2022
Question 1
In the northern hemisphere, the longest day of the year normally occurs in the:
(a) First half of the month of June
(b) Second half of the month of June
(c) First half of the month of July
(d) Second half of the month of July
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Motion of Earth
Summer Solstice (21st June):
| NOTE: This question is a repetition from 2019 only the sentences of both the question and options are twisted to confuse the candidate. Also UPSC has asked questions from similar themes in 2013, please refer to the PYQs for detailed explanation. |
Question 2
Consider the following statements:
1. High clouds primarily reflect solar radiation and cool the surface of the Earth.
2. Low clouds have a high absorption of infrared radiation emanating from the Earth’s surface and thus cause a warming effect.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Clouds
Statement 1 is incorrect: Low, thick clouds primarily reflect solar radiation and cool the surface of the Earth.
Statement 2 is incorrect: High, thin clouds primarily transmit incoming solar radiation. At the same time, they trap some of the outgoing infrared radiation emitted by the Earth and radiate it back downward, thereby warming the surface of the Earth.
Question 3
Consider the following States:
Kerala
Himachal Pradesh
Tripura
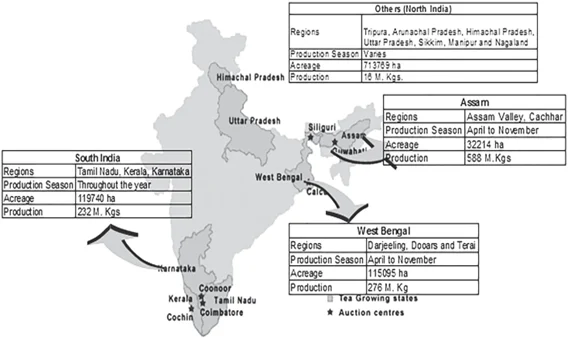
How many of the above are generally known as tea- producing States?
(a) Only one State
(b) Only two States
(c) Only three States
(d) All four States
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Tea production
Tea Climatic conditions:
Question 4
With reference to India, consider the following statements:
Monazite contains thorium.
Monazite occurs naturally in the entire Indian coastal sands in India.
In India, government bodies only can process or export monazite.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Rare Earth Metal
Statement 1 and 2 are correct: Rare earth metals are a group of 17 elements. They are lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals. China accounts for 90% of the world’s rare earth production. In India, monazite is the principal source of rare earths and thorium.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Monazite, though found in most coastal areas of India, is unlikely to be found along the entire coast. The main mines are found along the coasts of southern India in Kerala, Tamil Nadu and in Orissa.
Statement 4 is correct: As per Atomic Energy (Radiation Protection) Rules 2004, Indian Rare Earths Limited (IREL), a wholly owned Public Sector Undertaking of the Government of India (GOI) under DAE, is the only entity which has been permitted to produce and process monazite, and handle it for domestic use as well as for export.
| NOTE: In the question, in statement 3, the extreme word ‘entire’ is a red flag. |
Question 5
Gandikota canyon of South India was created by which one of the following rivers?
(a) Cauvery
(b) Manjira
(c) Pennar
(d) Tungabhadra
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Physical features of India
Question 6
Consider the following pairs:
| Peak | Mountains |
| 1. Namcha Barwa | Garhwal Himalaya |
| 2. Nanda Devi | Kumaon Himalaya |
| 3. Nokrek | Sikkim Himalaya |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 only
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Physical features of India
Pair 1 is incorrect: Namcha Barwa is not situated in Garhwal Himalaya. It is situated in the Eastern Himalaya.
Pair 2 is correct: The part of the Himalayas lying between Satluj and Kali rivers is known as Kumaon Himalayas. Nanda Devi is part of the Kumaon Himalayas, and is located in the state of Uttarakhand, between the Rishi Ganga valley on the west and the Goriganga valley on the east.
Pair 3 is incorrect: Nokrek is situated in West Garo Hills of Meghalaya, not in Sikkim Himalaya.
Question 7
Consider the following pairs:
| Reservoirs | States |
| 1. Ghataprabha | Telangana |
| 2. Gandhi Sagar | Madhya Pradesh |
| 3. Indira Sagar | Andhra Pradesh |
| 4. Maithon | Chhattisgarh |
How many pairs given above are not correctly matched?
(a) Only one pair
(b) Only two pairs
(c) Only three pairs
(d) All four pairs
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Reservoir and their location
Pair 1 is incorrect: The Ghataprabha Reservoir is located in the Belagavi district of the state of Karnataka.
Pair 2 is correct: The Gandhi Sagar Dam is one of the four major dams built on India’s Chambal River located in the Mandsaur, districts of the state of Madhya Pradesh.
Pair 3 is incorrect: The Indira Sagar Dam is the largest dam in India, in terms of volume of water stored in the reservoir. It is located on the Narmada River at the town of Narmada Nagar, Punasa in the Khandwa district of Madhya Pradesh in India.
Pair 4 is incorrect: The Maithon Dam is constructed on the Barakar River and it is located at Maithon, 48 km from Dhanbad, in the state of Jharkhand in India.
2021
Question 1
Consider the following statements
In the temperate zone, westerlies make the eastern sections of oceans warmer than the western sections.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Wind Movement
Statement 1 is correct: The Trade winds originate from subtropical high pressure regions and move toward the equatorial low pressure belt. At the equator, the trade winds from the two hemispheres collide, rising and bringing torrential rainfall. The Northeast trade winds in the Northern hemisphere of the tropical zone move warmer water westward through the ocean. As a result of the cool ocean currents, the eastern regions of the trade winds are drier and more stable than the western parts of the ocean.
Statement 2 is correct: The westerlies are the winds blowing from the subtropical high pressure belts towards the sub polar low pressure belts.The Westerlies play an important role in carrying the warm, equatorial waters and winds to the western coasts of continents that is eastern section of the Oceans in the temperate zone.
Question 2
“Leaf litter decomposes faster than in any other biome and as a result the soil surface is often almost bare. Apart from trees, the vegetation is largely composed of plant forms that reach up into the canopy vicariously, by climbing the trees or growing as epiphytes, rooted on the upper branches of trees.”
This is the most likely description of
(a) Coniferous forest
(b) Dry deciduous forest
(c) Mangrove forest
(d) Tropical rainforest
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Major Climate of the World
Hot, Wet Equatorial Climate:
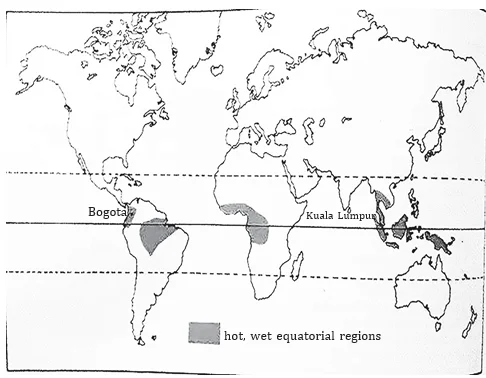
NOTE: UPSC has this habit of picking lines from GC Leong and frame it as a question. Please learn to pick the hints from the UPSC question, here in the above sentence observe the keywords like ‘Leaf litter decomposes faster’; ‘canopy’; ‘epiphytes’; etc. these are enough/sufficient hints to answer this question. Now if you have read NCERTs and GC Leong you could easily identify that these are the characteristics of ‘Tropical Rainforest’ or ‘Hot, Wet Equatorial Climate’.
Question 3
The black cotton soil of India has been formed due to the weathering of:
(a) Brown forest soil
(b) Fissure volcanic rock
(c) Granite and schist
(d) Shale and limestone
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Type of Soil
Option (b) is correct: The black cotton soils of India have been formed due to the weathering of the fissure volcanic rock.
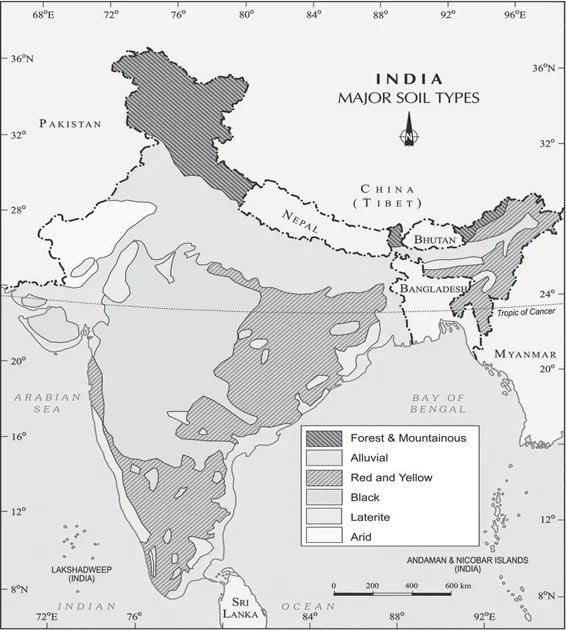
Major Soils Types
Question 4
Among the following, which one is the least water- efficient crop?
(a) Sugarcane
(b) Sunflower
(c) Pearl millet
(d) Red gram
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Water efficient crop
Option (a) is correct: Sugarcane requires around 1800 to 2200 mm and basically it is a heavy water intensive crop.
Option (b) is incorrect: Major oilseeds like soyabean, castor seeds, cotton seeds, linseed and sunflower, etc. requires around 672.4 mm.
Option (c) is incorrect: Millets can be grown even in dry regions without irrigation facilities. Pearl millets require around 350 mm of water.
Option (d) is incorrect: Pulses like red gram require around 200-450 mm of water.
Question 5
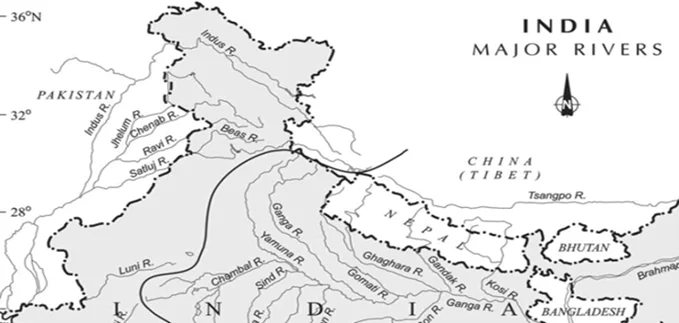
With reference to the Indus River system, of the following four rivers, three of them pour into one of them which joins the Indus directly. Among the following, which one is such a river that joins the Indus directly?
Chenab
(b) Jhelum
(c) Ravi
(d) Sutlej
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Indus River System/Drainage
Option (a) is incorrect: The Chenab joins the Satluj in Panchnad(Pakistan) after receiving the waters of the Jhelum and Ravi rivers.
Option (b) is incorrect: The Jhelum joins the Chenab near Jhang in Pakistan.
Option (c) is incorrect: The Ravi debouches into the Chenab near Sarai Sidhu, a little above Rangpur in Pakistani Punjab.
Option (d) is correct: The Satluj receives the collective drainage of the Ravi, Chenab and Jhelum rivers. It joins the Indus a few kilometers above Mithankot.
Question 6
With reference to India, Didwana, Kuchaman, Sargol and Khatu are the names of
(a) Glaciers
(b) Mangrove areas
(c) Ramsar sites
(d) Saline lakes
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Physiography of India
About Playas (Salt Lake):
Question 7
Consider the following rivers:
Nagavali
Subarnarekha
Vamsadhara
Which of the above rise from the Eastern Ghats?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 4
(c) 3 and 4
(d) 1 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Peninsular Drainage (Small East Flowing Rivers)
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Brahmani river comes into existence by the confluence of the Koel and the Shankh rivers near Rourkela.
Statement 2 is correct: Nagavali River originates in Kalahandi District, in the Eastern Ghats.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The Subarnarekha originates from the Ranchi Plateau in Jharkhand forming the boundary between West Bengal and Odisha in its lower course.
Statement 4 is correct: It is an east-flowing river that originates in the Kalahandi district of Odisha, Eastern Ghat, flows in Odisha, along its boundary with Andhra Pradesh and finally joins the Bay of Bengal at Kalingapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
2020
Question 1
Consider the following statements
Only some cyclones develop an eye.
The temperature inside the eye of a cyclone is nearly 10°C less than that of the surroundings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Wind Movement
Jet Stream:
Statement 1 is not correct: In both the hemispheres, jet streams run from 20 degrees latitude to the poles.
Statement 2 is correct: Only some cyclones develop an eye. The eye is not present in a temperate cyclone since there is not a single location where the winds and precipitation are not present.
Statement 3 is not correct: The tropical cyclone’s eye is the area with the lowest surface pressure and the warmest air above it (in the upper levels). The eye temperature may be 10°C or more above the surrounding air at a height of 12 km, whereas it is only 0–2°C warmer at the surface.
Question 2
With reference to Ocean Mean Temperature (OMT), which of the following statements is/are correct?
OMT collected during January–March can be used in assessing whether the amount of rainfall in monsoon will be less or more than a certain long-term mean.
Select the correct using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Oceanography
About Ocean Mean Temperature (OMT):
Statement 1 is incorrect: OMT is measured up to a depth of 26°C isotherm at depths varying from 50-100 meters not 129 meters
Statement 2 is correct: OMC is analyzed by measuring the ocean thermal energy during the January-March period – can better predict Indian summer monsoon than the SST.
Question 3
Consider the following minerals:
Chromite
Kyanite
Sillimanite
In India, which of the above is/are officially designated as major minerals?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Major Minerals in India
Question 4
“The crop is subtropical in nature. A hard frost is injurious to It requires at least 210 frost-free days and 50 to 100 centimeters of rainfall for its growth. A light well-drained soil capable of retaining moisture is ideally suited for the cultivation of the crop.”
Which one of the following is that crop?
(a) Cotton
(b) Jute
(c) Sugarcane
(d) Tea
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Major Crop
Cotton:
NOTE: Learn to pick keywords/keyphrases from these long sentences to reach the correct answer. Here the keywords are – ‘subtropical’; ‘210 frost-free days’; ‘50 to 100 centimeters of rainfall’; ‘well- drained soil’. These keywords/keyphrases are enough to mark the correct answer. Also, this underlines the importance of reading NCERTs. UPSC asks questions on various crop/crops and their characteristics every alternate year. It is advisable to read India People and Economy class XII NCERT thoroughly.
Question 5
Which of the following Protected Areas are located in Cauvery basin?
Papikonda National Park
Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Major Places and Rivers/Map based
Option 1 is correct: The Nagarahole River flows through the park, which joins the Kabini River which also is a boundary between Nagarahole and Bandipur National Park. Kabini, a tributary of the Cauvery River, is the largest river draining the park.
Option 2 is incorrect: The Papikonda park lies on the left and right banks of the river Godavari and cuts through the Papikonda hill range of Eastern Ghats.
Option 3 is correct: Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve (STR) is located at the confluence region of Western and Eastern Ghats, in the Erode district of the state of Tamil Nadu. In the northern part of Erode district, the Palar river flows and drains into the Cauvery river.
Option 4 is correct: Kabini river, a tributary of the Cauvery river flows through the Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary.
Question 6
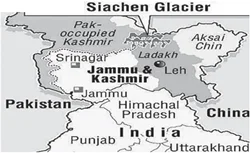
Siachen Glacier is situated to the:
(a) East of Aksai Chin
(b) East of Leh
(c) North of Gilgit
(d) North of Nubra Valley
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Map based
The Siachen Glacier is situated to the North of the Nubra Valley.
About Siachen Glacier:
Siachen Glacier is located in the eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas at about 421226°N 77.109540°E, just northeast of the point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends. The 75 km long Siachen Glacier in the north of Nubra valley has the distinction of being the largest glacier outside the polar and the subpolar regions. It is also the world’s highest battlefield.
|
NOTE: Siachen Glacier was in the news. This is purely a map based question and anyone with a little bit of knowledge can easily solve this question. Observing the map carefully, East of Aksai Chin is China Administered Tibet, while Leh is situated South of Siachen, and Gilgit is on the western side of Siachen. |
Question 7
Consider the following pairs:
| River | Flow into |
| 1. Mekong | Andaman Sea |
| 2. Thames | Irish Sea |
| 3. Volga | Caspian Sea |
| 4. Zambezi | Indian Ocean |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2 and 4 only
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Map based
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Mekong River originates in the icy headwaters of the Tibetan highlands. It flows through the steep canyons of China, known as the upper basin, through lower basin countries Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, and Cambodia, before fanning an expansive delta in Vietnam and emptying into the South China Sea.
Statement 2 is incorrect: It is the longest river in England, flowing 215 miles from the Cotswolds to the North Sea. The main tributaries of Thames are Buscot, Reading, and Kingston.
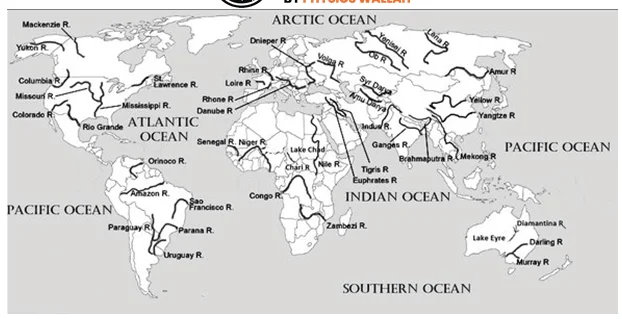
Statement 3 is correct: The Volga River, the longest river in Europe, runs through Russia with its delta flowing into the Caspian Sea just south of the Kazakhstan border.
Statement 4 is correct: The Zambezi is the fourth-largest river after the Congo/Zaire, Nile and Niger in Africa. It rises in the Kalene hills in north-western Zambia and flows eastwards for about 3000 km to the Indian Ocean.
Question 8
With reference to pulse production in India, consider the following statements:
Green-gram alone accounts for nearly half of pulse
In the last three decades, while the production of kharif pulses has increased the production of rabi pulses has decreased.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Major crops
Statement 1 is correct: In India, the important pulse crops grown in winter (rabi) are chickpea, lentil, lathyrus, field pea and kidney bean. However, green gram, black gram and cowpea are grown in both spring and rainy season.
Statement 2 is incorrect: According to the Directorate of Economics and Statistics (DES), the share of pulse production in 2018- 19 was comprised of Tur (15.34%), Gram (43.29%), Moong (green gram,10.04%), Urad (black gram, 13.93%), Lentil (6.67%), and Other Pulses (10%).
Statement 3 is incorrect: In the last three decades, both, the production of kharif pulses and the production of rabi pulses have increased.
2019
Question 1
On 21st June, the Sun:
(a) Does not set below the horizon at the Arctic Circle
(b) Does not set below the horizon at Antarctic Circle
(c) Shines vertically overhead at noon on the Equator
(D) Shines vertically overhead at the Tropic of Capricorn
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Motion of Earth
Option (a) is correct: Areas near the poles receive less heat as the rays of the sun are slanting.The North Pole is inclined towards the sun and the places beyond the Arctic Circle experience continuous daylight for about six months.
Summer Solstice (21st June):
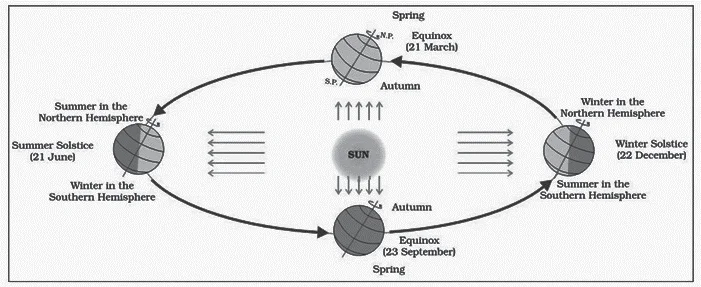
Revolution of the Earth and Seasons
Question 2
Why are dewdrops not formed on a cloudy night?
(a) Clouds absorb the radiation released from the Earth’s surface.
(b) Clouds reflect back the Earth’s radition.
(c) The Earth’s surface would have low temperatures on cloudy nights.
(d) Clouds deflect the blowing wind to ground level
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Dew Formation/Water in Atmosphere
Option (b) is correct: The dew drops are not formed on a cloudy night because the Clouds reflect back the Earth’s radiation.
Question 3
With reference to the management of minor minerals in India, consider the following statements:
State Governments have the power to grant mining leases of minor minerals, but the powers regarding the formation of rules related to the grant of minor minerals lie with the Central government.
The State Government has the power to frame rules to prevent illegal mining of minor minerals.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Minor Minerals in india
Statement 1 is correct: Sand is a ‘minor mineral’ according to the prevailing law in the country.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Any mineral which by the notification of the Central Government may declare to be a minor mineral.
Statement 3 is correct: The State Government may, by notification in the Official Gazette, make rules for regulating the grant of quarry leases, mining leases or other mineral concessions in respect of minor minerals and for purposes connected there with.
Question 4
With reference to the cultivation of Kharif crops in which in the last five years, consider the following statements:
Area under cultivation of jowar is more than that of oilseeds.
Area of cotton cultivation is more than that of
Area under sugarcane cultivation has steadily
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Major Crops
Statement 1 is correct: The area under rice cultivation in India, in 2013-14 was 44.13 million hectares while in 2015-16, it became 43.39 million hectares and is highest amongst all.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The annual area under Jowar ranges between 17 and 18 million hectares while the oilseed area is 28 million hectares (2013-14), 26.1 million hectares (2015-16) i.e area under the cultivation of Jowar is less than that of oilseeds.
Statement 3 is correct: The area under sugarcane cultivation is 4.99 million hectares (2013-14), 5.066 million hectares (2014-15), 4.953 million hectares (2015-16). The area under cotton cultivation is 11.96 million hectares (2013-14), 12.81 million hectares (2014-15), and 11.87 million hectares (2015-16). Hence the area under cotton cultivation is more than sugar cultivation.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The area under sugarcane cultivation has not steadily decreased.
Question 5
What is common to the places known as Aliyar, Isapur and Kangsabati?
(a) Recently discovered uranium deposits
(b) Tropical rain forests
(c) Underground cave systems
(d) Water reservoirs
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Current Affairs
Aliyar, Isapur and Kangsabati are the names which have water reservoirs common to the people.
About Water Reservoirs:
Question 6
Consider the following pairs:
|
Famous Place |
River |
| 1. Pandharpur | Chandrabhaga |
| 2. Tiruchirappalli | Cauvery |
| 3. Hampi | Malaprabha |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Famous places of India
Pair 1 is correct: Pandharpur city is on the banks of Chandrabhaga River in Maharashtra. The famous Lord Vitthal-Rukmini Mandir is located in this city.
Pair 2 is correct: Tiruchirappalli is an Indian city of Tamil Nadu on the banks of river Cauvery. The famous Sri Ranganathaswamy Temple is located in Tiruchirappalli.
Pair 3 is incorrect: Hampi was the capital of the Vijayanagara kingdom and is located on the bank of the Tungabhadra River in present state of Karnataka. Many famous temples like Virupaksha Temple, Nandi Statue etc are located in Hampi. Pattadakal or Pattadakal is situated on the banks of the river Malaprabha and is located in Karnataka.
Question 7
Consider the following pairs:
|
Sea |
Bordering Country |
| 1. Adriatic Sea | Albania |
| 2. Black Sea | Croatia |
| 3. Caspian Sea | Kazakhstan |
| 4. Mediterranean Sea | Morocco |
| 5. Red Sea | airyS |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: World Map
Pair 1 is correct: The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula. The countries with coasts on the Adriatic sea: Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Italy, Montenegro and Slovenia. Mnemonic: ISC-MBA (Italia, Slovenia, Croatia, Montenegro, Bosnia, Albania).
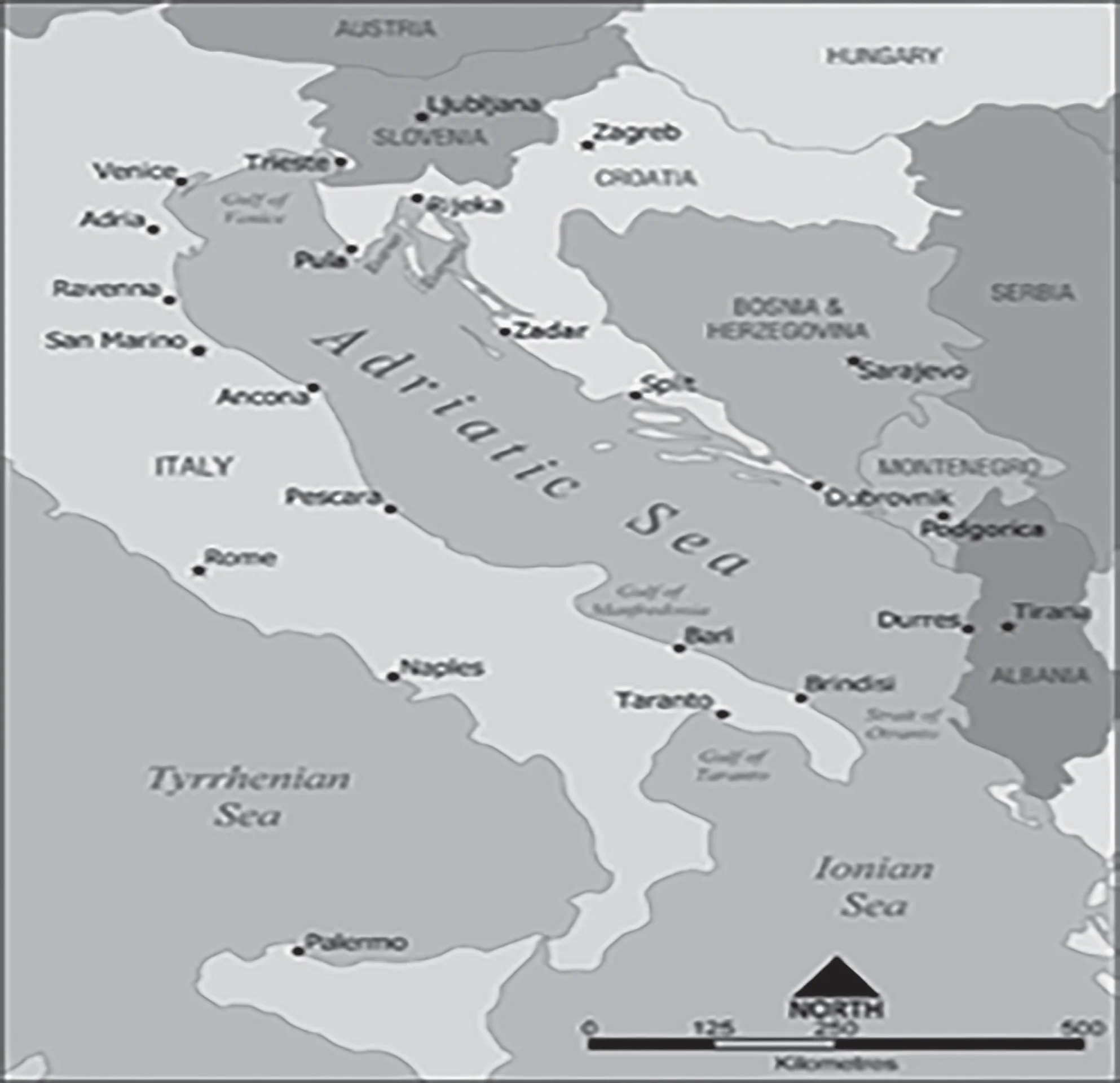
Pair 2 is incorrect: Black Sea is a large inland sea situated at the southeastern extremity of Europe. It is bordered by Ukraine to the north, Russia to the northeast, Georgia to the east, Turkey to the south, and Bulgaria and Romania to the west. Black Sea is not bordered by Croatia. Mnemonic: Tea & BURGeR (Turkey, Bulgaria, Ukraine, Russia, Georgia, Romania).
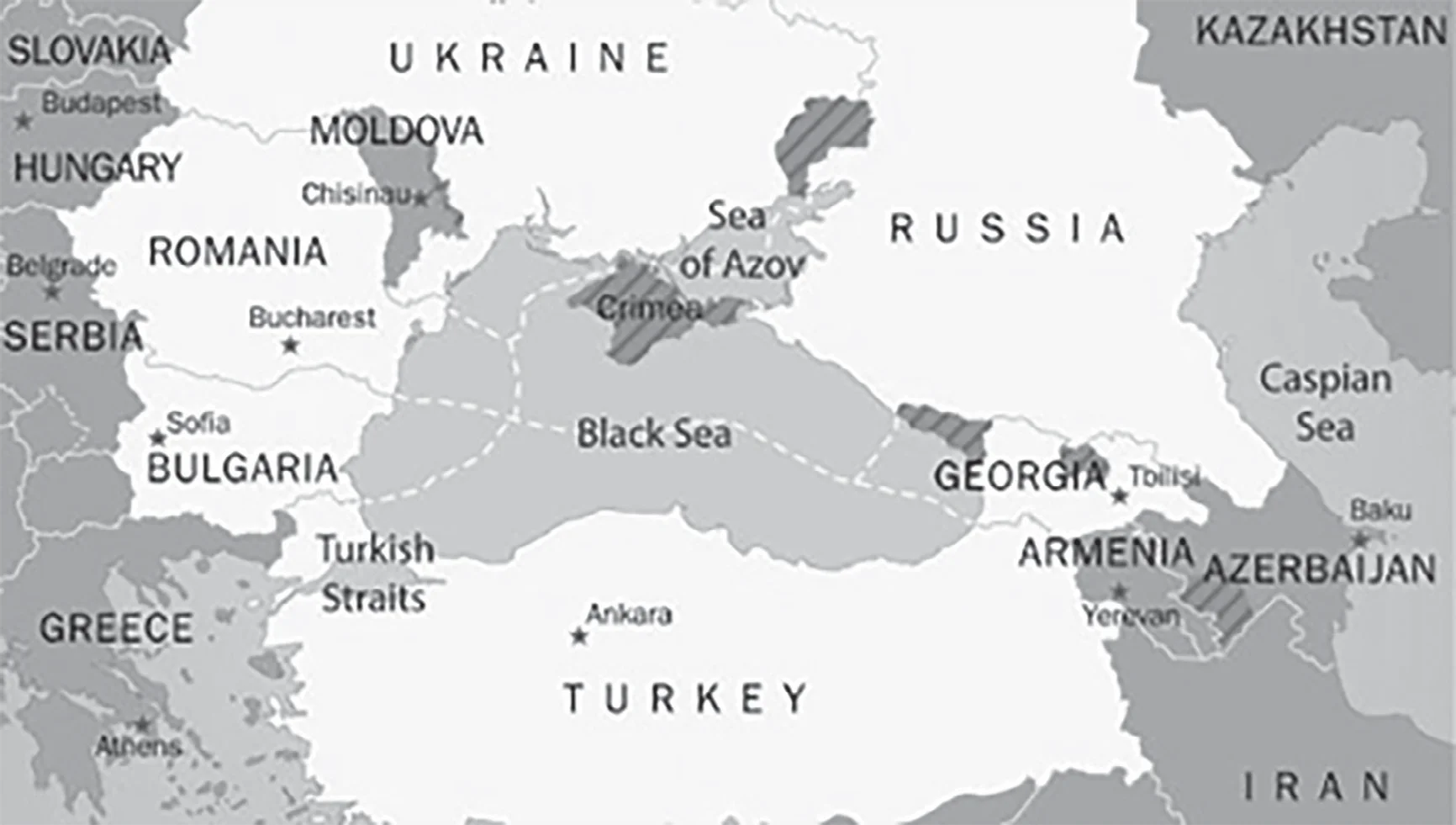
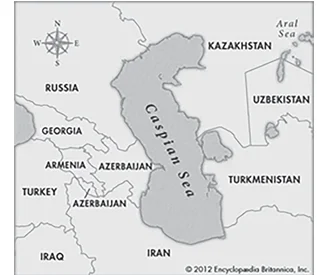
Pair 3 is correct: Caspian Sea is the world’s largest inland body of water, variously classed as the world’s largest lake or a full-fledged sea. It is an endorheic basin (a basin without outflows) located between Europe and Asia. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the west, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast. Mnemonic: TARIK (Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, Russia, Iran, Kazakhstan).
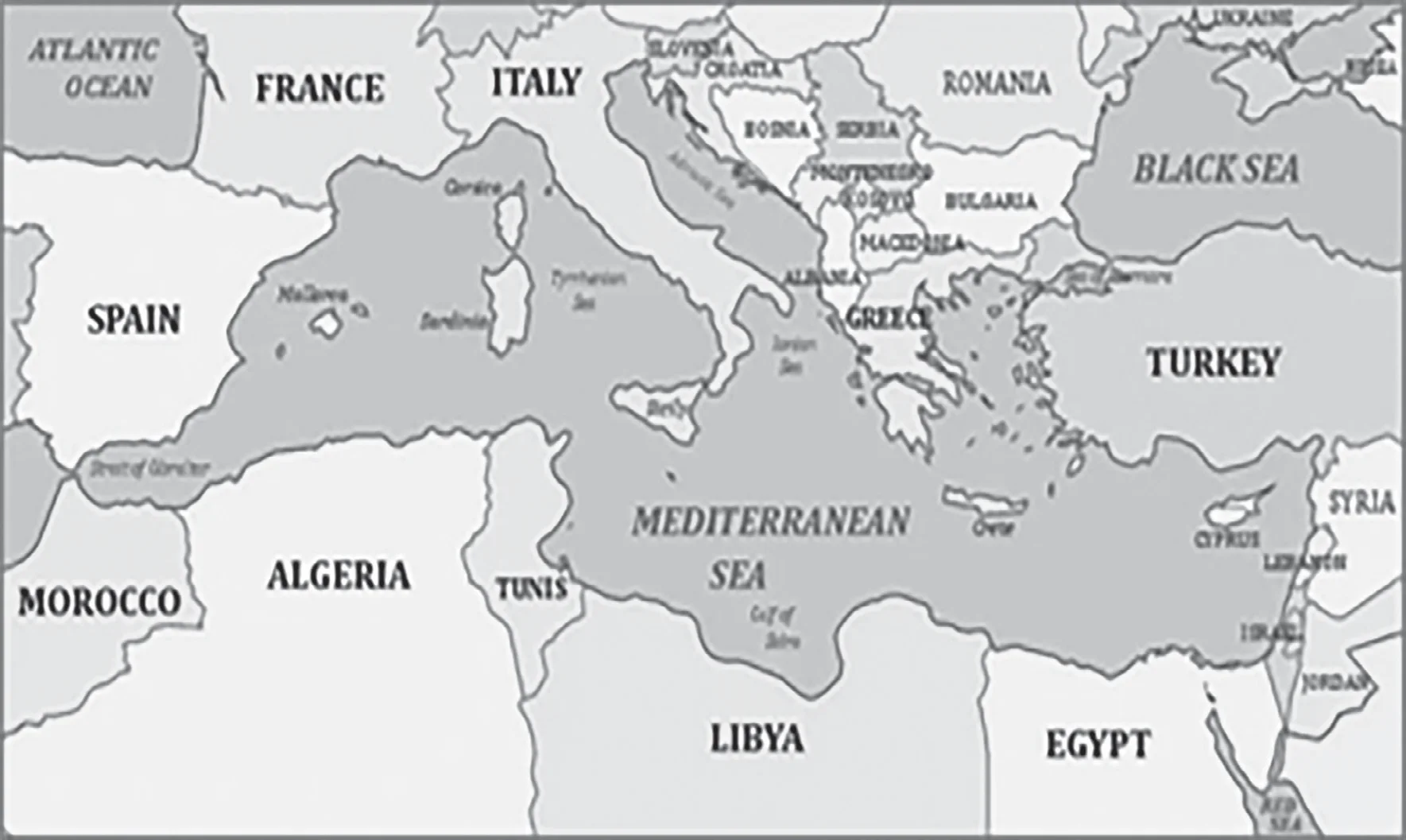
Pair 4 is correct: The Mediterranean Sea is an intercontinental sea that stretches from the Atlantic Ocean on the west to Asia on the east and separates Europe from Africa. The countries surrounding the Mediterranean in clockwise order: Spain, France, Monaco, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece, Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, and Morocco.
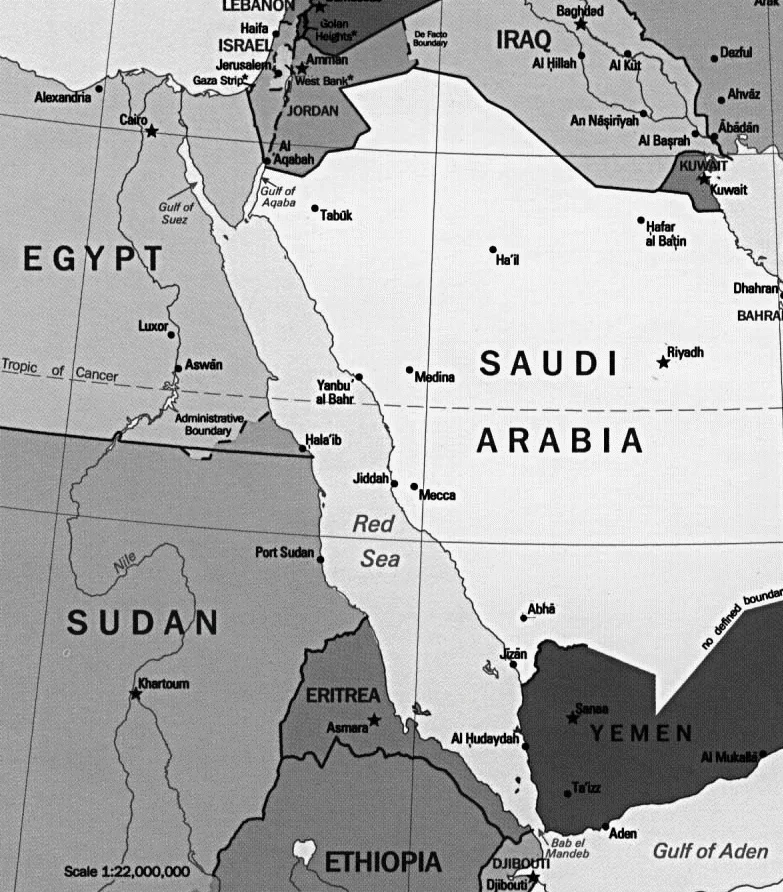
Pair 5 is incorrect: Red Sea is a narrow strip of water extending south-eastward from Suez, Egypt, for about 1,930 km to the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, which connects with the Gulf of Aden and thence with the Arabian Sea. The six countries bordering the Red Sea: Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea and Djibouti. The Red Sea is not bordered by Syria. Mnemonic: DESSEY (Djibouti, Eritrea, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Egypt, Yemen).

2018
Question 1
Consider the following statements
More than one-third of the world’s coral reefs are located in the territories of Australia, Indonesia and Philippines.
Coral reefs host far more animal phyla than those hosted by tropical rainforests.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
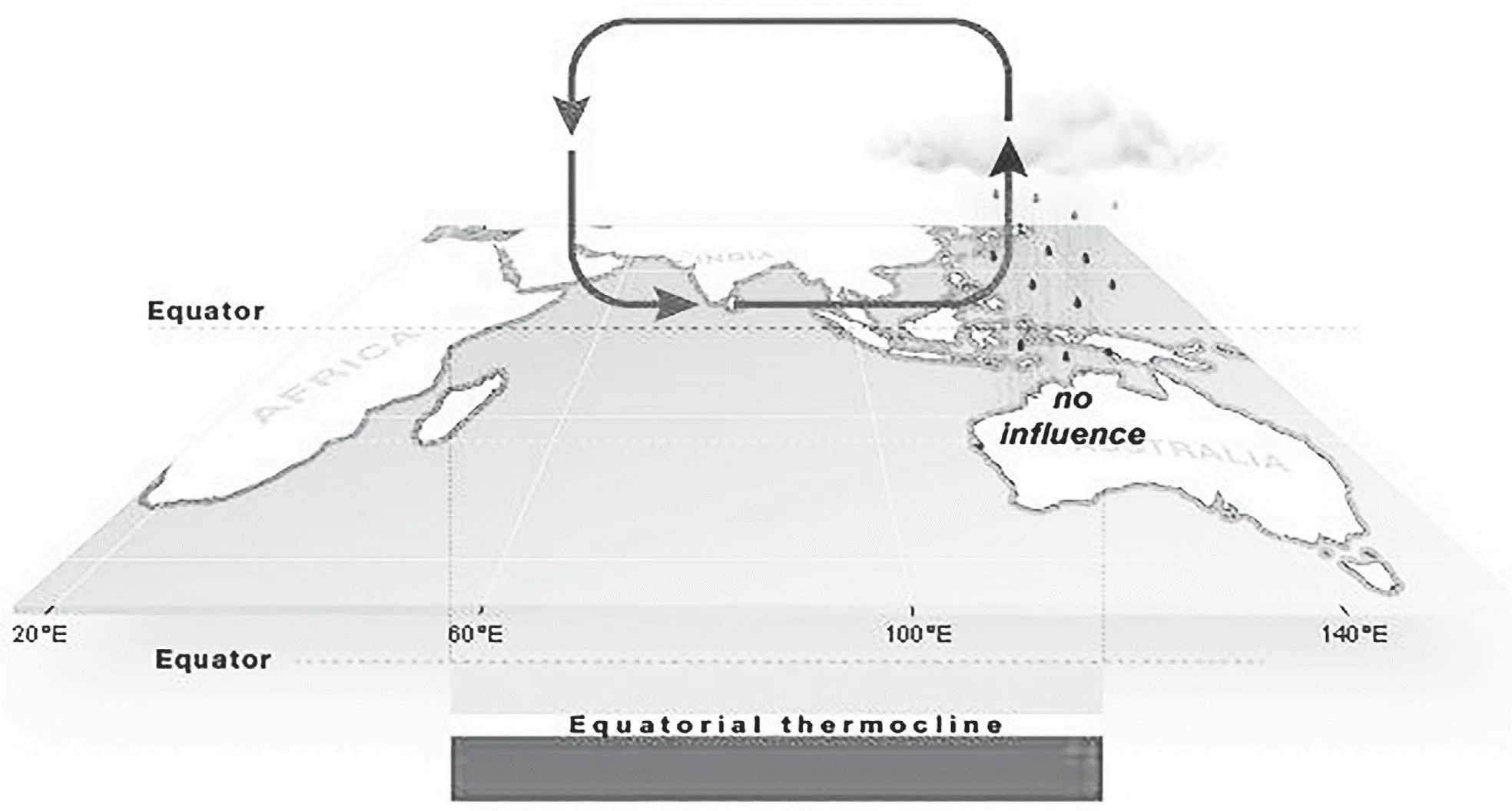
Sub-Theme: Coral reef distribution
Statement 1 is correct: The majority of reef- building corals are found within tropical and subtropical waters. These typically occur between 30° north and 30° south latitudes.
 Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD): Neutral Phase
Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD): Neutral Phase
Statement 2 is correct: The Indonesian/ Philippines archipelago, Great Barrier Reef of Australia, the Red Sea, and the Caribbean has the world’s greatest concentration of reefs and the greatest coral diversity.
Statement 3 is correct: Some scientists estimate that more than 25,000 described species from thirty-two of the world’s thirty-three animal phyla live in reef habitats four times the number of animal phyla found in tropical rainforests.
Question 2
Consider the following statements:
Andhra Pradesh and Jharkhand do not have gold mines.
Rajasthan has iron ore mines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 only
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Mines and Mineral/Mineral Rules
Statement 1 is incorrect: As per the MMDR Amendment Act 2015, the state governments will conduct auctions for grant of mineral concessions. The role of the central government is to prescribe the terms and conditions and procedures subject to which the auction shall be conducted.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Largest gold ore (primary) are located in Bihar (44%) followed by Rajasthan (25%) and Karnataka (21%), West Bengal, and Andhra Pradesh (3% each).
Statement 3 is correct: Hematite and magnetite are the most important iron ores in India and resources of hematite are spread in Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Meghalaya, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh.
Question 3
Which one of the following is an artificial lake?
(a) Kodaikanal (Tamil Nadu)
(b) Kolleru (Andhra Pradesh)
(c) Nainital (Uttarakhand)
(d) Renuka (Himachal Pradesh)
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Important Lakes of India
About Kodaikanal Lake:
Question 4
Consider the following statements:
Barren Island lies about 140 km east of Great Nicobar.
The last time the Barren Island volcano erupted was in 1991 and it has remained inactive since then.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Physiography of India
Statement 1 is correct: Barren Island Volcano is a part of Indian Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar islands is an active volcano in South Asia (along a chain of volcanoes from Sumatra to Myanmar).
Statement 2 is incorrect: Barren Island is located in Andaman Sea, about 140 km northeast of Port Blair.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The last time the volcanic eruptions were reported and linked to 28 September 2018 earthquakes in Sulawesi, Indonesia.
| NOTE: In 2015 UPSC has asked a question on Andaman & Nicobar Island, so for detailed information on A&N Islands please refer to the 2015 PYQ. |
Question 5
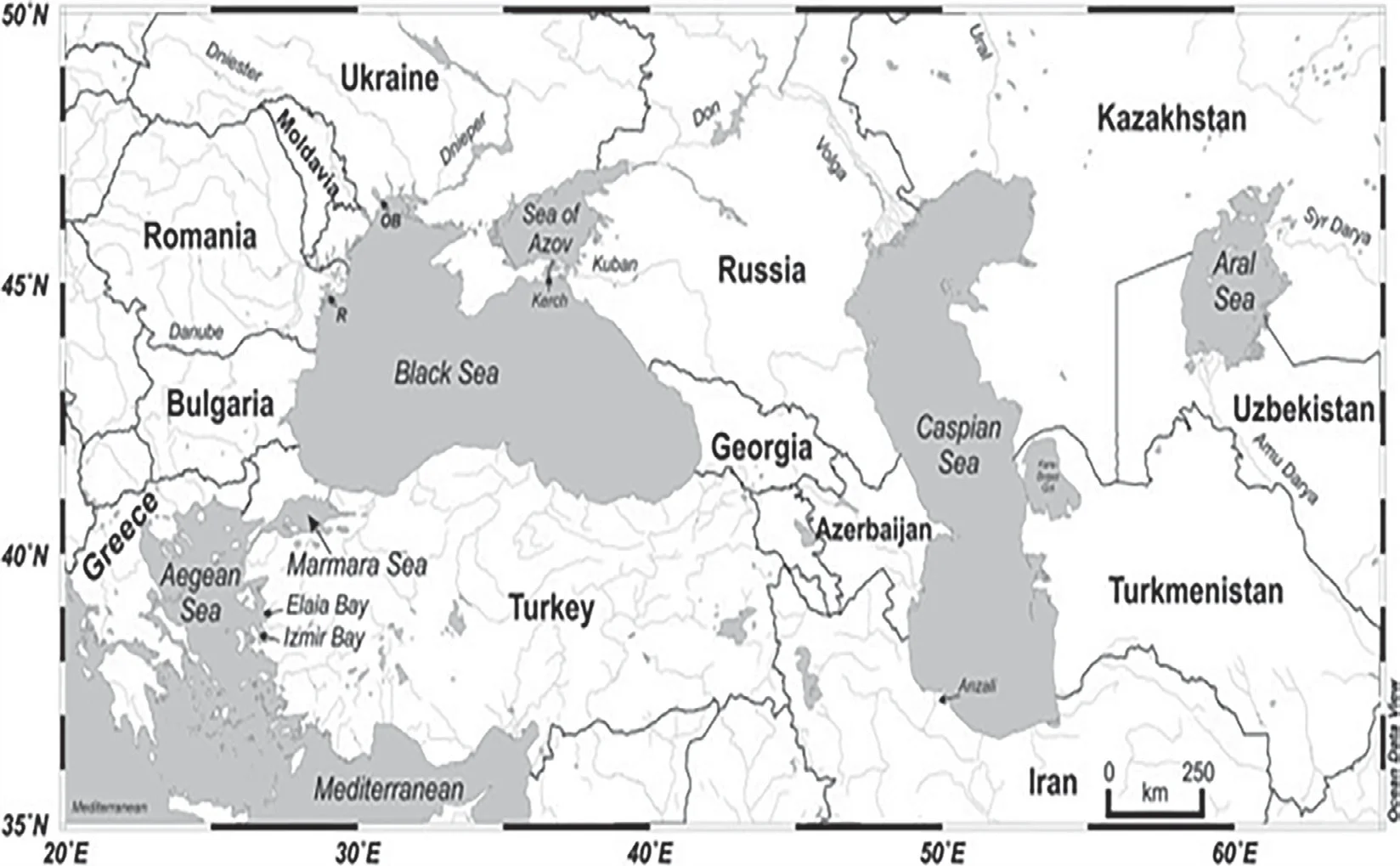
Which of the following has/have shrunk immensely/ dried up the recent past due to human activities?
Black Sea
Lake Baikal
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: World Map/Environment and Ecology
About Aral Sea:
Question 6
Among the following cities, which one lies on a longitude closest to that of Delhi?
(a) Bengaluru
(b) Hyderabad
(c) Nagpur
(d) Pune
ExplanationLongitude of Indian Cities
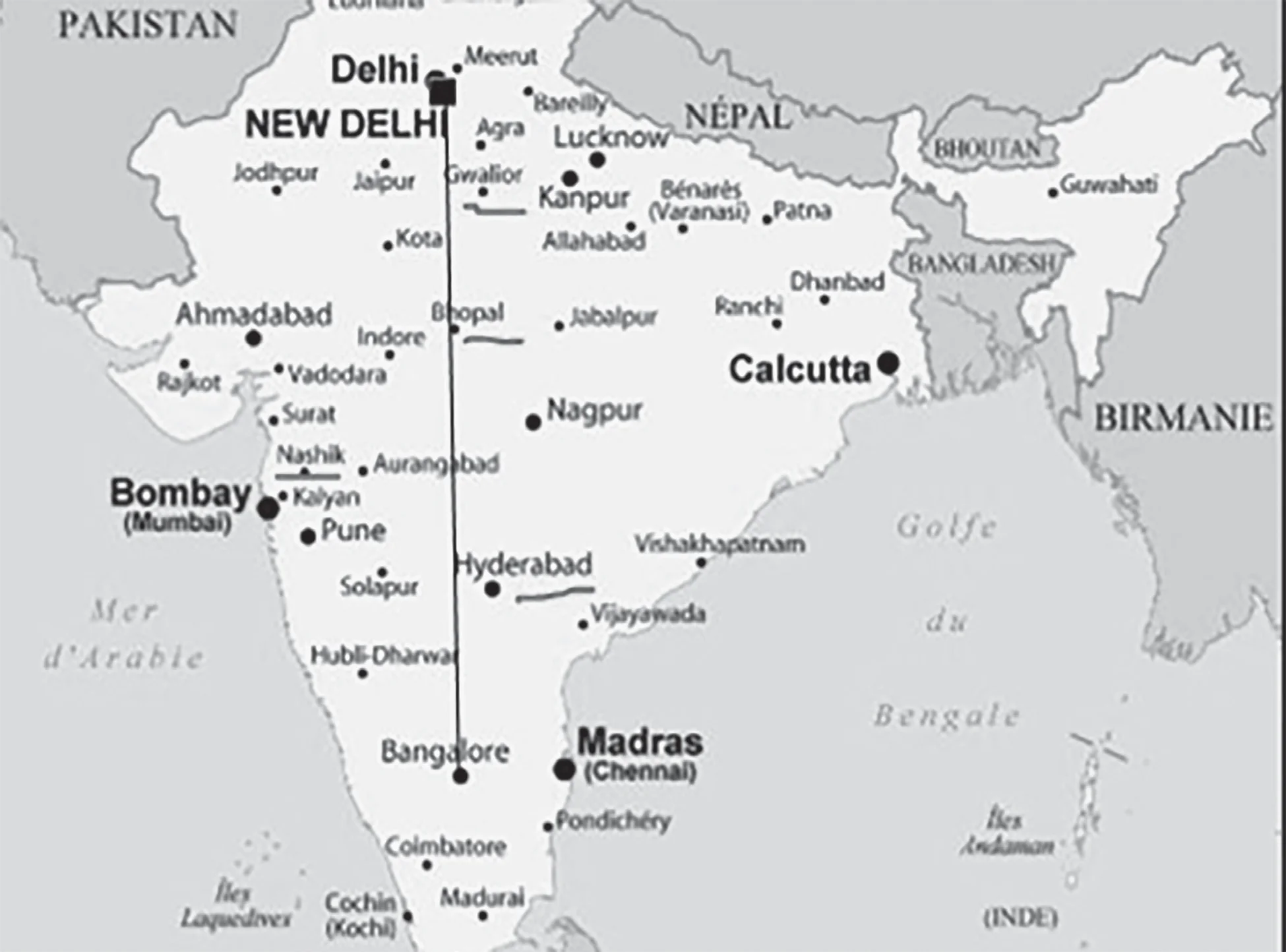
| NOTE: Map Practicing will not only help you to answer such questions but also it will help you to fetch some extra marks in UPSC Mains as well. |
Question 7
Consider the following pairs:
| Regions sometimes mentioned in news | Country |
| 1. Catalonia | Spain |
| 2. Crimea | Hungary |
| 3. Mindanao | Philippines |
| 4. Oromia | Nigeria |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 4 only
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Places was in News
Pair 1 is correct: Catalonia is located in Spain bordered by France and Andorra in the north, the Mediterranean Sea to the east, the autonomous community of Valencia to the south, and the autonomous community of Aragon to the west.
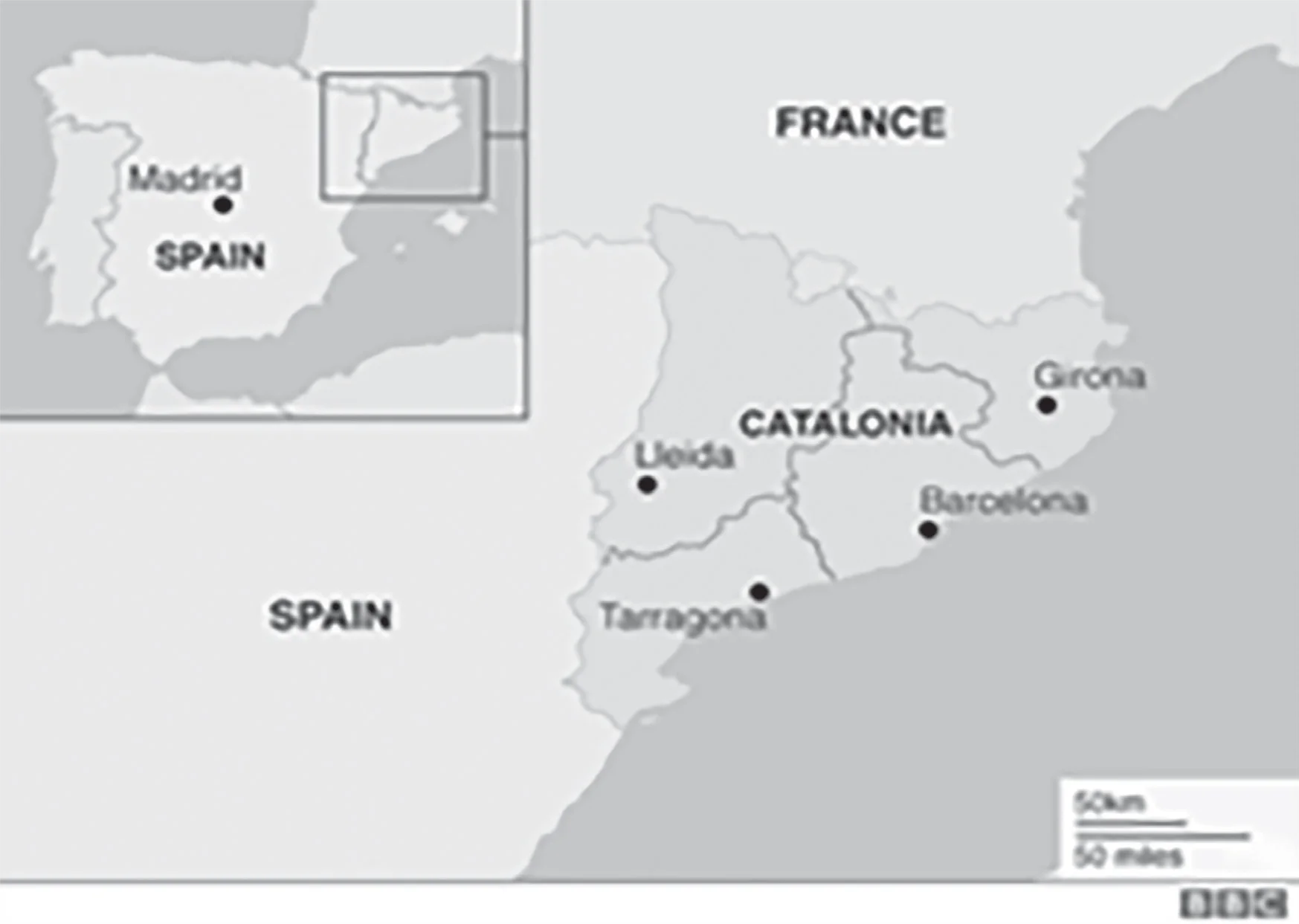
Pair 2 is incorrect: The Republic of Crimea, officially part of Ukraine, lies on a peninsula stretching from the south of Ukraine between the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov. It is separated from Russia by the narrow Kerch Strait.
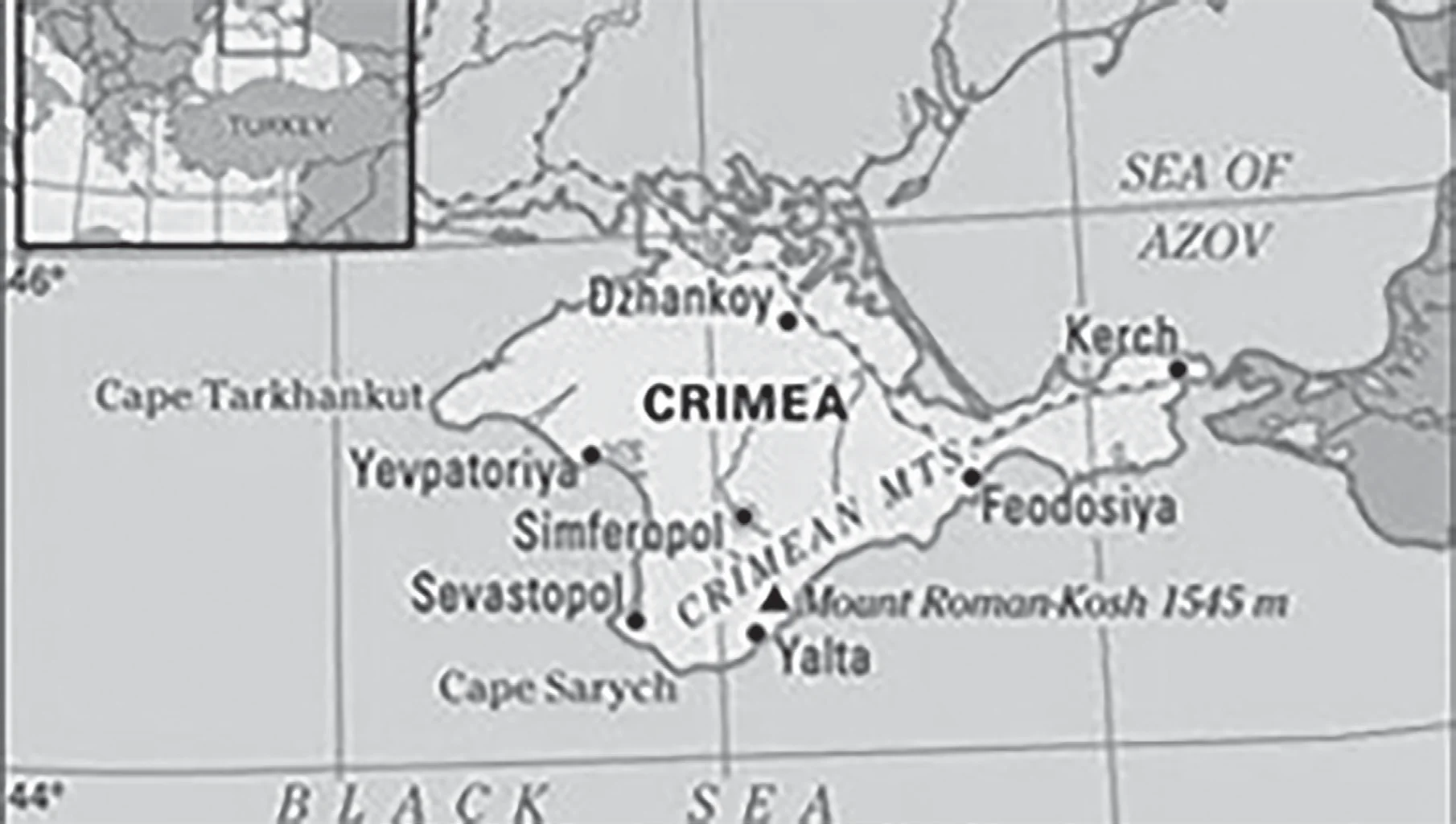
Pair 3 is correct: Mindanao is an island located in the Philippines. It is surrounded by the Bohol, Philippine, Celebes, and Sulu seas.
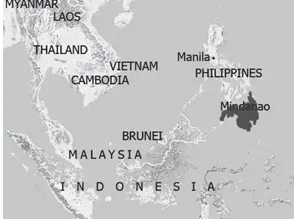
Pair 4 is incorrect: Oromia is a regional state of Ethiopia. Also, it is to be remembered that Ethiopia is a landlocked country located in Eastern Africa.
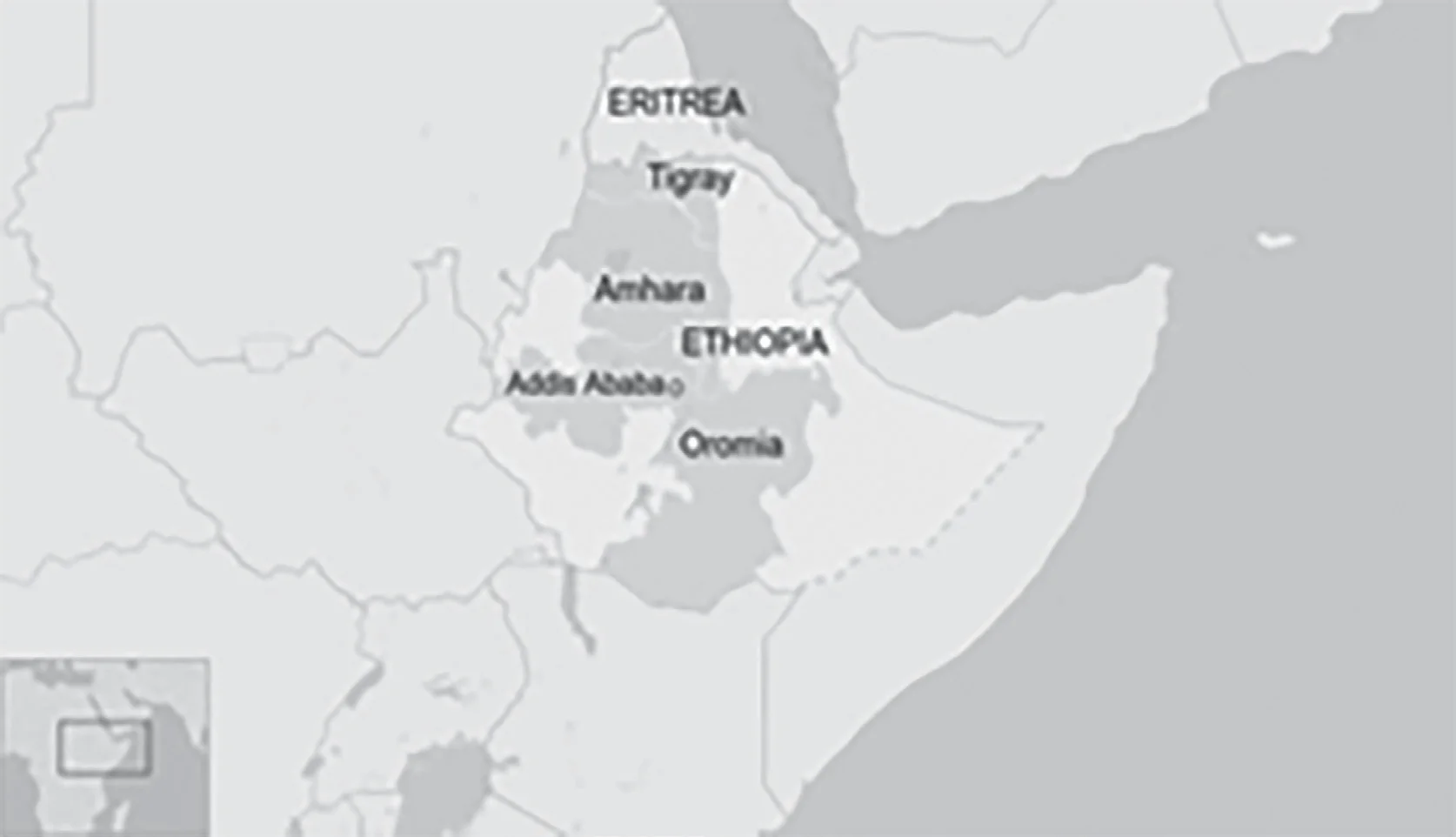
Question 8
Consider the following pairs:
| Towns sometimes mentioned in news | Country |
| 1. Aleppo | Syria |
| 2. Kirkuk | Yemen |
| 3. Mosul | Palestine |
| 4. Mazar-i-sharif | Afghanistan |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1 and 4
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 and 4
Ans: b
Sub-Theme: Places in News
Name of Cities and Countries:
2017
Question 1
With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct?
An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Indian Ocean Dipole
Statement 1 is incorrect: IOD is the difference in sea surface temperature between two poles or areas i.e. an eastern pole in the eastern Indian Ocean south of Indonesia, and a western pole in the Arabian Sea (western Indian Ocean).
Statement 2 is correct: Negative IOD events are often associated with La Nina and positive IOD events with El Nino.
Question 2
At one of the place in India, if you stand on the seashore and watch the sea, ‘you will find that the sea water recedes from the shore line a few kilometres and comes back to the shore, twice a day, and you can actually walk on the seafloor when the water recedes.’ This unique phenomenon is seen at
(a)Bhavnagar
(b) Bheemunipatnam
(c) Chandipur
(d) Nagapattinam
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Basic Trivia
About Chandipur Sea Beach:
Question 3
With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements:
1. The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim.
2. River Rangeet originates in Sikkim and it is a tributary of river Teesta.
3. River Teesta flows into Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Himalayan River/Drainage
Statement 1 is incorrect: Teesta originates in the Himalayas near Chunthang, Sikkim and flows to the south through West Bengal before entering Bangladesh.
Statement 2 is correct: River Rangeet originates in Sikkim, which is the largest river of Sikkim and also a tributary of river Teesta.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Originally, the river continued southward to empty directly into the Padma River (the main channel of Ganga in Bangladesh) but around 1787 the river changed its course to flow eastward to join the Jamuna river.
Question 4
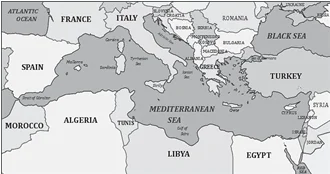
Mediterranean Sea is a border of which of the following countries?
Iraq
Lebanon
Syria
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4 only
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: World Map
Mediterranean Sea Bordering countries:
Question 5
Which of the following is geographically closest to Great Nicobar?
(a) Sumatra
(b) Borneo
(c) Java
(d) Sri Lanka
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Indian Ocean Region
About Great Nicobar:
Question 6
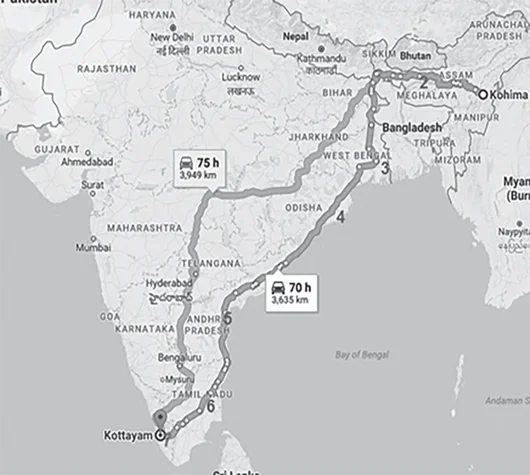
If you travel by road from Kohima to Kottayam, what is the minimum number of States within India through which you can travel, including the origin and the destination?
(a) 6
(b) 7
(c) 8
(d) 9
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: India Map
Question 7
Consider the following statements:
Western Ghats are spread over five states
Pulicat Lake is spread over two States only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: India Map
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Himalayas is spread across 12 Indian States: Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, two districts of Assam namely Dima Hasao and Karbi Anglong and Darjeeling and Kalimpong in West Bengal).
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Western Ghats are spread over six states namely Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Goa, Maharashtra and Gujarat.
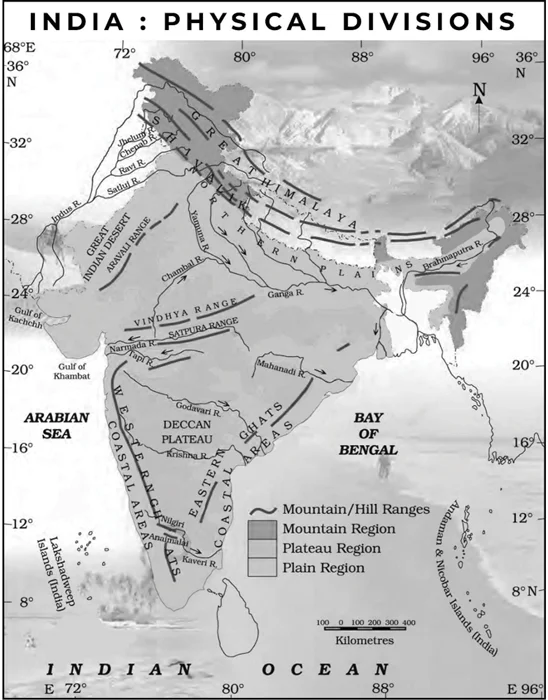
Statement 3 is correct: Pulicat Lake is the second largest brackish water lake in India and spreads over the two states namely Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. Large varieties of birds, including painted storks and Grey pelicans, frequent the area every year. Grey Pelican and Painted Stork both are near-threatened species under IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
2016
Question 1
Consider the following pairs:
| Famous Place | Region |
| 1. Bodhgaya | Baghelkhand |
| 2. Khajuraho | Bundelkhand |
| 3. Shirdi | Vidarbha |
| 4. Nasik (Nashik) | Malwa |
| 5. Tirupati | Rayalaseema |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched? (a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 2, 3, 4 and 5
(c) 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 3, 4 and 5
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Religious Places
Pair 1 is incorrect: Bodh Gaya is a holy landmark and pilgrimage destination linked with the Mahabodhi Temple Complex in Gaya, Bihar, India. It is one of the four main pilgrimage sites related with the life of Gautama Buddha, the other three are Kushinagar, Lumbini, Sarnath. In 2002, UNESCO declared the Mahabodhi Temple in Bodh Gaya a World Heritage Site.
Pair 2 is correct: The Khajuraho Temples in Madhya Pradesh’s Bundelkhand region are some of the most exquisite examples of medieval architecture in the world. It was built by the Chandela Dynasty between 950 and 1050 AD. There are Hindu and Jain temples among the monuments. In 1986, UNESCO designated these temples as World Heritage Sites. The temples are renowned for the symbolic architecture in the Nagara style. Initially reported in 1022 AD by Abu Raihan al Biruni and in AD 1335 by Ibn Battuta.
Pair 3 is incorrect: Shirdi is a city located in the Rahata taluka of Ahmednagar District, Maharashtra. According to legend, Sai Baba arrived in Shirdi in 1872 and remained there until his death on October 15, 1918.
Pair 4 is incorrect: Nashik is situated on the banks of river Godavari in the northwest region of Maharashtra and is famous for Kumbh Mela, which is held every 12 years.
Pair 5 is correct: Tirupati is a city situated in the Rayalaseema region of the Chittoor district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. Shri Venkateswara Temple is well-known for being a Hindu temple.
Question 2
Which of the following is/are tributary/ tributaries of Brahmaputra?
Kameng
Lohit
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Himalayan Drainage System/ Brahmaputra
Option 1 and 3 are correct: Dhansiri, Dibang and Lohit are the left bank tributaries of Brahmaputra River.
Option 2 is correct: Kameng is a right bank tributary of Brahmaputra River. Other major right bank tributaries of Brahmaputra are Subansiri, Manas, Sankosh.
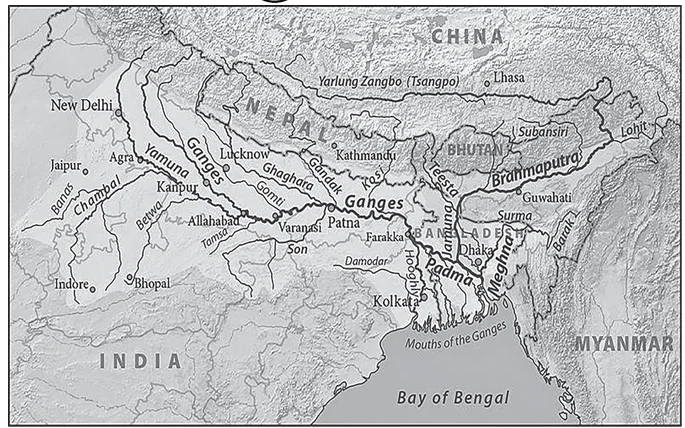
Question 3
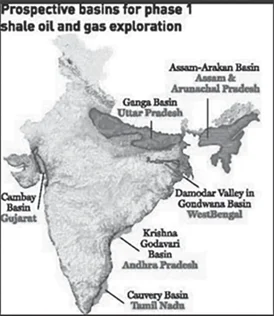
In which of the following regions of India are shale gas resources found?
Cauvery Basin
Krishna-Godavari Basin
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Resource/Map
About Shale Gas in India:
2015
Question 1
In the South Atlantic and South-Eastern Pacific regions in tropical latitudes, cyclone does not What is the reason?
(a) Sea surface temperatures are low
(b) Inter-tropical Convergence Zone seldom occurs
(c) Coriolis force is too weak
(d) Absence of land in those regions
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Wind Movement
Option (b) is correct: The absence of cyclones can be demonstrated by the seldom occurance of ITCZ Convergence zone in the south east Pacific and south Atlantic regions. Due to this there is no creation of ideal conditions for Tropical Cyclone, for e.g. instead of low, there is high vertical wind sheer.
Cyclone:
Classification of Cyclone:
Temperate cyclone
Factors Responsible for for Tropical Cyclone Formation:
Question 2
Consider the following statements:
1. The winds which blow between 30 N and 60 S latitudes throughout the year are known as westerlies.
2. The moist air masses that cause winter rains in North-Western region of India are part of westerlies
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Wind Movement/Indian Monsoon Option (b) is correct: Generally the westerlies flow between 30° and 60°N and 30° and 60°S
latitude respectively. The moist air masses that
cause winter rains in North-Western region of India are part of westerlies which are also known as winter disturbances.
Westerlies:
|
Note: In this question, the examiner made a simple but difficult to observe change in latitudes i.e “30 N and 60 S latitudes” to make the statement incorrect. Always read questions carefully and cautiously. Although we read incorrect statements in the exam hall, our mind correlates it to what we have read in the textbook/standard book, making it difficult to identify minor twists and twicks. Earlier, UPSC had asked questions on westerlies in 2011. Revising PYQ and doing peripheral research is always important from prelims perspective. |
Question 3
“Each day is more or less the same, the morning is clear and bright with a sea breeze; as the Sun climbs high in the sky, heat mounts up, dark clouds form, then rain comes with thunder and lightning. But the rain is soon over.”
Which of the following regions is described in the above passage?
(a) Savannah
(b) Equatorial
(c) Monsoon
(d) Mediterranean
ExplanationAns: (b)
Sub-Theme: Biomes/World Climate
Option (b) is correct: The above sentence indicates the characteristics of the Equatorial region.
Equatorial Climate:
|
NOTE: Again a direct question came from GC Leong. Also please learn to identify keywords/keyphrases, anyone with a decent reading of NCERTs and GC Leong could easily answer this question. Questions on Equatorial climate have been repeated in 2013, therefore for detailed explanation on Equatorial Biomes please refer to respective PYQs. |
Question 4
What explains the eastward flow of the equatorial counter current?
(a) The Earth’s rotation on its axis
(b) Convergence of the two equatorial currents
(c) Difference in salinity of water
(d) Occurrence of the belt of calm near the equator
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Equatorial Counter Currents
Option (a) is incorrect: As the earth rotates from west to east, water near the equator tends to move from east to west (due to the prevailing winds). This leads to the formation of Equatorial currents, both North and South of the equator.
Option (b) is correct: Piling up of water in the western pacific due to the convergence of the North Equatorial Current and South Equatorial Current. This piled up water then flows from west to east, under the effect of gravity, resulting in Counter Equatorial Current (CEC).
Option (c) is incorrect: Difference in salinity of water greatly influences vertical currents and its influence on horizontal movement is less significant.
Option (d) is incorrect: The Doldrums/ Equatorial belt around the Equator are zones of very calm winds, it has little effect on eastward flow of equatorial counter current.
Question 5
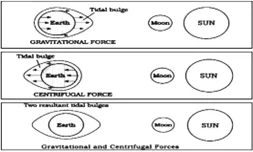
Tides occur in the oceans and seas due to which among the following?
Gravitational force of the Moon
Centrifugal force of the Earth
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Formation of Tides
Question 6
In India, the steel production industry requires the import of:
(a) Saltpetre
(b) Rock phosphate
(c) Coking coal
(d) All of the above
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Industry
Option (a) is incorrect: Saltpetre (Potassium nitrate) is not used in the production of Steel. It is used in the production of fertilizers, tree stump removal, rocket propellants and fireworks.
Option (b) is incorrect: Rock phosphate is used in the production of fertilizer and not for the production of Steel.
Option (c) is correct: The production of steel requires 0.8 tonnes of coking coal to produce one tonne of Steel. And about 85% of the coking coal requirement of the domestic steel industry is presently being met through imports.
Question 7
In India, in which one of the following types of forests is teak a dominant tree species?
(a) Tropical moist deciduous forest
(b) Tropical rainforest
(c) Tropical thorn scrub forest
(d) Temperate forest with Grasslands
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Natural Vegetation of India About Tropical Moist Deciduous Forest:
Climatic Conditions:
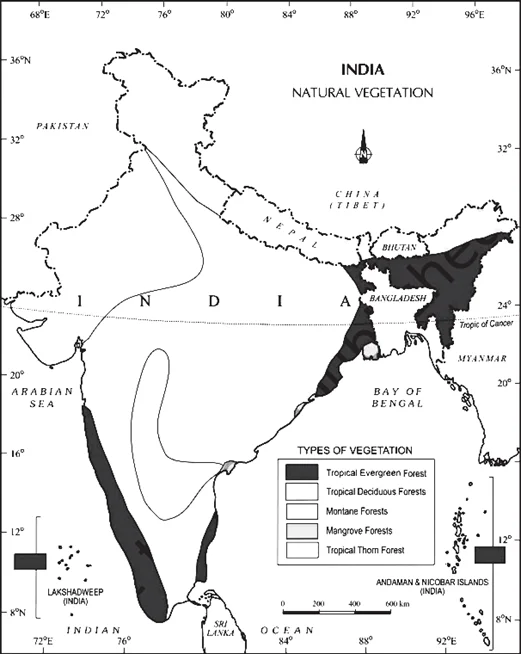
Characteristics:
Question 8
Consider the following rivers:
Indravati
Pranahita
Pennar
Which of the above are tributaries of Godavari?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 2 and 3 only
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Peninsular Drainage/River
About River Godavari:
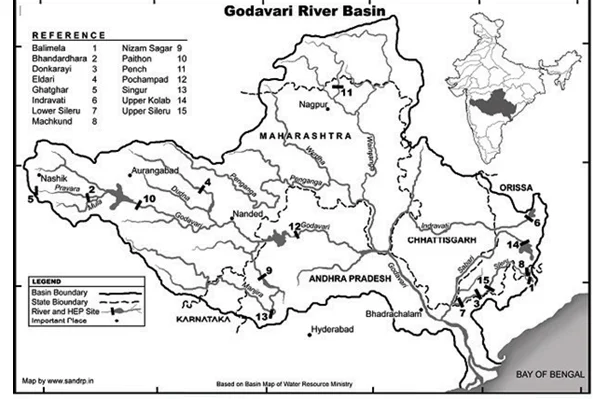
Additional Information:
Question 9
In a particular region in India, the local people train the roots of living trees into robust bridges across the As the time passes, these bridges become stronger. These unique ‘living root bridges’ are found in
(a) Meghalaya
(b) Himachal Pradesh
(c) Jharkhand
(d) Tamil Nadu
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Living Root Bridges
Living root bridges also known as Jing Kieng Jri are found in Meghalaya are the aerial bridges that are built by weaving and manipulating the roots of the Indian rubber tree.

About Living Root Bridges:
Question 10
Consider the following States:
Himachal Pradesh
Mizoram
In which of the above States do ‘Tropical Wet Evergreen Forests’ occur?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Natural Vegetation of India
Option 1 and 3 are correct: In India, tropical wet evergreen forests are found on the eastern and western slopes of the Western Ghats in such states like Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala and Maharashtra. And also found in Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Tripura, Mizoram, West Bengal and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Option 2 is incorrect: Himachal Pradesh comes under the Montane type of forest.
Question 11
Which one of the following regions of India has a combination of mangrove forest, evergreen forest and deciduous forest?
(a) North Coastal Andhra Pradesh
(b) South-West Bengal
(c) Southern Saurashtra
(d) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Natural vegetation of India
About Andaman and Nicobar Islands:
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands have a tropical rainforest canopy. The Middle Andamans harbours mostly moist deciduous forests. North
Andamans is characterised by the wet evergreen type, with plenty of woody climbers. Also The coastal regions have mangrove forests.
Question 12
Which one of the following pairs of States of India indicates the easternmost and westernmost State?
(a) Assam and Rajasthan
(b) Arunachal Pradesh and Rajasthan
(c) Assam and Gujarat
(d) Arunachal Pradesh and Gujarat
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Basic Understanding of Indian map
Most Points of India:
Question 13
Consider the following pairs:
| Place of Pilgrimage | Location |
| 1. Srisailam | Nallamala Hills |
| 2. Omakareshwar | Satmala Hills |
| 3. Pushkar | Mahadeo Hills |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Famous pilgrim places of India
Pair 1 is correct: Srisailam is the shrine of Lord Mallikarjuna on the flat top of Nallamala Hills in Andhra Pradesh.The temple is dedicated to the deities Shiva and Parvati. This temple is one of Lord Shiva’s twelve Jyotirlingas and one of Goddess Parvati’s eighteen Shakti Peethas. The lingam is a representation of Shiva, who is worshiped as Mallikarjuna. Bhramaramba is a representation of Parvati.
Pair 2 is incorrect: Omkareshwar is situated on the Mandhata hills in Madhya Pradesh (ancient name: Shivpuri). The name “Omkareshwar” comes from the way the River Narmada flows here as it circles the Mandhata hill in the shape of a “Om.” Omkareshwar is a Hindu temple where the god Shiva is worshiped. It is one of Shiva’s 12 cherished Jyotirlinga shrines.
Pair 3 is incorrect: The Mahadeo Hills are a range of hills in Madhya Pradesh state of central India. Whereas, Pushkar is situated on the shore of Pushkar Lake in Ajmer, Rajasthan. It is famous for the red spired Brahma Temple.
Question 14
Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea?
(a) Syria
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Israel
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: World Map
Correct answer is Option (b): Jordan is a landlocked country and doesn’t have any opening into the Mediterranean Sea.
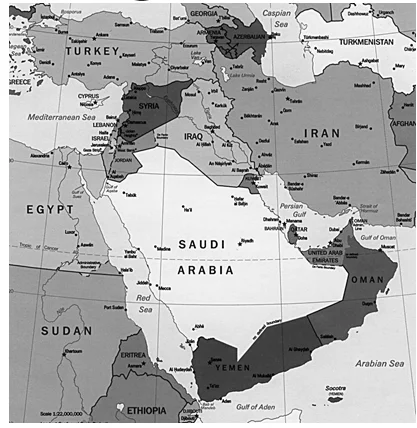
NOTE: In terms of world map, UPSC absolutely loves this region and there are many instances that they have asked questions from this region. Also, This region also very much remains in the news. Therefore, reading newspapers and practicing maps is very important for UPSC.
2014
Question 1
The seasonal reversal of winds is the typical characteristic of
(a) Equatorial climate
(b) Mediterranean climate
(c) Monsoon climate
(d) All of the above climates
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Biomes/World Climate The Monsoon Climate (Am):
The monsoon climate is a type of weather where it rains a lot.
Question 2
Which of the following phenomena might have influenced the evolution of organisms?
Glacial cycles
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Evolution vs Glacial cycle
Factors that might have influenced the Evolution of Organisms:
Question 3
In India, the problem of soil erosion is associated with which of the following?
Deforestation
Tropical climate
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Soil degradation
Statement 1 is incorrect: Terracing is the practice of creating nearly level areas in a hillside area. protected from erosion by other soil barriers.
Statement 2 is correct: Deforestation is one of the major reasons for soil erosion. It includes cutting and felling of trees, removal of forest litter. Browsing and trampling by livestock, forest fires, also leads to deforestation, etc.
Statement 3 is incorrect: In the tropical monsoon climate people are mainly engaged in agriculture. Crops growing: rice, wheat, pulses, cotton, jute, sugarcane, oilseeds, coffee, tea and various types of fruits and vegetables.
Question 4
Consider the following pairs:
| Region | Well-known for the production of |
| 1. Kinnaur | Areca nut |
| 2. Mewat | Mango |
| 3. Coromandel | Soya bean |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Famous crop and places
Pair 1 is incorrectly matched: Kinnaur is mostly famous for apples. The production of Areca nuts is mostly confined to Karnataka, Kerala and Assam.
Pair 2 is incorrectly matched: The main occupation of Mewat is agriculture along with allied and agro-based activities, it is not famous for mango. Major mango-growing states are Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka,
Pair 3 is incorrectly matched: In the Coromandel Coast, major cultivations are Rice, pulses, sugarcane, cotton, peanuts, etc. Production of soybean in India is dominated by Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh which contribute 89 percent of the total production.
Question 5
Consider the following towns of India:
Chanderi
Kancheepuram
Karnal
Which of the above are famous for the production of traditional sarees/fabric?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 1, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Traditional Saree/fabric
Option 1 and 4 are incorrect: Bhadrachalam and Karnal are not famous for the production of traditional sarees/fabric.
Option 2 and 3 are correct: Chanderi sarees is a traditional sari made in Chanderi, Madhya Pradesh, India. Kanjeevaram is a traditional sari from Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu, India, that is usually handwoven in mulberry silk and has pure gold or silver zari that renders it a festive quality.
Question 6
If you travel through the Himalayas, you are likely to see which of the following plants are naturally growing there?
Rhododendron
Sandalwood
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Natural Vegetation of India
Statement 1 is correct: Evergreen broad-leaf trees, such as oaks and chestnuts, belong to wet temperate types of forests (1000 and 2000 metres).
Statement 2 is correct: Coniferous trees like Rhododendron, pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce and cedar, are found in the temperate forests (1500 and 3000 metres).
Statement 3 is incorrect: Sandalwoods are found in tropical moist deciduous forests or monsoon forests which are found in western ghats, Deccan plateau, northern plains.
|
NOTE: This is straight from Class 9 Geography NCERT Chapter 5. This underlines the importance of reading NCERTs both for UPSC Pre and Mains perspective. |
Question 7
With reference to ‘Changpa’ community of India, consider the following statements:
They rear the Pashmina goats that yield fine wool
They are kept in the category of Scheduled tribes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Tribe of India
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Changpa are a semi-nomadic people, they are mainly found in the Changtang, a high plateau that stretches across the cold desert of Ladakh.
Statement 2 is correct: They are raised for ultra- fine cashmere wool, also known as pashmina once woven.
Statement 3 is correct: In 1989, Changpas were declared as the Scheduled Tribes.
Question 8
Which of the following have coral reefs?
Gulf of Kachchh
Gulf of Mannar
Sunderbans
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Coral Reef
Coral reefs are underwater ecosystems formed by colonies of tiny animals called coral polyps. These animals secrete a hard, calcium carbonate exoskeleton that provides a foundation for the growth of other corals and a diverse array of marine organisms. Coral reefs are found in tropical and subtropical waters around the world, particularly in the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and the Caribbean Sea.
Statement 1, 2 and 3 are correct: Coral reefs in India are found in a lot of areas including the Gulf of Kutch, Gulf of Mannar, Palk Bay, Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep Islands.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Sundarban is the largest deltaic region of the world and encompasses over hundreds of islands (105), with a maze of innumerable rivers, rivulets, and creeks but does not have any coral reef.
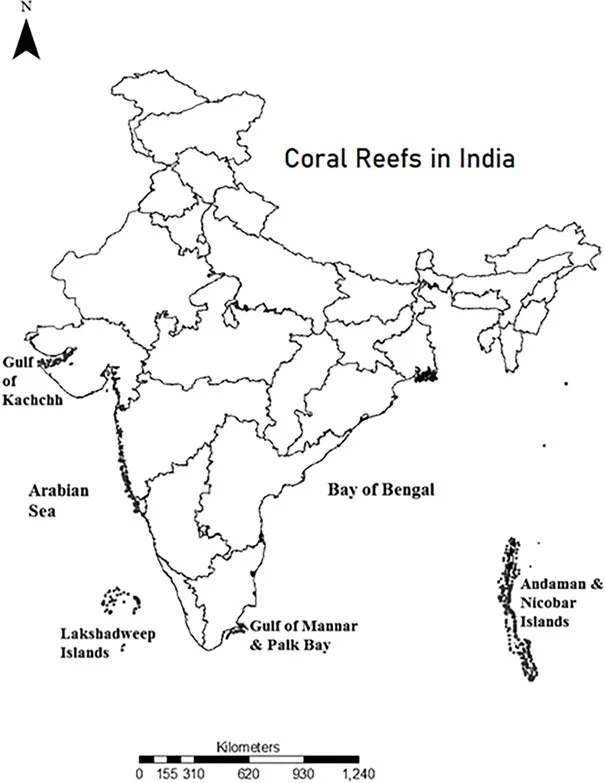
Question 9
Consider the following pairs:
| National Highway | Cities Connected |
| 1. NH4 | Chennai and Hyderabad |
| 2. NH6 | Mumbai and Kolkata |
| 3. NH15 | Ahmedabad and Jodhpur |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched ?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: National Highway/Map based
| National Highway | Cities Connected | Length (km) |
| NH 4 | Mayabunder to Port Blair- Chidiyatapu (Andaman) | 230 |
| NH 6 | Jorabat (Meghalaya) – Selling (Mizoram) | 1873 |
| NH 15 | Baihat (Assam) – Wakro (Arunachal Pradesh) | 664 |
Question 10
Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’?
(a) Andman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Andaman Map based
The 10 degree channel is a water body that separates Andaman in the North and Nicobar in the South. Both the Andaman Islands and Nicobar Islands together form the Indian Union Territory (UT) of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
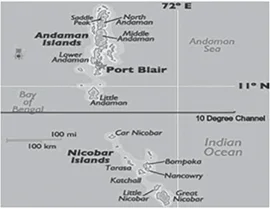
Additional Information:
Question 11
Consider the following pairs:
1. Dampa Tiger Reserve : Mizoram
2. Gumti Wildlife Sanctuary : Sikkim
3. Saramati Peak : Nagaland
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: c
Sub-Theme: Major places of States
Statement 1 is correct: The Dampa tiger reserve is located in Mizoram. It is located in the Lushai Hills and spans an area of around 500 km2 at an altitude of 800-1,100 m. It is a component of Project Tiger and was designated a tiger reserve in 1994.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Gumti Wildlife Sanctuary is a Wildlife Sanctuary in Tripura. This sanctuary is the place for many animals like elephants, sambar, buffalo, yapping deer, wild goats and numerous more. The sanctuary has become a haven for reptiles as well.
Statement 3 is correct: Saramati peak rising above the surrounding peaks at the mountainous border of Nagaland state, India. It is one of the ultra-prominent peaks of Southeast Asia. It forms a natural boundary between India and Myanmar.
Question 12
Consider the following rivers:
Lohit
Subansiri
Which of the above flows/flow through Arunachal Pradesh?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Brahmaputra and its tributary
Statement 1 is incorrect: Barak river is one of the major rivers of South Assam. The 564 km long river is part of the Surma-Meghna River System. It rises in the Manipur Hills in northern Manipur state, India, where it is called the Barak. The Barak River flows through the states of Manipur, Nagaland, Mizoram, and Assam in India and into the Bay of Bengal.
Statement 2 is correct: Lohit River is a tributary of the Brahmaputra River. It flows into Arunachal Pradesh after starting from eastern Tibet’s Zayal Chu range.
Statement 3 is correct: Both the Tibetan Autonomous Region of China and the Indian states of Assam and Arunachal Pradesh are traversed by the Subansiri River. It is the biggest tributary of River Brahmaputra.
Question 13
Consider the following pairs:
| Hills | Region |
| 1. Cardamom Hills | Coromandel Coast |
| 2. Kaimur Hills | Konkan Coast |
| 3. Mahadeo Hills | Central India |
| 4. Mikir Hills | North-East India |
Which of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 3 and 4
(d) 2 and 4
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Physiography of India/Map based
Pair 1 is incorrect: Cardamom Hills are located in Kerala and south-west Tamil Nadu. It is situated on India’s southwest coast, whereas, the Coromandel coast is located in Tamil Nadu’s eastern coastal plain
Pair 2 is incorrect: Kaimur Hills is in the eastern portion of the Vindhya Range, present in Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
Pair 3 is correct: Mahadeo Hills are located in the northern part of the Satpura Range in Madhya Pradesh state of central India.
Pair 4 is correct: Mikir Hills can be found in Assam, south of Kaziranga National Park. It is a region of the Karbi- Plateau in northeastern India. The highest mountain in the Mikir Hills is Dambuchko.
Question 14
Turkey is located between:
(a) Black Sea and Caspian Sea
(b) Black Sea and Mediterranean Sea
(c) Gulf of Suez and Mediterranean Sea
(d) Gulf of Aqaba and Dead Sea
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: World Map
Option (b) is correct: Turkey is located between Black Sea and Mediterranean Sea.
About Geographic Boundary of Turkey:
Turkey is bordered on its northern side by the Black Sea, on its northeast by Georgia and Armenia, on its east by Azerbaijan and Iran, on its southeast by Iraq and Syria, on its southwest and western edges by the Mediterranean Sea and the Aegean Sea, and on its northwest by Greece and Bulgaria.
Question 15
What is the correct sequence of occurrences of the following cities in South-East Asia as one proceeds from south to north?
Hanoi
Jakarta
Singapore
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 4-2-1-3
(b) 3-2-4-1
(c) 3-4-1-2
(d) 4-3-2-1
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Major cities/capital cities
The correct sequence of cities in South-East Asia as one proceeds from south to north would be Jakarta > Singapore > Bangkok > Hanoi.
2013
Question 1
Variations in the length of daytime and night time from season to season are due to:
(a) The earth’s rotation on its axis
(b) The earth’s revolution around the sun in an elliptical manner
(c) Latitudinal position of the place
(d) Revolution of the earth on a tilted axis
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Motion of the Earth
Option (d) is correct: Variations in the length of daytime and night time from season to season due to revolution of the earth on a tilted axis. Movement of the earth around the sun in a fixed path or orbit.It takes 365¼ days (one year) to revolve around the sun. As a result of the earth’s revolution, you can observe that there are days and nights as well as seasonal fluctuations.
Question 2
Which of the following is/are unique characteristic/ characteristics of equatorial forests?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Major Climate of the World
Statement 1 is correct: The tropical rain forest appears from above as a dense canopy of greenery, only disturbed by huge rivers or areas cleared for farming.
Statement 2 is correct: The higher temperatures in the tropics cause higher rates of metabolism, ecological dynamics and coevolutionary processes, which generate and maintain higher biodiversity, which results in the coexistence of a large number of species.
Statement 3 is correct: All plants (most epiphytes) strive upwards for sunshine, resulting in an odd layer structure. Numerous evergreen trees that produce tropical hardwoods like mahogany, ebony, dyewoods, etc. make up the equatorial vegetation.
Natural Vegetation:
Question 3
The annual range of temperature in the interior of the continents is high as compared to coastal areas. What is/are the reason/reasons?
Variation in altitude between continents and oceans
Presence of strong winds in the interior
Heavy rains in the interior as compared to coasts
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Distribution of the temperature of Earth
Statement 1 is correct: One major factor affecting the distribution of the temperature of Earth is the distribution of Land and Oceans. The loss of heat from the continents is greater than that from the oceans because there is more land in the northern hemisphere and more water in the southern hemisphere, and because the specific heat of land and water differs greatly.
Statement 2 is not correct: The variation in altitude between continents and oceans is not a valid reason for the high annual range of temperature in the interior of the continent as compared to coastal areas. This is because as compared to oceans, the lands heats up and cools down faster.
Statement 3 is not correct: Annual precipitation is usually low in the interior areas as well as the presence of weak winds in the interior.
Statement 4 is not correct: The interiors in Central Asia receive very poor rainfall due to distance from the sea.
Question 5
“Climate is extreme, rainfall is scanty and the people used to be nomadic herders.”
The above statement best describes which of the following regions?
(a) African Savannah
(b) Central Asian Steppe
(c) North American Prairie
(d) Siberian Tundra
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Biomes/World Climate
Steppe Climate or Temperate Continental Climate or Temperate Grassland Climate:
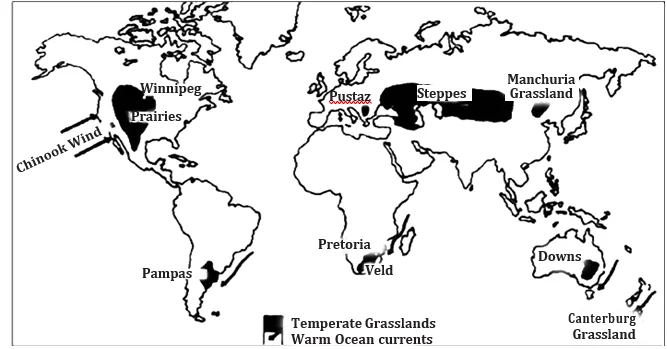
Temperature:
Precipitation:
Nomadic herding in Asian Steppes
| NOTE: Learn to pick keywords/keyphrases from the sentence. Here – ‘extreme climate’; ‘scanty rainfall’; ‘nomadic herders’, etc. all these keywords resemble the characteristics of the Central Asian Steppe region. Earlier UPSC had asked questions about Tropical Savannah Region and equatorial climate in 2012 and 2013 respectively. So preparing about various Biomes/World Climate and their significant features is crucial. |
Question 6
During a thunderstorm, the thunder in the skies is produced by the:
Lightning that separates the nimbus cloud.
Violent upward movement of air and water particles.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) None of the above produces the thunder
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Wind Movement
Statement 1 is not correct: Thunder is the sound caused by a lightning discharge. Lightning heats the air in its path and causes a large over- pressure of the air within its channel. The channel expands supersonically into the surrounding air as a shock wave and creates an acoustic signal that is heard as thunder.
Statement 2 is not correct: The thunderstorms are associated with the cumulonimbus clouds not nimbus.
Statement 3 is not correct: The updraft and downdraft determine the path of the thunderstorm.
Additional Information:
Question 7
Which of the following statements regarding laterite soils of India are correct?
They are rich in nitrogen and potash.
They are well-developed in Rajasthan and UP.
Tapioca and cashew nuts grow well on these Soils.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 4
(d) 2 and 3 only
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Soil Characteristics
Statement 1 is correct: Laterite soil is reddish- brown in colour due to the presence of iron oxide.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Laterite soil is rich in bauxite or ferric oxide. Poor in lime, magnesia, potash and nitrogen.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The laterite soils are commonly found in Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh and the hilly areas of Orissa and Assam.
Statement 4 is correct: Suitable crops grown in laterite soil are Groundnut, cashew nut, coffee, rubber, cinchona, arecanut, tapioca, etc.
Question 8
Consider the following statements:
Mica occurs in abundance in Kodarma.
Dharwars are famous for petroleum.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) None
ExplanationAns: b
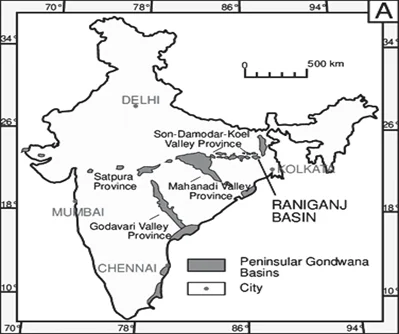
Sub-Theme: Gondwana System
Statement 1 is incorrect: Gondwana rocks contain nearly 98 per cent of India’s coal reserves.
Statement 2 is correct: Koderma is a well-known place for mica production in Jharkhand.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The Dharwar system is economically the most important rocks because they possess valuable minerals like high-grade iron-ore, manganese, copper etc not petroleum.
Question 9
Consider the following:
Geothermal energy
Gravitational force
Plate movements
Rotation of the earth
Revolution of the earth
Which of the above are responsible for bringing dynamic changes on the surface of the earth?
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3, 5 and 6 only
(c) 2, 4, 5 and 6 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Dynamic Changes of The Earth
Factors of The Dynamic Changes of The Earth:
Question 10
Contour bunding is a method of soil conservation used in:
(a) Desert margins, liable to strong wind action
(b) Low flat plains, close to stream courses, liable to flooding
(c) Scrublands, liable to spread of weed growth
(d) None of the above
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Soil Conservation
Option (d) is correct: Contour bunding is a method of soil conservation used in Terrace Farming.
Question 11
Which of the following adds nitrogen to the soil?
Burning of coal by man
Death of vegetation
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Soil Fertility
Statements 1 and 3 are correct: Animal waste like urea, uric acid and death of vegetation add nitrogen in the form of nitrates directly into the soil.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Burning coal releases CO, CO2, sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen – air pollutants to the atmosphere.
Question 12
Which of the following is/are the characteristic/ characteristics of Indian coal?
Low sulphur content
Low ash fusion temperature
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Major Mineral
Option (a) is correct: The India Coal is mainly characterised by High Ash COntent and Low Sulphur Content.
Question 13
Consider the following crops
Groundnut
Rice
Wheat
Which of these are Kharif crops?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Major Crops
Option (c) is correct: Cotton, Groundnut and Rice are Kharif Crops in India.
About Kharif Crops:
About Rabi Crops:
Question 14
Which one among the following industries is the maximum consumer of water in India?
(a) Engineering
(b) Paper and pulp
(c) Textiles
(d) Thermal power
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Water consumption Consumption of water in various industries:
Question 15
Consider the following pairs:
| Tribe | States |
| 1. Limboo (Limbu) | Sikkim |
| 2. Karbi | Himachal Pradesh |
| 3. Dongaria Kondh | Odisha |
| 4. Bonda | Tamil Nadu |
Which of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Tribes of India
Pair 1 is correct: Tamang , Limbu, Bhutia, Khas, Lepchas are the tribal community of Sikkim.
Pair 2 is incorrect: Karbi is a tribal community from Karbi Anglong of Assam.
Pair 3 is correct: Dongaria tribal community is from Odisha.
Pair 4 is incorrect: Bonda is the most primitive tribal group in Odisha.
About Tribal Community and States:
Sikkim
Question 16
The Narmada River flows to the west, while most other large peninsular rivers flow to the Why?
It flows between the Vindhyas and the satpuras.
The land slopes to the west from Central India.
Select the correct answer using the codes given
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) None
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: West Flowing Peninsular Rivers
Statement 1 is correct: Narmada and Tapi flow through faults (linear rift, rift valley, trough) created due to the bending of the northern peninsula during the formation process of Himalayas.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Narmada flows through the faults, which run parallel to the Vindhyas and the Satpuras.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Narmada flows towards the west not because of land slopes to the west from central India, but it is flowing west because of the rift valleys only.
Question 17
Consider the following pairs:
| National Park | River flowing
through the Park |
| 1. Corbett National Park | Ganga |
| 2. Kaziranga National Park | Manas |
| 3. Silent Valley National Park | Kaveri |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) None
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Geography of Protected Areas
Pair 1 is incorrect: Ramganga, Sonanadi, Mandal, Palain and Kosi are the major rivers flowing through the Corbett National Park.
Pair 2 is incorrect: The Kaziranga National Park is circumscribed by the Brahmaputra River, which forms the northern and eastern boundaries, and the Mora Diphlu, which forms the southern boundary. Other notable rivers within the park are the Diphlu and Mora Dhansiri.
Pair 3 is incorrect: The Kunthipuzha River drains the entire 15 km length of the Silent Valley park from north to south into the Bharathapuzha River.
Question 18
Consider the following pairs:
Logtak (Loktak) Lake – Barail Range
Namdapha National Park – Dafla Hills
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Map based
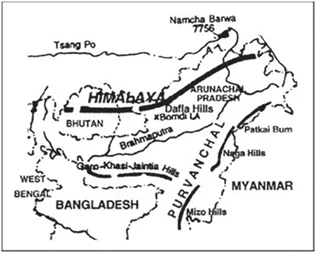
Pair 1 is correct: Nokrek Biosphere Reserve is located in the Garo Hills district of Meghalaya. The biosphere reserve’s name comes from Nokrek Hill, the highest peak of the Garo Hills. Nokrek National Park was included on UNESCO’s list of biosphere reserves in May 2009.
Pair 2 is incorrect: The Loktak Lake is a freshwater lake in Manipur, it is well-known for the phumdis that float above it. On this lake is Keibul Lamjao National Park, the only floating national park in the world. The northern, middle, and southern zones of the lake are separated.
Pair 3 is incorrect: Namdapha National Park is situated between the Dapha Bum range and the Patkai range in the Changlang district of Arunachal Pradesh. The Noa Dihing River runs east to west through the national park. It has dipterocarp woods, the northernmost lowland evergreen rainforests in the world.
Question 19
Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched?
| Geographical Feature | Region |
| (a) Abyssinian Plateau Arabia | Arabia |
| (b) Atlas Mountains | North-Western Africa |
| (c) Guiana Highlands | South-Western Africa |
| (d) Okavango Basin | Patagonia |
Ans: b
Sub-Theme: World Map
Atlas Mountain: The Maghreb, often referred to as Northwest Africa, the Greater Maghreb, and historically as the Barbary Coast, is where the Atlas Mountains is situated. The Atlas Mountains divide the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean and Atlantic coasts. The highest point of this mountain range, Toubkal (4167 m), is found in Morocco. The mountains are found in Algeria and Tunisia in addition to Morocco. The Atlas Mountains are home to populations of Berber people.
Additional Information:
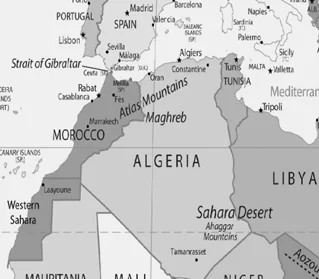
Abyssinian Plateau: The Ethiopian Plateau is also referred to as Altipiano Etiopico, Amhara Plateau, Ethiopian Massif, and Ethiopian Plateau. The Abyssinian Plateau was formerly known as Ethiopia, hence the name. The Blue Nile, which emerges from Lake Tana, is the most notable river to cross the plateau.
Okavango Basin: The Okavango Basin is situated in southwest Africa comprising Botswana, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Angola, and other countries. Whilst, Patagonia refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile.
Guiana Highlands: In South America, the Guiana Highlands are situated in the south of the Orinoco River and north of the Amazon River. Parts of Venezuela, the Guianas, Brazil, and Colombia are included in the Guiana Highlands. Mount Roraima, located in the Guiana Highlands, has the highest elevation (2772 m).
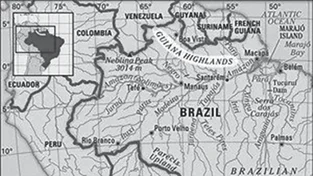
2012
Question 1
A person stood alone in a desert on a dark night and wanted to reach his village which was situated 5 km east of the point where he was standing. He had no instruments to find the direction but he located the polestar. The most convenient way now to reach his village is to walk in the
(a) Direction facing the polestar
(b) Direction opposite to the polestar
(c) Direction keeping the polestar to his left
(d) Direction keeping the polestar to his right
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Basics of Solar System
Option (a) is incorrect: The North star/Pole Star indicates the north direction, therefore walking in the direction of the pole star will lead him towards NORTH of his current position.
Option (b) is incorrect: Walking in the opposite direction will lead him towards SOUTH of his current position.
Option (c) is correct: Walking in the direction while keeping the polestar to his left would lead him towards EAST of his current position and he can reach his village.
Option (d) is incorrect: Walking in the direction while keeping the pole star to his right would lead him towards WEST of his current position.

|
Note: The Pole star is not visible from the southern hemisphere. Some of the north- ern constellations like Ursa Major may also not be visible from some points in the south- ern hemisphere. |
Question 2
Electrically charged particles from space traveling at speeds of several hundred km/sec can severely harm living beings if they reach the surface of the Earth. What prevents them from reaching the surface of the Earth?
(a) The Earth’s magnetic field diverts them towards its poles.
(b) Ozone layer around the Earth reflects them back to outer space.
(c) Moisture in the upper layers of the atmosphere prevents them from reaching the surface of the
(d) None of the statements (a), (b), and (c) given above is correct.
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Basics of Solar System
Earth’s Magnetic Field Diverts Electrically Charged Particles:
Option (a) is correct: Earth’s field lines start near the South Pole of the Earth, curve around in space, and converge again near the North Pole, it forms the magnetosphere, which deflects the Sun’s ions and electrons before they reach us. Most of the solar wind is diverted to poles.
Option (b) is incorrect: The ozone layer absorbs a range of ultraviolet energy, it has nothing to do with Electrically charged particles.
Option (c) is incorrect: Moisture in the upper layers of the atmosphere i.e. The Stratosphere prevents Ultraviolet rays from reaching the surface of the earth.
Question 3
Normally, the temperature decreases with the increase in height from the Earth’s surface, because
1. The atmosphere can be heated upwards only from the Earth’s surface
2. There is more moisture in the upper atmosphere.
3. The air is less dense in the upper atmosphere.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Atmosphere
Statement 1 is correct: Normal lapse rate that is 1-degree Celcius temperature falls at a height of every 165 mt in the troposphere. As we increase elevation, the air pressure decreases as there is less air above us. As the pressure decreases, air molecules spread out further i.e. air expands, and the temperature decreases and the atmosphere can be heated upwards only from the Earth’s surface. Temperature falls off with height at a predictable rate because the air near the surface is heated and becomes light, and the air higher up cools to space and becomes heavy.
Statement 2 is not correct: The water vapour, which accounts for around 1% of air varies greatly in the troposphere and decreases rapidly with altitude.
Statement 3 is correct: The air density in the atmosphere decreases with height and it helps in decreasing temperature.
Question 4
Which one of the following is the characteristic climate of the Tropical Savannah Region?
(a) Rainfall throughout the year
(b) Rainfall in winter only
(c) An extremely short dry season
(d) A definite dry and wet season
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Biomes/World Climate
Option (d) is correct: The Tropical Savannah Region is characterized by a definite dry and wet season.
Tropical Savannah Region:
Question 5
The acidification of oceans is increasing. Why is this phenomenon a cause of concern
1. The growth and survival of calcareous phytoplankton will be adversely affected.
2. The growth and survival of coral reefs will be adversely affected.
3. The survival of some animals that have phytoplanktonic larvae will be adversely
4. The cloud seeding and formation of clouds will be adversely affected.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Ocean Acidification
Statement 1 is correct: Ocean acidification ecreases the calcifying ability of corals, calcareous plankton, crustaceans etc.
Statement 2 is correct: Ocean acidification will affect corals and this will, in turn, affect one million species that have made corals their homes.
Statement 3 is correct: Coral reefs will erode faster than they can rebuild. When shelled organisms are at risk, the entire food web may also be at risk.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Atmospheric sulfur is produced and emitted by phytoplankton from the ocean in the form of dimethyl sulfide, the increase in ocean acidification led to an adverse impact on phytoplankton development and which led to a low amount of sulfur emission. This will decrease cloud formation in small amounts and not adversely affect indirectly on cloud formation.
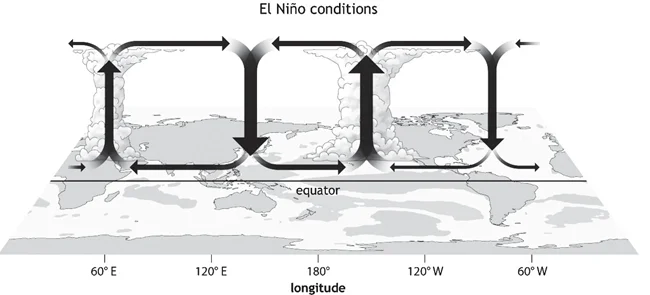
Question 6
Consider the following factors
Air pressure and wind
Density of ocean water
Revolution of the Earth
Which of the above factors influence the ocean currents?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Factors Influence the Ocean Currents
Statement 1 is correct: The Coriolis force is the result of the earth’s rotation. It intervenes and causes the water to move to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere.
Statement 2 is correct: Wind blowing on the surface of the ocean pushes the surface water along with it and the friction between the wind and the water surface affects the movement of the water body in its course.
Statement 3 is correct: Differences in water density affects vertical mobility of ocean currents. Water with high salinity is denser than water with low salinity and in the same way cold water is denser than warm water. Denser water tends to sink, while relatively lighter water tends to rise.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The revolution of the earth does not influence the ocean currents.
Question 7
Which of the following is the chief characteristic of ‘mixed farming’?
(a) Cultivation of both cash crops and food
(b) Cultivation of two or more crops in the same
(c) Rearing of animals and cultivation of crops
(d) None of the above.
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Agricultural pattern/type
Option (c) is correct: Mixed Farming is a situation in which both raising crops and rearing animals are carried on simultaneously.
Option (a) and (b) are incorrect: Cultivation of both cash crops and food crops and Cultivation of two or more crops in the same field are related to the practice of mixed cropping or inter cropping.
Question 8
Consider the following crops of India:
Sesamum
Pearl millet
Which of the above is/are predominantly rainfed crop/crops?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ExplanationAns: d
Option (d) is correct: The crops which are predominantly rainfed in India are Groundnut, Sesamum and Pearl millets.
|
NOTE: Question on crops earlier came in CSE-2011. Reading about important crops and their characteristics from NCERT (Class 12th – India people and Economy) is important. |
Question 9
When you travel in Himalayas, you will see the following:
U-turn river courses
Parallel mountain ranges
Steep gradients causing land-
Which of the above can be said to be the evidence for Himalayas being young fold mountains?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Physiography of India
Deep Gorges, U-turn river courses, Parallel mountain ranges and steep gradients causing landslides – all these are representations or characterics of Himalayan youthful topography.
About Himalayan Physiography:
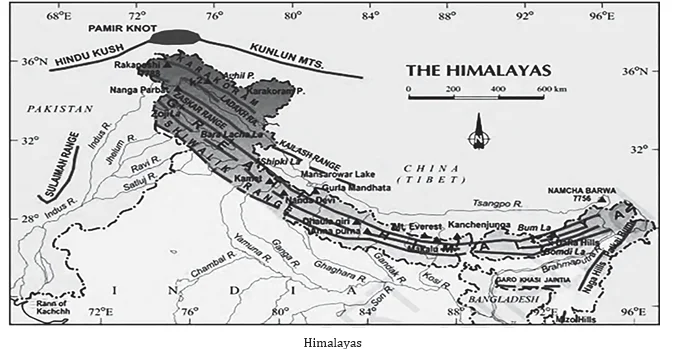
Question 10
Consider the following statements:
The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Indian Monsoon
Statement 1 is correct: Due to its proximity to the sea, India’s southern region has earlier and longer rainy seasons than its northern region. Rainfall in the northern section of India diminishes as rain-bearing winds cross the western ghats and humidity decreases. The southwest monsoon and the retreating monsoon (northeast monsoon) bring rain to India’s southern region.
Statement 2 is correct: With growing distance from the sea, monsoon rainfall tends to decrease. During the southwest monsoon, Kolkata receives 119 cm, Patna 105 cm, Allahabad 76 cm, and
Delhi 56 cm.
Question 11
A particular State in India has the following characteristics:
1. It is located on the same latitude which passes through northern Rajasthan.
2. It has over 80% of its area under forest
3. Over 12% of forest cover constitutes the Protected Area Network in this State.
Which one among the following States has all the above characteristics?
(a) Arunachal Pradesh
(b) Assam
(c) Himachal Pradesh
(d) Uttarakhand
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: State of India/Map based
Question 12
With reference to the wetlands of India, consider the following statements:
In India, the total geographical area of coastal wetlands is larger than that of inland wetlands.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: State of India/Wetland
Wetlands:
Statement 1 is correct: The total wetland area in Gujarat is 23.14% of the total wetland of the country.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The area under inland wetlands accounts for 69%, coastal wetlands 27%, and other wetlands (smaller than 2.25 ha) 4%.
| NOTE: Please refer to PYQ 2011 for detailed information on the state of Gujarat. |
2011
Question 1
Westerlies in the southern hemisphere are stronger and persistent than in northern hemisphere. Why?
1. Southern hemisphere has less landmass as compared to northern hemisphere.
2. Coriolis force is higher in southern hemisphere as compared to northern hemisphere.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Wind System
Option (a) is correct: The Southern hemisphere has less landmass as compared to the northern hemisphere. The Coriolis force is the same in both hemispheres.
Landmass in both the Hemispheres:
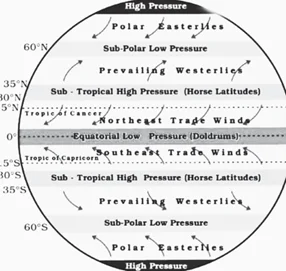
The latitude and airspeed have a direct correlation with the amount of deflection the air makes. At the equator, the Coriolis force is zero, while maximum at the poles.
Question 2
What could be the main reason/reasons for the formation of the African and Eurasian desert belt?
1. It is located in the sub-tropical high-pressure cells.
2. It is under the influence of warm ocean currents.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct in this context?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Desert
Option (a) is correct: The main reason/reasons for the formation of the African and Eurasian desert belt is because they are located in the sub-tropical high-pressure cells.
Deserts:
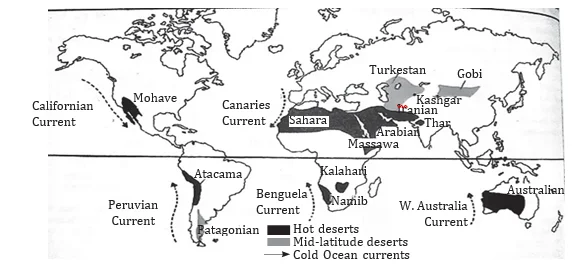
Question 3
The jet aircraft fly very easily and smoothly in the lower stratosphere. What could be the appropriate explanation?
1. There are no clouds or water vapour in the lower stratosphere.
2. There are no vertical winds in the lower Stratosphere.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct in this context?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: c
Sub-Theme: Layers of Atmosphere
Option (c) is correct: The conditions are practically perfect for flying airplanes since this layer is almost completely devoid of clouds and related weather disturbances. So airplanes fly in the lower stratosphere, sometimes in the upper troposphere where weather is calm.
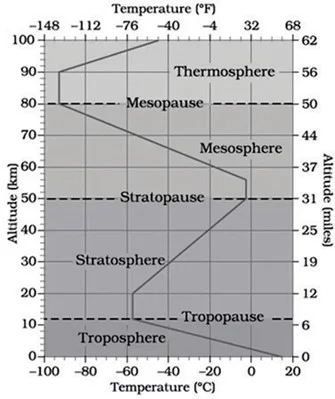
About Stratosphere:
Question 4
The 2004 Tsunami made people realize that mangroves can serve as a reliable safety hedge against coastal calamities. How do mangroves function as a safety hedge?
(a) The mangrove swamps separate the human settlements from the sea by a wide zone in which people neither live nor venture out
(b) The mangroves provide both food and medicines which people are in need of after any natural disaster.
(c) The mangrove trees are tall with dense canopies and serve as an excellent shelter during a cyclone or tsunami
(d) The mangrove trees do not get uprooted by storms and tides because of their extensive roots.
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: Mangroves
Option (d) is correct: because mangroves function as a safety hedge in preserving ecological stability. The dense tangle of roots allows the trees to withstand storms, cyclones or even the daily rise and fall of tides.
Mangroves:
Question 5
La Nina is suspected to have caused recent floods in How is La Nina different from El Nino?
1. La Nina is characterized by unusually cold ocean temperature in the equatorial Indian Ocean whereas El Niño is characterized by unusually warm ocean temperature in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
2. El Nino has adverse effects on the south-west monsoon of India, but La Niña has no effect on monsoon climate.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: d
Sub-Theme: El niño & La-nina
Statement 1 is incorrect: La Nina is characterized by unusually cold ocean temperatures in the Equatorial Pacific, compared to El Nino, which is characterized by unusually warm ocean temperatures in the Equatorial Pacific.
Statement 2 is incorrect: La Nina causes drought in Peru and Ecuador, heavy floods in Australia, high temperatures in Western Pacific, Indian Ocean, off the Somalian coast, and good monsoon rains in India. El Nino: It occurs more frequently than La Nina. This event is not an usual cycle, they are not predictable and occur irregularly at 2 to 7 year intervals. When the coastal waters become warmer in the eastern tropical Pacific (El Niño) it leads to the decrease of atmospheric pressure above the oceans.
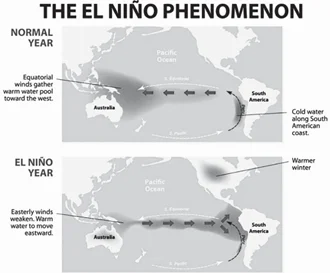
Question 6
The lower Gangetic plain is characterized by a humid climate with high temperature throughout the year. Which one among the following pairs of crops is most suitable for this region?
(a) Paddy and cotton
(b) Wheat and Jute
(c) Paddy and Jute
(d) Wheat and cotton
ExplanationAns: (c)
Sub-Theme: Major crops in India
Option (c) is correct: The crop suitable to be grown in the lower Gangetic plain, which is characterized by a humid climate with high temperature throughout the year, is Paddy and Jute.
Question 7
Among the following States, which one has the most suitable climatic conditions for the cultivation of a large variety of orchids with minimum cost of production, and can develop an export oriented industry in this field?
(a) Andhra Pradesh
(b) Arunachal Pradesh
(c) Madhya Pradesh
(d) Uttar Pradesh
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: State of India
About Orchid in Arunachal Pradesh:
The ecological condition and climate variation in Arunachal Pradesh are so favorable that the state holds about 60% of the Indian variety of orchids. Arunachal Pradesh is often called the Orchid State of India.
Question 8
The Brahmaputra, Irrawaddy and Mekong rivers originate in Tibet and flow through narrow and parallel mountain ranges in their upper Of these rivers, Brahmaputra makes a “U’’ turn in its course to flow into India. This “U” turn is due to
(a) Uplift of folded Himalayan series
(b) Syntaxial bending of geologically young Himalayas
(c) Geo-Tectonic disturbance in the tertiary folded mountain chains
(d) Both (a) and (b)
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Himalayan River System/Drainage
Brahmaputra makes a “U” turn in its course to flow into India due to the Syntaxial bending of geologically young Himalayas.
About Syntaxial Bends/Syntaxis:
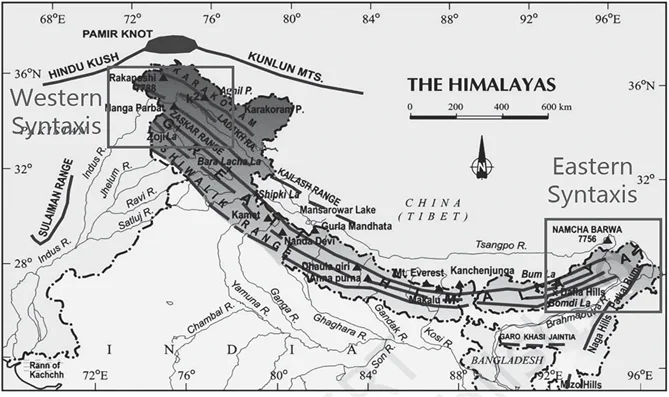
Question 9
A state in India has the following characteristics:
1. Its northern part is arid and semi-arid.
2. Its central part produces cotton.
3. Cultivation of cash crops is predominant over food crops.
Which one of the following states has all of the above characteristics?
(a) Andhra Pradesh
(b) Gujarat
(c) Karnataka
(d) Tamil Nadu
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: State of India
The state of Gujarat is characterised by its northern part having arid and semi arid climate. Its central part produces cotton and the Cultivation of cash crops is predominant over food crops.
About Gujarat (Gandhinagar):
Question 10
Between India and East Asia, the navigation-time and distance can be greatly reduced by which of the following?
1. Deepening the Malacca straits between Malaysia and Indonesia.
2. Opening a new canal across the Kra isthmus between the Gulf of Siam and Andaman Sea.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ExplanationAns: b
Sub-Theme: Map based
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Malacca Strait is situated between Malaysia and Indonesia and is one of the main shipping lanes. The narrow waterway creates a chokepoint between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. Hence, the broadening (not Deepening) the Malacca straits between Malaysia and Indonesia will reduce the navigation time and distance.
Statement 2 is correct: Kra isthmus is the narrowest part of the Malay Peninsula. It is bordered to the west by the Andaman Sea and to the east by the Gulf of Thailand. Thus, opening a new canal across the Kra isthmus between the Gulf of Siam and the Andaman Sea can reduce the navigation time and distance.
Question 11
Two important rivers- one with its source in Jharkhand (and known by a different name in Odisha), and another, with its source in Odisha- merge at a place only a short distance from the coast of Bay of Bengal before flowing into the This is an important site of wildlife and biodiversity and a protected area.
Which one of the following could be this?
(a) Bhitarkanika
(b) Chandipur-on-sea
(c) Gopalpur-on-sea
(d) Simlipal
ExplanationAns: a
Sub-Theme: Physiography of India
About Bhitarkanika National Park
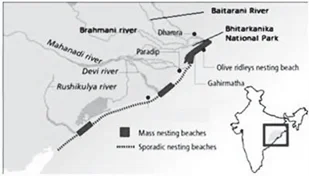
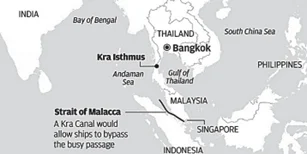
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
