b) is correct: List of Tiger Reserve
| State | Tiger Reserves |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Namdapha; Kamlang Tiger Reserve; Pakke |
| Assam | Manas; Nameri; Orang Tiger Reserve; Kaziranga |
| Andhra Pradesh | Nagarjunasagar Srisailam |
| Bihar | Valmiki |
|
Chattisgarh |
Udanti-Sitanadi; Achanakmar; Indravati; Guru Ghasidas National Park and Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary (latest) |
| Jharkhand | Palamau |
|
Karnataka |
Bandipur; Bhadra; Dandeli-Anshi; Nagarhole; Biligiri Ranganatha Temple |
| Kerala | Periyar; Parambikulam |
|
Madhya Pradesh |
Kanha; Pench (contiguous with Maharashtra); Bandhavgarh; Panna; Satpura; Sanjay-Dubri |
|
Maharashtra |
Pench (contiguous with Madhya Pradesh); Melghat; Tadoba-Andhari; Sahyadri; Nawegaon-Nagzira; Bor |
| Mizoram | Dampa |
| Odisha | Simlipal; Satkosia |
|
Rajasthan |
Ranthambore; Sariska; Mukundra Hills; Ramgarh Vishdhari Wildlife Sanctuary |
|
Tamil Nadu |
Kalakad-Mundanthurai; Annamalai Mudumakai; Sathyamangalam; Srivilliputhur Megamalai |
| Telangana | Kawal; Amrabad |
|
Uttar Pradesh |
Dudhwa; Pilibhit; Amangarh (Buffer of Corbett TR) |
| Uttarakhand | Corbett; Rajaji |
| West Bengal | Sundarban; Buxa |
Question 10
In which one among the following categories of protected areas in India are local people not allowed to collect and use the biomass?
(a) Biosphere Reserves
(b) National Parks
(c) Wetlands declared under Ramsar Convention
(d) Wildlife Sanctuaries
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: National Parks/ Tiger Reserve/ Biosphere Reserve/Wildlife Sanctuary/Wetland
Option (a) is incorrect: A biosphere reserve is an area of land or water that is protected by law in order to support the conservation of ecosystems, as well as the sustainability of mankind’s impact on the environment.
Option (b) is correct: No human activity is permitted inside the national park except for the ones permitted by the Chief Wildlife Warden of the state.
Option (c) is incorrect: It is an international treaty for “the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands”.
Option (d) is incorrect: The difference between a Sanctuary and a National Park mainly lies in the vesting of rights of people living inside. Unlike National Parks, certain rights can be allowed in Sanctuary.
Question 11
Consider the following kinds of organisms
Which of the above is/are pollinating agent/agents?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Species/Pollination
Option (d) is the correct answer: When a pollen grain moves from the anther (male part) of a flower to the stigma (female part), pollination happens and it is the first step in a process that produces seeds, fruits, and the next generation of plants. Pollinators are Vectors that move pollen within the flower and from flower to flower are called pollinators.
Pollinators (Bat, Bee, Birds)
Question 12
The Government of India encourages the cultivation of ‘sea buckthorn’. What is the importance of this plant:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Species
Option (c) is the correct answer: Seabuckthorn (soil binding, rich in vitamins)
Statements 1 and 3 are correct: Seabuckthorn is a soil-binding plant which prevents soil-erosion, it also has commercial value, as it is used in making juices, jams, nutritional capsules etc.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Though seabuckthorn is an important source of fuelwood and fodder, it is not a rich source of biodiesel.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Seabuckthorn has commercial value, as it is used in making juices, jams, nutritional capsules etc.
Question 13
Which one of the following groups of animals belongs to the category of endangered species?
(a) Great Indian Bustard, Musk Deer, Red Panda and Asiatic Wild Ass
(b) Kashmir Stag, Cheetal, Blue Bull and Great Indian Bustard
(c) Snow Leopard, Swamp Deer, Rhesus Monkey and Saras (Crane)
(d) Lion-tailed Macaque, Blue Bull, Hanuman Langur and Cheetal
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Threatened Species
Threatened Species: Great Indian Bustard, Musk Deer, Red Panda and Asiatic Wild Ass (Currently Vulnerable, but as the question is from 2012, we will consider it as Endangered) all are Endangered Species.
Option (a) is the correct answer: Great Indian Bustard, Musk Deer, Red Panda and Asiatic Wild Ass (Currently Vulnerable, but as the question is from 2012, we will consider it as Endangered) all are Endangered Species. Important species and their Conservation status are:
| Species | Particulars |
|
Great Indian Bustard |
• State bird of Rajasthan
• Flagship grassland species, representing the health of the grassland ecology. • States: Rajasthan and Gujarat. Small populations occur in Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. • Conservation Status: • IUCN Status: Critically Endangered • CITES: Appendix 1 • Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I • Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule 1 |
|
Musk Deer |
• Habitat: J&K, Uttarakhand. Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
• Conservation Status: • IUCN Status: Endangered |
|
Red Panda |
• State animal of Sikkim.
• Red panda is endemic to the temperate forests of the Himalayas. • Habitat: Sikkim and Assam, northern Arunachal Pradesh. • Threats: habitat loss and fragmentation, poaching, and inbreeding depression. • Conservation Status: • IUCN Status: Endangered • Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule 1 |
| • Scientific Name: Equus hemionus | |
| • Also called: Asiatic Wild Ass, Asian Wild Ass, Indian onager or, Ghudkhur and Khur (Gujarati language) | |
|
Asiatic Wild Ass |
• A subspecies of the onager native to Southern Asia.
• Habitat: Western India, southern Pakistan (i.e. provinces of Sindh and Baluchistan), Afghanistan, and south-eastern Iran. |
| • Conservation Status: | |
| • IUCN: currently listed as Near Threatened (Earlier it was listed under Endangered Category) |
Question 14
What is the difference between the antelopes Oryx and Chiru?
(a) Oryx is adapted to live in hot and arid areas whereas Chiru is adapted to live in steppes and semi-desert areas of cold high mountains.
(b) Oryx is poached for its antlers whereas Chiru is poached for its musk.
(c) Oryx exists in western India only whereas Chiru exists in north-east India only.
(d) None of the statements (a), (b) and (c) given above is correct.
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Species
Option (a) is the correct answer: Chiru, also Known as Tibetan antelope. Endemic to the Tibetan Plateau, the Tibetan antelope inhabits open alpine and cold steppe environments between 3,250 and 5,500 m (10,660 and 18,040 ft) elevation.
IUCN: Near Threatened.
Oryx is a genus consisting of four large antelope species called oryxes.
Oryx species prefer near-desert conditions and can survive without water for long periods.
IUCN: In 2011 it was down-listed from the Endangered category to Vulnerable. Hence, Oryx species prefer near-desert conditions and can survive without water for long periods and Chiru or Tibetan antelope inhabit open alpine and cold steppe environments.
Question 15
Consider the following:
Which of the above are naturally found in India?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Species
Statement 1 is correct: Black-necked crane is a state bird of Ladakh, therefore it ought to be naturally found in India at high altitude.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Cheetahs are believed to have disappeared from the country when Maharaja Ramanuj Pratap Singh Deo of Koriya hunted and shot the last three recorded Asiatic cheetahs in India in 1947.
Statement 3 is correct: Various species of Flying squirrel are naturally found in India.
Statement 4 is correct: In India, Snow Leopard’s geographical range encompasses through Western Himalayas: Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh. Eastern Himalayas: Uttarakhand and Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh. The Snow Leopard capital of the world is Hemis, Ladakh.
2011
Question 1
In the context of ecosystem productivity, marine upwelling zones are important as they increase marine productivity by bringing the:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-theme: Ecosystem productivity/Energy Flow
Option (b) is the correct answer: Marine upwelling brings nutrients to the surface.
Upwelling:
Question 2
If a tropical rainforest is removed, it does not regenerate quickly as compared to a tropical deciduous forest. This is because
(a) The soil of rainforest is deficient in nutrients
(b) Propagules of the trees in a rainforest have poor viability
(c) The rain forest species are slow-growing
(d) Exotic species invade the fertile soil of rainforest
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Types of ecosystem/Forest/ Biomes
Option (a) is correct: The high volume of rainfall in tropical rainforests leaches out most of the nutrients from the soil and makes these soils virtually useless and nutrient deficient for agricultural purposes.
Option (b) is incorrect: Propagule is a vegetative structure that can become detached from a plant and give rise to a new plant, e.g. a bud, sucker, or spore. Seed bearing plants are more significant than Propagules in rainforests.
Option (c) is incorrect: In the rainforest, the plant species generally compete with each other for sunlight and while doing so they grow so fast that they rapidly consume the nutrients from the decomposed leaf litter. As a result, most of the nutrients are contained in the trees and other plants rather than in the soil.
Option (d) is incorrect: Though the exotic invasive species are a threat to rainforests (E.g. Most plantation crops like rubber, palm etc.) but it is also true that the rainforest soil is heavily leached, nutrient deficient, and thus less fertile.
Question 3
The “Red Data Books” published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resource (IUCN) contain lists of
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Biodiversity Conservation
Option (b) is the correct answer: Red Data Books contain lists of Threatened plant and animal species.
Statements 1 and 3 are incorrect: The IUCN Red List of “threatened species” is the world’s most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of plant and animal species, which is a grouping of three categories: Critically Endangered, Endangered, and Vulnerable.
Statement 2 is correct: The IUCN Red List Categories define the extinction risk of species assessed. Nine categories extend from NE (Not Evaluated) to EX (Extinct). Among these nine categories, Critically Endangered (CR), Endangered (EN) and Vulnerable (VU) species are considered to be threatened with extinction.
Question 4
Which one of the following is not a site for the in-situ method of conservation of flora?
(a) Biosphere Reserve
(b) Botanical Garden
(c) National Park
(d) Wildlife Sanctuary
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Modes of Conservation
Option (b) is the correct answer: Botanical Garden
| Ex situ Conservation | In situ Conservation |
| • Ex situ conservation is the preservation of biodiversity away from their natural habitats. Here, zoological or botanical parks are places where animals and plants are raised or grown. | • In situ conservation refers to the
preservation of plants and animals in their natural environments. |
| • Another method of ex situ conservation is the reintroduction of an animal or plant into its former environment. For instance, the extinct Gangetic gharial has been brought back into the rivers of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
• Important locations for ex situ conservation include seed banks, botanical, horticultural, and recreational gardens. |
• This includes the establishment of:
1. National parks and sanctuaries 2. Biosphere reserves 3. Nature reserves 4. Reserved and protected forests 5. Preservation plots 6. Reserved forests |
Question 5
Three of the following criteria have contributed to the recognition of Western Ghats-Sri Lanka and Indo- Burma regions as hotspots of biodiversity:
Which three of the above are correct criteria in this context?
(a) 1, 2 and 6
(b) 2, 4 and 6
(c) 1, 3 and 5
(d) 3, 4 and 6
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Biodiversity Hotspot
Biodiversity Hotspot:
Statement 1 and 3 are correct: Species richness and endemism is one of the major criteria which must contain at least 1,500 species of vascular plants (> 0.5% of the world’s total) as endemics.
Statement 5 is correct: ‘Degree of Threat’ is also a major criteria for the recognition of biological hotspots. It has to have lost at least 70% of its original habitat. (It must have 30% or less of its original natural vegetation). In other words, it must be threatened.
Statement 2, 4 and 6 are incorrect: Are not the criteria for the recognition of Biodiversity Hotspots.
Question 6
Consider the following statements:
1. Biodiversity is normally greater in the lower latitudes as compared to the higher latitudes.
2. Along the mountain gradients, biodiversity is normally greater in the lower altitudes as compared to the higher altitudes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Biomes
Patterns of Biodiversity:
Statement 1 is correct: Diversity of plants and animals is not uniform throughout the world. Species diversity decreases as we move away from the equator towards the pole.
Statement 2 is correct: Elevational diversity gradient (EDG) is an ecological pattern where biodiversity changes with elevation. The EDG states that species richness tends to increase as elevation increases, up to a certain point, creating a “diversity bulge” at middle elevations, after which it decreases with altitude. Therefore, it is true that along the mountain gradients, biodiversity is normally greater in the lower altitudes as compared to the higher altitudes.
Question 7
Biodiversity forms the basis for human existence in the following ways:
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Services provided by Biodiversity
Services provided by Biodiversity: Biodiversity provides a number of natural services for human beings:
|
Ecosystem services |
• Protection of water resources
• Soils formation and protection • Nutrient storage and recycling • Pollution breakdown and absorption • Contribution to climate stability • Maintenance of ecosystems • Recovery from unpredictable events |
|
Biological services |
• Food
• Medicinal resources and pharmaceutical drugs • Wood products • Ornamental plants • Breeding stocks • Diversity in genes, species and ecosystems |
|
Social services |
• Research, education and monitoring
• Recreation and tourism • Cultural values |
Question 8
The Himalayan Range is very rich in species Which one among the following is the most appropriate reason for this phenomenon?
(a) It has high rainfall that supports luxuriant vegetative growth
(b) It is a confluence of different biogeographical zones
(c) Exotic and invasive species have not been introduced in this region
(d) It has less human interference
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Biomes
Option (b) is the correct answer: Being a confluence of different biogeographical zones Himalayan Range is very rich in species diversity.
Biogeographic Zones:
There are ten biogeographic zones in India:
Question 9
With reference to micro-irrigation, which of the following statements is/are correct?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Agriculture and Environment
Micro-irrigation:
Benefits of micro irrigation systems:
Statement 1 is correct: An efficient drip irrigation system reduces the consumption of fertiliser through fertigation.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Dryland farming is defined as the production of crops without irrigation in regions that receive rainfall of less than 500mm annually.
Statement 3 is correct: Micro-irrigation helps in water-saving and checking further groundwater depletion.
Question 10
There is a concern over the increase in harmful algal blooms in the seawaters of India. What could be the causative factors for this phenomenon?
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Water Pollution
Algal Bloom:
Responsible Factors for ALGAL BLOOM
| • Nutrients |
| • Temperature |
| • Light |
| • Stable (Calm Waters) Conditions |
| • Turbidity |
| • Aquaculture Operations |
Statement 1 is correct: Nutrients promote and support the growth of algae and Cyanobacteria. The Eutrophication (nutrient enrichment) of waterways is considered as a major factor behind the increase in harmful algal blooms.
Statement 2 is correct: External sources include runoff and soil erosion from fertilized agricultural areas, erosion from river banks, river beds, land clearing (deforestation), and sewage effluent.
Statement 3 is correct: Water that rises to the surface as a result of upwelling is typically colder and is rich in nutrients, which again leads to algal blooms.
Question 11
Human activities in the recent past have caused the increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, but a lot of it does not remain in the lower atmosphere because of
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Carbon Mitigation Strategies
Carbon Sequestration:
3 main steps to Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
Statement 1 is incorrect: Some amount of CO2 does escape but not much CO2 is denser than Nitrogen, Oxygen and Argon (the main components of the atmosphere) and thus this tend to stay more in the lower atmosphere, however, this does not stop some of it moving to the upper atmosphere by the process of diffusion.
Statement 2 is correct: The photosynthesis by phytoplankton in the oceans is natural carbon sequestration.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The trapping of CO2 by polar ice is not known.
Question 12
Consider the following:
Which of the above is/are the emission/emissions from coal combustion at thermal power plants?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Major air pollutants and their sources/Green House Gases
Option (d) is the correct answer: Emissions of all the above-mentioned gases i.e. Carbon dioxide, Oxides of Nitrogen and Oxides of Sulphur take place from coal combustion at thermal power plants.
Emission of Gases from Coal Combustion
| Gas | Sources and Causes |
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | Burning of fossil fuels, deforestation |
|
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) |
Refrigeration, solvents, insulation foams, aero propellants, industrial and commercial uses |
|
Methane (CH4) |
Growing paddy, excreta of cattle and other livestock, termites, burning of fossil fuel, wood, landfills, wetlands, fertilizer factories. |
| Nitrogen oxides (N2O) | Burning of fossil fuels, fertilizers; burning of wood and crop residue. |
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Iron ore smelting, burning of fossil fuels, burning e-waste. |
Question 13
The formation of ozone hole in the Antarctic region has been a cause of concern. What could be the reason for the formation of this hole?
(a) Presence of prominent tropospheric turbulence; and inflow of chlorofluorocarbons
(b) Presence of prominent polar front and stratospheric clouds; and inflow of chlorofluorocarbons.
(c) Absence of polar front and stratospheric clouds; and inflow of methane and chlorofluorocarbons.
(d) Increased temperature at polar region due to global warming
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Ozone Depletion
Option (b) is the correct answer: Formation of Polar front, Polar Stratospheric Clouds lead to formation of ozone hole in the Antarctic region.
Antarctic Ozone Hole:
Causes:
Question 14
Regarding “carbon credits”, which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) The carbon credit system was ratified in conjunction with the Kyoto Protocol
(b) Carbon credits are awarded to countries or groups that have reduced greenhouse gases below their emission quota
(c) The goal of the carbon credit system is to limit the increase of carbon dioxide emission
(d) Carbon credits are traded at a price fixed from time to time of the United Nation Environment Programme
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Carbon Mitigation Strategies
Carbon Credit:
Question 15
With reference to India, consider the following Central Acts:
Which of the above Acts have relevance to/bearing on the biodiversity conservation in the country?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(d) None of the above Acts.
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: National efforts to protect biodiversity/Laws and Legislations
|
The Indian Forest Act, 1927 |
• In order to increase accountability for forest protection, this act lays out the steps that must be taken when designating a region as a Reserved Forest, Protected Forest, or Village Forest. |
| Import and Export (Control) Act,
1947 |
• Import and export of GMOs or exotic species are prohibited whereas certain medicinal plants are subjected to high customs duties to regulate their trade. |
|
Mining and Mineral Development (Regulation) Act 1957 |
• Mining activities, whether occurring within or near Protected Areas, cause a range of environmental; consequences that can be severe and irreversible. Thus mining is restricted in reserved areas. |
|
Customs Act, 1962 |
• Import and export of GMOs or exotic species are prohibited whereas certain medicinal plants are subjected to high customs duties to regulate their trade. |

<div class="new-fform">
</div>