Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction:
- Introduce the issue of hunger in India and the debate on whether focusing on the lack of food availability distracts from ineffective human development policies.
Body
- Discuss the impact of ineffective human development policies on hunger and malnutrition, focusing on aspects like education, health, and social protection, and providing relevant examples.
- Explain the interconnectedness of food availability and human development policies, with examples illustrating the importance of a comprehensive approach that includes agricultural policies and infrastructure development.
Conclusion
- Write a relevant conclusion.
|
Introduction:
The 2022 Global Hunger Index ranks India 107th out of 121 countries, highlighting a critical hunger issue. With the world’s highest child wasting rate at 19.3%, the problem extends beyond food scarcity. It’s a complex interplay of socio-economic factors, health and sanitation issues, and the effectiveness of human development policies. Therefore, a comprehensive approach is vital to address India’s hunger challenge holistically.
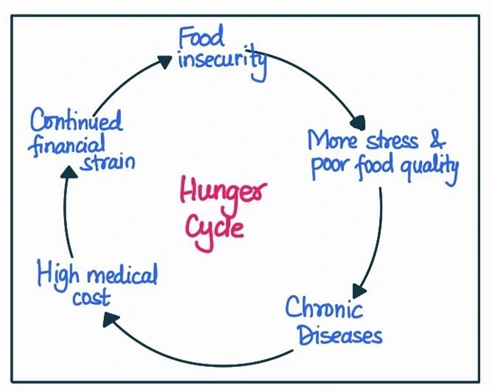
Body:
Impact of ineffective human development policies:
- Education: Limited access to quality education can hinder individuals’ ability to make informed choices about nutrition, health, and family planning, leading to intergenerational cycles of hunger and malnutrition. For instance, the poor implementation of ‘The Right to Education Act’ in certain regions has resulted in low literacy rates and limited knowledge of health and nutrition among the population.
- Health: Weak healthcare infrastructure and inadequate healthcare services can exacerbate hunger and malnutrition, especially among vulnerable sections like pregnant women and children. For instance, despite ‘The National Health Mission’, the shortage of healthcare professionals and limited access to primary healthcare in rural areas contribute to high maternal and child mortality rates.
- Social protection: Insufficient social protection programs may fail to provide adequate support to vulnerable populations, pushing them further into poverty and hunger. For instance, ‘The Public Distribution System (PDS)’, which aims to provide subsidized food to the poor, has faced issues of leakages, corruption, and inefficiencies, limiting its impact on reducing hunger.
Interconnectedness of food availability and human development policies:
- Agricultural policies: For instance, ‘The National Food Security Act’ aims to provide food grains at subsidized rates, but its implementation requires coordination with other human development policies to ensure better nutrition and overall well-being.
- Infrastructure development: For instance, ‘The Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY)’ has improved rural connectivity, enhancing access to markets, healthcare, and education, and thus contributing to human development and reduced hunger.
Conclusion:
Focusing solely on the lack of food availability as the main cause of hunger risks overshadowing the role of ineffective human development policies in perpetuating the problem. A comprehensive approach that addresses the interconnectedness of food availability, education, health, social protection, and infrastructure development is essential to tackle hunger and malnutrition in India effectively.
