Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Define agricultural subsidy.
Body
- Specifically mention how subsidies affect the cropping pattern, crop diversity and economy of farmers
- The specify the significance of the crop insurance, minimum support price and food processing for small and marginal farmers
Conclusion
- Conclude stating that agricultural subsidies are important but must be targeted properly.
|
Introduction:
An agricultural subsidy is an incentive paid by the government to the farmers as a supplement of their income to maintain the supply of the agricultural commodities. In India, the subsidy covers fertilizer, irrigation, equipment, credit subsidy, seed subsidy, export subsidy, etc.
Body:
Subsidies can affect the cropping pattern, crop diversity, and economy of farmers in several ways:
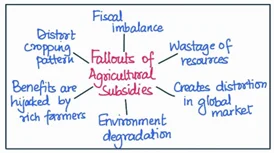
- Cropping pattern: Subsidies are directly responsible for cropping patterns of an area. The crops that receive better and more attractive subsidies are always selected for growing. The larger the subsidy the larger is the area of a particular crop in a region.
- For example, cheap electricity and irrigation subsidies motivated Punjab farmers to go for water guzzling crops like rice.
- Crop diversity: Farmers are more attracted for growing a crop which has support in the form of subsidies. By providing incentives for farmers to grow certain crops, subsidies can reduce crop diversity.
- For example governments have started announcing subsidies for crops other than paddy and wheat so as to increase crop diversity.
- Economy of farmers: Subsidies reduce the dependence of farmers on market forces by providing a guaranteed income for their crops.
- On the one hand, this can provide a safety net for farmers, allowing them to continue farming even in difficult market conditions.
- On the other hand, subsidies create a dependency on government support, which can lead to inefficiencies in the agricultural sector and limit the ability of farmers to respond to market signals.
Significance on small and marginal farmers
- Crop insurance: Crop insurance acts as cover against any incidents that can destroy crops and push a farmer, especially small and marginal farmers, towards poverty. By paying a small amount as premium, farmers can be assured of support in the future.
- Minimum Selling Price (MSP): The MSP provides a guaranteed minimum price for certain agricultural commodities, which can help small and marginal farmers receive a fair price for their produce, even if market prices are low.
- Food processing: Food processing industries act as a fixed market for small farmers and improves profit by enabling them to add value to their products. By processing and packaging their produce, farmers can sell their products at higher prices and improve their financial stability.
Conclusion:
Subsidies, crop insurance, minimum support price (MSP), and food processing can each play a role in supporting small and marginal farmers in different ways. However, it is important to carefully design and implement these policies to ensure that they achieve their intended goals and do not have unintended consequences.
