Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Start your answer India’s vulnerability to disasters.
Body
- Discuss the measures taken in India for DRR before signing Sendai Framework.
- Measures taken in India for DRR after signing Sendai Framework.
- The difference between Hyogo Framework and Sendai Framework.
Conclusion
- Summary of the answer with futuristic approach.
|
Introduction:
India is highly vulnerable to disasters due to its geography and limited resources. Disasters can be natural or man-made and cause extensive damage to life and property. India has implemented guidelines, laws, and signed the Sendai and Hyogo Frameworks to mitigate the impact of disasters.
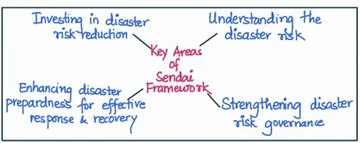
Body:
Measures taken in India for DRR before signing Sendai Framework:
- Disaster Management Act, 2005: Enacted to provide a legal framework for disaster management, including prevention, mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery.
- National Disaster Management Policy, 2009: Laid out the framework for disaster management, focusing on building a culture of prevention, preparedness, and mitigation, as well as improving coordination and capacity building.
- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF), 2006: A specialized force of the Indian government created to respond to natural and man-made disasters, including search and rescue operations.
- National Cyclone Risk Mitigation Project (NCRMP), 2016: A project aimed at reducing the vulnerability of coastal communities to cyclones by enhancing early warning systems, building infrastructure, and improving preparedness and response.
- National Earthquake Risk Mitigation Project (NERMP), 2010: A project aimed at reducing earthquake risks in India by strengthening building codes, conducting seismic zoning, and promoting awareness and preparedness.
- National Programme for Capacity Building of Engineers for Earthquake Risk Management (NPCBEERM), 2010: A program aimed at enhancing the capacity of engineers in earthquake risk management through training, education, and research.
- National Programme for School Safety (NPSS), 2016: A program aimed at enhancing school safety in India by developing guidelines, conducting safety audits, and promoting disaster preparedness and resilience in schools.
Measures taken in India for DRR after signing Sendai Framework:
- National Disaster Management Plan (NDMP), 2016: A comprehensive plan aimed at providing a framework for disaster management at all levels, including prevention, mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery.
- National Disaster Risk Reduction Fund (NDRRF), 2015: A fund established to provide financial resources for disaster risk reduction, response, and recovery measures.
- National Platform for Disaster Risk Reduction (NPDRR), 2017: A platform aimed at enhancing coordination and collaboration among various stakeholders involved in disaster risk reduction and management.
- National Disaster Database (NDDB), 2017: A database aimed at improving data management and analysis for disaster risk reduction and management.
- One Nation One Scheme for Disaster Management, 2018: A scheme aimed at providing financial support to states for disaster management activities, including prevention, mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), 2016: An insurance scheme aimed at providing financial support to farmers affected by natural disasters, including drought, floods, and landslides.
- Climate Change Action Plan, 2018-2023: A plan aimed at addressing the impact of climate change on disaster risk and reducing the vulnerability of communities and ecosystems to climate-related hazards.
The difference between Hyogo Framework and Sendai Framework:
- Focus: While the HFA focuses on reducing disaster risks and increasing disaster resilience, the SFDRR has a broader focus on preventing and mitigating disasters, as well as enhancing recovery and rehabilitation.
- Goals and Targets: The SFDRR has seven global targets and four priorities for action, while the HFA has five priorities for action and several goals and targets.
- Participation: The SFDRR emphasizes the importance of involving all stakeholders, including governments, civil society, private sector, and local communities, in disaster risk reduction, while the HFA focuses more on government-led initiatives.
- Implementation: The SFDRR aims to be more action-oriented and implementation-focused than the HFA, with a stronger emphasis on monitoring and evaluation to track progress towards achieving its targets.
Conclusion:
India’s efforts towards disaster risk reduction have evolved over time, with a stronger emphasis on involving all stakeholders and implementing comprehensive strategies that address the interconnectedness of disaster risk with other global challenges. The country has made significant progress in disaster risk reduction, but there is still a need for continued efforts to build resilience and reduce the impact of disasters on vulnerable communities.
